What is E-Commerce?
E-Commerce is defined as the buying and selling of goods and services including digital products over digital and electronic networks. Electronic commerce (E-commerce) draws on technologies such as mobile commerce, electronic funds transfer, supply chain management, Internet marketing, online transaction processing, electronic data interchange (EDI), inventory management systems, and automated data collection systems.
It is important for IAS Exam from the perspective of current affairs and Indian Polity.
E-commerce – UPSC Notes:- Download PDF Here
| Table of Contents: |
| Start your preparation for the upcoming IAS Exam with the UPSC Previous Year Question Papers.
Also, complement your preparation with the help of following links: |
Who is an E-Commerce Entity
It means a company that is incorporated under the Companies Act,1956 or the Indian Companies Act 2013 or a foreign company covered under the Companies Act 2013 or an office, branch or agency in India as provided in FEMA 1999, owned or controlled by a person resident outside India and conducting the e-commerce business.
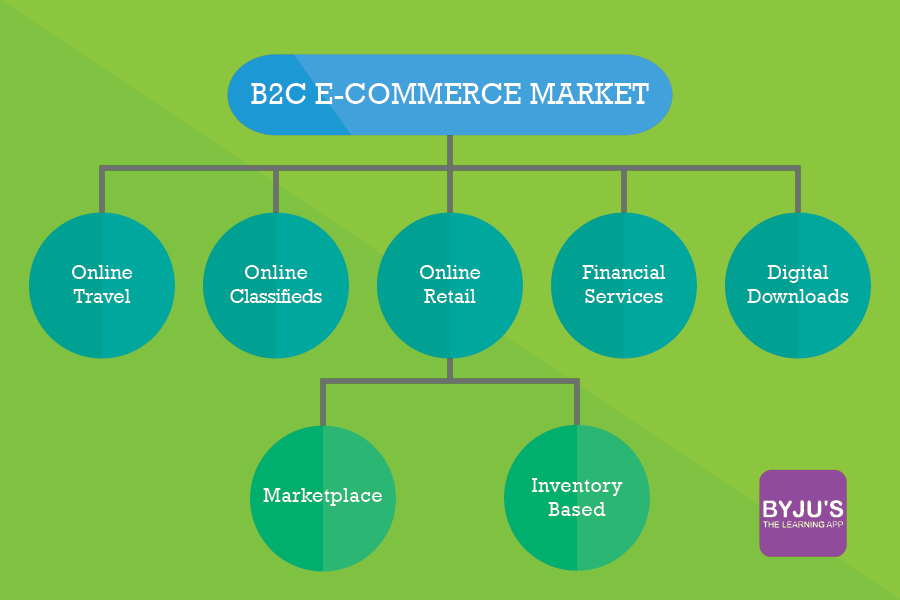
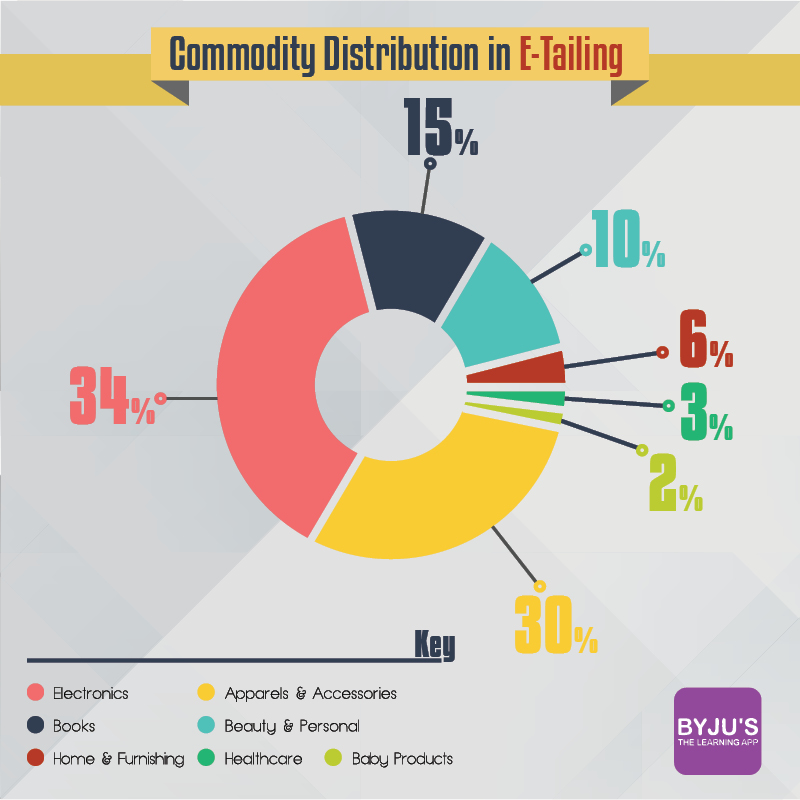
Let us study from the image below, the sectors that contribute the most to e-commerce :
Why e-commerce is in the news?
