There are three main types of rocks: sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic. Each of these rocks are formed by physical changes—such as melting, cooling, eroding, compacting, or deforming—that are part of the rock cycle.
To know about the different Types of Rocks for UPSC preparation and get NCERT notes on the same at the linked article.
NCERT notes on important topics are crucial when it comes to cracking the UPSC civil services exam. These short-format notes, along with being easy to remember at through a quick lance, will also be useful for other competitive exams like banking PO, SSC, state civil services exams and so on. This article talks about the Rock Cycle for IAS Exam Geography syllabus.
| The NCERT Notes for UPSC page is an important asset for a robust IAS preparation plan. Visit the page now!!
The following links will be of immense help to the candidates attempting the exam this year: |
Rock Cycle (UPSC Notes):- Download PDF Here
Rock Cycle Notes
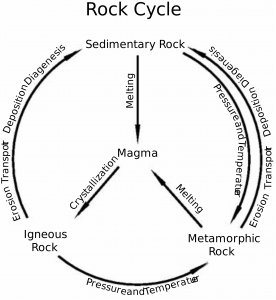
- The rock cycle is a basic concept in geology that defines the laborious transitions through geologic time among the three main rock types:
- Igneous rocks
- Sedimentary rocks
- Metamorphic rocks
- Rocks do not remain in their original form for a long period as they undergo a transformation.
- This cycle is an uninterrupted process through which old rocks are converted into new ones.
- Igneous rocks are primary rocks.
- These rocks can be changed into metamorphic rocks.
- Sedimentary and metamorphic rocks form from these primary rocks.
- The fragments evolved out of metamorphic rocks and igneous again form into sedimentary rocks.
- Sedimentary rocks themselves can develop into fragments.
- The crustal rocks -igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary-once formed may be carried down into the interior of the earth through subduction.
- In this process, parts or entire crustal plates subduct under another plate and the same melt at high temperature in the interior.
- This results in the formation of molten magma, the unique source for igneous rocks.
- The rock cycle encompasses several processes.
- The key processes of the rock cycle are:
- Crystallization
- Erosion and sedimentation
- Metamorphism
- Plate tectonics
- Spreading ridges
- Subduction zones
- Continental collision
- Accelerated erosion
- Water
Rock Cycle (UPSC Notes):- Download PDF Here
Also, refer to:
| Carbon Cycle | Nitrogen Cycle |
| Oxygen Cycle | Hydrological Cycle |
Frequently Asked Questions about Rock Cycle
What are the processes involved in rock cycle?
What is meant by rock cycle?
For the updated UPSC Syllabus for the prelims and mains examination candidates can refer to the linked article, and accordingly, start their preparation.
Visit BYJU’S for exam updates, study material and preparation tips.

Comments