
| Symbol | Xe |
| Atomic Number | 54 |
| Atomic Mass | 131.293 g.mol −1 |
| Discovered by | William Ramsay in the year 1898 |
What is Xenon?
- Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54 in the periodic table.
- It was discovered by William Ramsay in the year 1898.
Table of Contents
- Chemical Properties of Xenon
- Physical properties of Xenon
- Applications and effects of Xenon
- Interesting Facts about Xenon
- XeF4 and XeF6 are expected to be
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Chemical Properties of Xenon
| Group | 18 | Melting point | −111.75°C/ −169.15°F/ 161.4 K |
| Period | 5 | Boiling point | −108.099°C, −162.578°F, 165.051 K |
| Block | p | Density (g cm−3) | 0.005366 |
| Atomic number | 54 | Relative atomic mass | 131.293 |
| State at 20°C | Gas | Key isotopes | 132Xe |
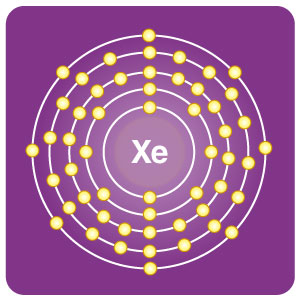
| Electron configuration | [Kr] 4d105s25p6 | CAS number | 7440-63-3 |
| ChemSpider ID | 22427 | ChemSpider is a free chemical structure database | |
Physical properties of Xenon
- Xenon is a rare, colourless, odourless, tasteless and chemically unreactive gas.
- Xenon is a trace gas ( i.e., which makes up less than 1 % by volume of Earth’s atmosphere. It is found as a component in gases released from a few mineral springs.
- It is also released as a by-product when the air is separated into Nitrogen and Oxygen.
- The element has an atomic number 54 as its nucleus contains 54 protons. It is available in all forms i.e., solids, liquids, and gases.
Applications and effects of Xenon
Optics and illumination
- It is used in Flash lamps called Xenon flash lamps.
- It is also used in Stroboscopic lamps and photographic flashes.
- Lasers are generated with the help of Xe gas.
Medicine
- The element Xe acts as a natural anaesthetic.
- Inhaling the mixture of oxygen and xenon produces a hormone which helps to increase Red Blood Cell (RBC) production.
- It is used to measure the flow of blood and also used to image the Brain, Heart, and Lungs.
- Also, the element is used in NMR spectroscopy
Interesting Facts about Xenon
- The name Xenon is derived from the Greek word Xenos which means “stranger”.
- It is the most expensive and most dense of all the gases.
- It produces a bluish-purple colour when electrified.
- It forms very good compounds with Fluorine.
XeF4 and XeF6 are expected to be
XeF4 oxidises potassium iodide
XeF4 + 4I– → 2I2 + 4F– + Xe
XeF4 and XeF6 are expected to be oxidising because in both the reactions XeF4 and XeF6 both caused the oxidation. XeF6 oxidises hydrogen-like other xenon fluorides.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is the geometry of XeF4?
The shape of XeF4 is square planar. The central Xe atom has 4 bond pairs of electrons and two lone pairs of electrons. It undergoes sp3d2 hybridization which results in octahedral electron geometry and square planar molecular geometry. The two lone pairs are at opposite corners of an octahedron.
What is XeF4 used for?
XeF4 is a compound that normally occurs as a colourless/white, crystalline solid. This compound is made of up xenon (a noble gas) and fluoride (a naturally occurring mineral). XeF4 can be used to help find and analyse trace metals that contaminate silicone rubber.
Is Xe element a metal?
Xenon (Xe) exists as a colourless, odourless gas and is chemically inert. It has the atomic number 54 in the periodic table and belongs in Group 18, the Noble Gases. It is a non-metal with the symbol Xe. Xenon was discovered in 1898 by William Ramsay and Morris Travers.
What are some characteristics of xenon?
Xenon is one of the inert or noble gases and is odourless, colourless, tasteless and chemically non-reactive. While not toxic on its own, its compounds are strong oxidising agents that are highly toxic.
Xenon hexafluoride has a distorted octahedral geometry. Due to the presence of one lone pair on a xenon atom, the octahedral geometry is distorted.
Xenon hexafluoride has a distorted octahedral geometry. Due to the presence of one lone pair on a xenon atom, the octahedral geometry is distorted.
Xenon hexafluoride has a distorted octahedral geometry. Due to the presence of one lone pair on a xenon atom, the octahedral geometry is distorted.
Xenon hexafluoride has a distorted octahedral geometry. Due to the presence of one lone pair on a xenon atom, the octahedral geometry is distorted.


Comments