Table of Contents
- Protein Structure
- Protein Synthesis
- Types of Proteins and Their Functions
- Functions of Proteins
- Frequently Asked Questions

We often see bodybuilders and physical trainer drinking whey protein along with milk to build-up metabolism and strength.When it comes to our body, our hair and nails are mostly made of proteins. Basically, proteins are the fundamental building blocks of our body. They are large and complex macromolecules or bio-molecules which perform a major role in the functioning and regulating of our body cells, tissues and other organs in the human body. They are also used in providing strength to our body in producing hormones, enzymes, and other metabolic chemicals. They are also involved in functioning and regulating of our body cells, tissues and organs.
Proteins are composed of amino acids, arranged into different groups. These fundamental amino acids sequences are specific and its arrangements are controlled by the DNA. Since our body cannot synthesize these essential amino acids by its own, we should have plenty of protein foods in our everyday diet to keep our body metabolisms stable.
Protein Structure
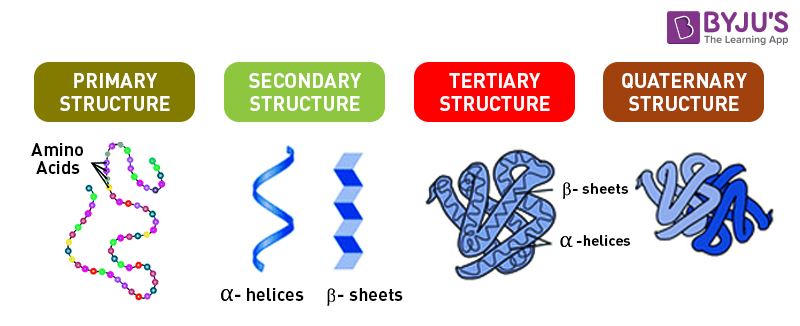
In general, they are two types of protein molecules fibrous proteins and globular proteins. Fibrous proteins are insoluble and elongated. Globular proteins are soluble and compact. Fibrous and Globular proteins may comprise one or four types of protein structures and they include primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure.
Primary Structure: It is a specific sequence of amino acids. The order of amino acids bonded together is detected by information stored in genes.
Secondary Structure: It is a three-dimensional form of a local segment of proteins. They are formed by hydrogen bonds between the atoms along the backbone of the polypeptide chain.
Tertiary Structure: It is determined by R-groups. It is a three-dimensional shape of a protein. Many numbers of tertiary structure fold to form Quaternary Structure.
Quaternary Structure: It is the arrangement of multiple folded protein subunits in a multi-subunit complex.
Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis takes place through a process called translation. This process occurs in the cytoplasm. It involves the rendering of genetic codes. Ribosomes of a cell help in translating genetic codes into a polypeptide chain. These polypeptide chains become functioning proteins only after undergoing certain modifications.
Types of Proteins and Their Functions

Although there are debates about the intake of carbohydrates and fats in order to maintain a proper health, a minimum amount of daily protein intake is always a doctor’s first recommendation. The common examples of proteins in biology are eggs, almond, chicken, oats, fish and seafood, soy, beans and pulses, cottage cheese, Greek yogurt, milk, broccoli, and quinoa.
Functions of Proteins
- Enzymes: Enzymes mostly carry out all numerous chemical reactions which take place within a cell. They also help in regenerating and creating DNA molecules and carry out complex processes.
- Hormones: Proteins are involved in the creation of various types of hormones which help in balancing the components of the body. For example hormones like insulin, which helps in regulating blood sugar and secretin. It is also involved in the digestion process and formation of digestive juices.
- Antibody: Antibody also known as an immunoglobulin. It is a type of protein which is majorly used by the immune system to repair and heal the body from foreign bacteria. They often work together with other immune cells to identify and separate the antigens from increasing until the white blood cells destroy them completely.
- Energy: Proteins are the major source of energy that helps in the movements of our body. It is important to have the right amount of protein in order to convert it into energy. Protein, when consumed in excess amounts, gets used to create fat and becomes part of the fat cells.
Listed below are few functions of Proteins.
| Aspect | Functions of Proteins in Human Body | Examples |
| Storage | Legume Storage, albumin, and proteins. | Supplies food during the early stage of the seedling or embryo. |
| Hormone Signalling | Counterpart activities of different body parts. | Glucagon and Insulin. |
| Transport | It transport substances throughout the body through lump or blood cells. | Hemoglobin. |
| Contraction | To carry out muscle contraction. | Myosin. |
| Digestive Enzyme | Breaks down nutrients present in the food into smaller portions so that it can be easily absorbed | Pepsin, Amylase, and Lipase |
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about Proteins.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is protein and why is it necessary?
Proteins are the building blocks of living beings. Protein is present in every human cell. An amino acid chain forms the basic building block of proteins. For our body to repair damaged cells and create new ones, we need protein in our daily diet. Children, teenagers, and pregnant women all need protein for healthy growth and development.
What is protein deficiency?
When protein consumption is insufficient to meet our body’s needs, we have a protein deficiency. Worldwide, an estimated 1 billion people experience inadequate protein intake. Up to 30% of South Asia and Central Africa children have insufficient protein intake, making these regions among the worst affected.
What are the four types of proteins?
Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure are the four levels of complexity that can be used to characterise the entire structure of a protein.


Comments