- 100% Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is permitted through the automatic route in the market place model of e-commerce.
- The above development indicates that 100% FDI is not permitted in the inventory-based model.
- This FDI is permitted only for B2B (Business-to-Business) model and not for B2C (Business-to-Consumer).
E-Commerce in India
As in 2019, India has an internet user base of about 40% of the total Indian population, especially with regard to e-commerce. E-commerce in India has been budding since 2009 and many major e-commerce companies have grown their businesses in India.
There are typically two patterns in which e-commerce works in India:
1. Multi-product E-Commerce – The portals which sell multiple products on the same website or application are Multi-product E-Commerce companies. This includes Amazon, Flipkart, Snapdeal, where garments, furniture, books, stationery, etc. are all available at a single platform
2. Single Product E-Commerce – Under this, the companies which sell only a single type of product online are called Single-Product E-commerce companies. This includes portals like Makemytrip which enables all kinds of tourism-related services, similarly specific e-commerce companies for eyewear, furniture, gadgets, automobiles, etc.
Types of E-Commerce Models
There are mainly four types of E-Commerce Models which are followed in India. Discussed below are the same:
- Business to Business (B2B) – The selling of products between the manufacturer, retailers and wholesalers is called the B2B model of e-commerce. Here the customer is not involved in the transfer of products or goods
- Business to Consumer – This is the generally used online portals where the e-commerce company sells directly to the consumer
- Consumer to Consumer (C2C) – The best example of this is OLX, where consumer can upload their old products and resale them directly to the buyer. There is no interference of the manufacturers or retailers
- Consumer to Business – When a person designs or creates something new, they can sell it to the e-commerce company for further sales. This is called the Consumer to Business model
Also, read FDI in E-commerce: Whom will it benefit?
Aspirants can refer to the linked articles mentioned below which are related to e-commerce:
| FDI Confidence Index | Global Innovation Index | Inclusive Development Index |
| India’s New FDI Reforms | New E-commerce rules in India | FDI in Retail |
Under what conditions FDI is granted here?
- A manufacturer will be permitted to sell its manufactured products in India through E-Commerce retail.
- A single brand retail entity operating through brick and mortar store is permitted to undertake retail trading through E-Commerce.
- An Indian manufacturer is permitted to sell its own single brand products through E-Commerce retail. Indian manufacturer would be the investee company, which is the owner of the Indian brand and which manufactures in India, in terms of value, at least 70% of its products in house, and sources, at most 30% from Indian manufacturers.
The conditions levied are as follows:
- E-Commerce marketplace may provide support services to sellers in respect of warehousing, logistics, order fulfilment, call centre, payment collection and other services.
- The E-Commerce entity providing the marketplace will not exercise ownership over the inventory i.e. goods purported to be sold. Such an ownership over the inventory will render the business into an inventory-based model in which FDI is not permitted.
