G.S. Paper -2
Topic: Polity
- Punjab amends Excise Act to allow clubs, hotels near highways to serve liquor
Context: Last year, the SC scrapped licences for liquor sale along highways.
Reason: that drunken driving was the main culprit for the large number of road accidents in the country.
In news:
- Punjab has become the first State to take the amendment route to make way for liquor sale near highways as the Assembly passed a legislation enabling hotels, restaurants and clubs to serve alcohol within 500 metres of highways.
- The Bill stated that it aims to ensure that hotels, restaurants, clubs and other notified places are allowed to serve alcohol to customers only for consumption within their premises to secure the livelihood of a large segment of population.
- However, sale of liquor for takeaway purposes shall be permitted only through licensed vends which shall not be located within 500 metres from the outer range of the National or State Highway or a service lane of those roads
Measures taken by other states:
- States such as Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, West Bengal and the Union Territory of Chandigarh denotified hundreds of kilometres of highways as local roads in order to bypass the Supreme Court ruling.
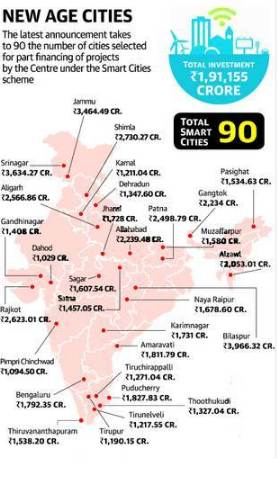
- Centre announces 30 more Smart Cities
In news:
- Thirty more cities from across the country have been added to the Centre’s Smart Cities Mission, with a proposed investment of Rs.57,393 crore in various projects under the scheme.
- Smart Cities Mission
- Second year anniversary.
- total number of cities covered 90 (including the 30 newly recognized ones)
- The cities were picked on the basis of the proposals they submitted for the Smart Cities Challenge. Among the cities selected, Kerala’s capital, Thiruvananthapuram, topped the challenge.
Cities selected:
-
- Tamil Nadu emerged as the State with the highest number of cities selected in this round, with Tirupur, Tirunelveli, Thootukudi and Tiruchirappalli making it to the Mission.
- Uttar Pradesh and Gujarat had three cities each selected for the Mission. While Jhansi, Allahabad and Aligarh made it from U.P., Rakjot, Gandhinagar and Dahod were the picks from Gujarat.

- Madhya Pradesh (Sagar and Satna), Bihar (Patna and Muzaffarpur), Chhattisgarh (Naya Raipur and Bilaspur) and Jammu and Kashmir (Srinagar and Jammu) had two cities each selected.
- Andhra Pradesh’s new capital, Amaravati, was also selected, as was Karimnagar in neighbouring Telangana.
- Among the 11 State capitals selected were Bengaluru in Karnataka, Shimla in Himachal Pradesh, Aizawl in Mizoram and Gangtok in Sikkim. The other cities selected were Puducherry, Karnal in Haryana, Dehradun in Uttarakhand, Pimpri Chinchwad in Maharashtra, and Pasighat in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Modi government launches Liveability Index for 116 cities to measure quality of life
In news:
- The central government launched the “City Liveability Index” – a first of its kind initiative introduced by the Urban Development Ministry – to measure the quality of life in 116 major cities including capital cities and those with population over one million.
- Urban Development Minister M.Venkaiah Naidu launched the Index at a National Workshop on Urban Transformation.
Parameters:
- The cities will be assessed on a comprehensive set of 79 parameters to capture the extent and quality of infrastructure including availability of roads, education and health care, mobility, employment opportunities, emergency response, grievance redressal, pollution, availability of open, green spaces, and culture.
Reform incentive fund:
- Progress in respect of reforms like e-governance, audit of accounts, tax revision policies and extent of tax revenue collection, energy and water audit, establishing state level financial intermediaries for resource mobilisation and credit rating was taken into account.
- Marks scored by states were considered for deciding the quantum of incentive with high scorers getting more.
- The Urban Development Ministry also increased reform incentive fund for the next three financial years from Rs 900 crore to Rs 10,000 crore “to promote next generation reforms that would make a substantial difference to urban governance and service delivery and resource mobilization by urban local bodies,”
- The Ministry disbursed Rs 500 crore as incentive to 16 states that performed well in implementing urban reforms during 2016-17.
(Facts and figures not important)
Andhra Pradesh topped the list scoring 96.06 per cent marks. Others who received the incentive fund in order of merit were Odisha (95.38 per cent), Jharkhand (91.98 per cent), Chhattisgarh (91.37 per cent), Madhya Pradesh (90.20 per cent), Telangana (86.92 per cent) and Rajasthan (84.62 per cent).
