Genetic information which is transferred from parent to offspring is the basis of inheritance. The process begins with the replication of DNA, followed by transcription and translation. During transcription, the genetic information stored in the DNA is copied into another form of RNA. The whole process is governed by the complementary base pairs of the two nucleic acids. However, the latter process of translation is not controlled by complementary but by the genetic code. The translation is the process of converting nucleic acid information into amino acids. Let’s learn more in detail about the genetic code.
Genetic Code
The genetic code comprises the complete information of the protein manufactured from RNA. It is the sequence of base pairs of amino acids that code for protein to be synthesized. Thus a change in this sequence can alter the formation of amino acids. Decoding the genetic code was a real challenge for scientists.
A physicist by name of George Gamow suggested a solution to break this challenge. He applied the concepts of permutation and combination to decipher this genetic code. He suggested that genetic code should be made of three nucleotides which code for 20 amino acids with four bases.
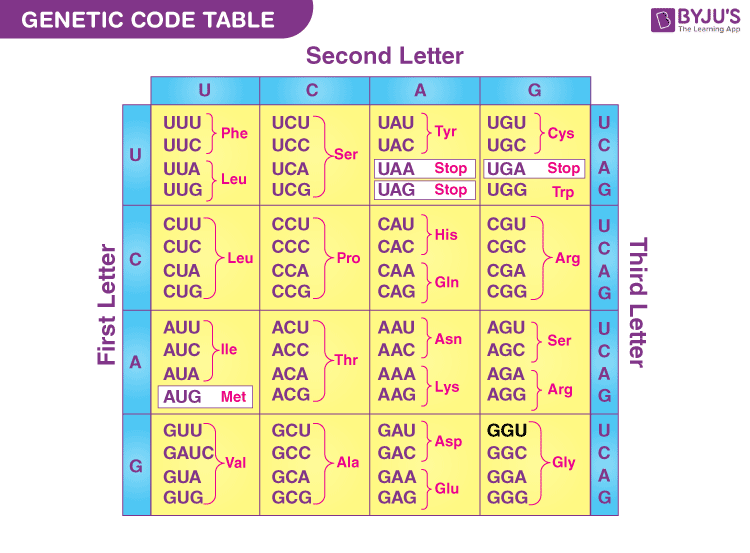
Four nitrogenous bases and three nucleotides together form a triplet codon which codes for one amino acid. Thus, the number of possible amino acids would be 4 x 4 x 4 = 64. But we have 20 naturally existing amino acids.
This was explained by the features of the genetic code, which are as follows:
- Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon, thus making them degenerate.
- Each codon codes only for one specific amino acid.
- The codes are universal irrespective of the type of organism, i.e. CGU would code for Arginine in animals as well as in bacteria, but exceptions exist.
- Out of 64 codons, 3 are stop codons which do not code for any amino acids and thus end the process of translation.
- AUG coding for Methionine is the only codon that acts as an initiator codon.
For more information on genetics and genetic code, visit BYJU’S.


Comments