- An e-commerce entity will not permit more than 25% of the sales affected through its marketplace from one vendor or other group companies.
- Post-sales, delivery of the goods, the satisfaction of the customer, warrantee/ guarantee of the goods and services will be the responsibility of the seller.
- In a market-based model, payment for sales may be facilitated by the e-commerce entity in conformity with the guidelines of the Reserve Bank of India.
- E-commerce entities providing marketplace will not directly or indirectly influence the sale price of goods or services and shall maintain a level playing field.
The table below how the two models of e-commerce work:
(Source: DIPP)
Market-Based Model: Under this model, an e-commerce entity acts as a facilitator of goods and services by providing an information technology platform to the buyers and sellers
Inventory Based Model: Under this model, the e-commerce entity owns an inventory of good and services to be sold to the buyers directly
Implications of FDI in E-Commerce Good points:
- The B2B business model in the market place has been officially recognized by the government of India and hence ended much ambiguity in the policy.
- The discount wars will end providing some relief to the brick and mortar retailers and provide a level playing field.
- It will allow the traditional brick and mortar sellers to come out of their geographical barriers.
- It will help connect the long chain of demand in India with a long chain of supply.
- Indian offline manufacturers can go online and attract foreign investment now.
Advantages of E-Commerce Industry in India
Discussed below are the advantages of the E-Commerce Industry in India:
- Business can be done from anywhere can the products can be sold both within the country as well as Internationally
- One can promote their work and sell their products directly to the consumers without the interference of middlemen
- Goods can be delivered to the doorstep from any part of the country or the world
- Reduced the investment cost since in many cases money can be saved on buying a storeroom for the display of products
- 24×7 facility to order products online. The only requirement is an internet connection
- Through the four different models of electronic commerce in the country, businessmen can choose their target consumers and sell directly to the customers or to other retailers as well
What are the Challenges of the Indian e-commerce industry?
- High competition: There are different players in the same area of business leading to decrease in profitability due to reasons such as aggressive pricing strategies, heavy discounts and offers, free delivery, high commissions to affiliates and vendors during sale period to name a few. These firms are losing billions to attracting customers.
- Poor logistic & supply chains: E-commerce companies need to maintain the stock to get the benefit of reach and the ability to stock more items than physical stores as these are their biggest differentiators. With this benefit also comes the challenge of robust supply chains and logistics networks, which are not comparable and developed to global standards in India.
- Payments: While offering a wide variety of payment options, Cash on Delivery(CoD) option in India is the most prevalent as customers fear to share information online and do not trust the website for secure payments. Also, the return percentage of orders in CoD is much higher compared to online payments.
- Trust of the customer: Due to the constraints of quality, colour and texture recognition especially in apparels and luxury products, the customers are not able to trust that what is shown will be delivered.
E-commerce – UPSC Notes:- Download PDF Here
Frequently Asked Questions on E-Commerce
Q 1. What is E-Commerce?
Q 2. What are the different types of e-commerce models?
Ans. There are a total of 4 types of e-commerce models. These include:
- Business to Business (B2B)
- Business to Consumer
- Consumer to Consumer (C2C)
- Consumer to Business
Q 3. What are the benefits of E-Commerce?
Ans. E-Commerce has benefitted both the consumer and the seller/manufacturer equally. Given below are the advantages of E-Commerce:
- Less Start-up cost for the seller
- 24×7 online access to shop and order
- Goods can be delivered Nationally and Internationally
- One does not need to be physically present at the store to shop
- Easy Access to e-commerce websites and application
Q 4. How does e-commerce works?
Ans. The E-commerce companies create websites and applications where all the available products and goods are uploaded. A consumer can scroll through the products, choose the ones they like, add their delivery address and contact details and pay through online or COD mode for the products.
UPSC Preparation:
| UPSC 2023 Calendar | UPSC Books |
| UPSC Syllabus | UPSC Notes |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Prelims |
| UPSC CSAT | UPSC Current Affairs |
Comments