Punjab also scored 77.02 per cent along with Kerala (75.73 per cent), Goa (75.38 per cent), Mizoram (75 per cent), Gujarat (73.80 per cent), Chandigarh (72.73 per cent), Uttar Pradesh (70.67 per cent) and Maharashtra (70.52 per cent).
- Panel to oversee progress in UN’s SDG
In news:
- The Centre will soon set up a high-level committee headed by Chief Statistician of India to oversee the country’s progress towards UN’s Sustainable Development Goals aimed at ending poverty, fighting inequalities and tackling climate change.
- A dashboard is also being developed with technical support from the UN Development Programme (UNDP) to “strengthen the mechanism” for monitoring progress on these global goals.
National indicators
- The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation has already developed a list of draft national indicators to measure progress of SDGs. These draft indicators have been put out in public domain. Based on the inputs received, national-level indicators will be finalised.
- India will hold bi-annual reviews with the State governments for identifying good practices and challenges.
G.S. Paper -3
Topic: Economic
- Software export growth set to slow: Nasscom
In News:
- The country’s software export growth is set to slow to 7-8% this fiscal year, down from 8.6% a year earlier, according to industry body Nasscom
- The domestic market was projected to grow faster than the export market during this fiscal
Factors that affect software exports:
- Increased rhetoric on protectionism
- Elections, Brexit and visa issues
- Macroeconomic uncertainties
- Focus on cost optimisation
- Currency volatility
Inflection point in industry and way forward:
- Improvements in financial services and a high potential in digital businesses would be the key growth drivers
- An improvement in legacy business and increased automation-based projects would also be among the growth drivers
- The demand will be for technology-skilled professionals and it was imperative for new and existing people to reskill themselves.
Topic: Agriculture
- Are farm loan waivers really so bad?
Context:
- There has been a rising trend of farm loan waivers in country in recent times and after UP, Maharashtra and Punjab, Karnataka has also announced waivers for few categories of farmers.
What do farm loan waivers leads to?
- Farm loan waiver undermines an honest credit culture, it impacts credit discipline, it blunts incentives for future borrowers to repay
- Waivers engender moral hazard.
- It also entails at the end of the day, transfer from taxpayers to borrowers
- On account of this, overall government borrowing goes up and yields on government bonds also are impacted
- It can also lead to the crowding out of private borrowers as higher government borrowing can lead to an increase in cost of borrowing for others
Present demands and reasons behind them:
- The present demands are an outcome of the fact that the government is willing to provide for “acts of God”, not for “acts of state”
- The policy framework for farm loans has a provision that when the Centre declares a drought, farm loans in officially designated “affected districts” are rolled over, initially for a year, up to a maximum of three years
- Farmers’ problems in 2016-17 are almost entirely the outcome of demonetisation: there was no clear geographical demarcation, and there has been no rolling over of loans
What if farm loans are not waived?
- Agricultural loans by banks in India are compulsorily insured by the Agricultural Insurance Company of India (AIC)
- Its liabilities are back-stopped by the Centre through budgetary support
- Even if loans aren’t waived, there is no loss to banks
- In situations of widespread and acute farmer distress leading to substantial defaults, the Centre will have to step in and provide funds
- The difference is that waivers are borne by states, and defaults are borne by the Centre
How this all started?
- To improve farmer livelihoods and check food inflation, our agricultural strategy has been based upon persuading farmers to move away from traditional subsistence agriculture towards more commercial operations
- This entails farmers investing much more and taking higher risks
Economic consequences:
- Traditional farm finance sources like moneylenders can neither provide the requisite volume of funds nor do they allow enough margins to make risk-taking worthwhile
- Forcing farmers back to moneylenders will retard diversification, thereby increasing the risk of accelerating food inflation
The ‘sub-sovereign’ dilemma:
- At the heart of this problem are constitutional provisions
- Health of the banks is the Centre’s concern while the health of the farmers is that of the states (Center, state and concurrent lists)
- This division of responsibility is asymmetric in that if states protect the interest of farmers, they also protect banks; while the Centre can protect banks without concern for farmers
Possible solutions:
- The Centre and states need to work together to evolve a farm loan model which protects both farmers and banks without bringing politics into it
- This is the essence of “cooperative federalism”
Topic: Science and Technology
- ISRO puts 31 satellites in space
In news:
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched 31 satellites — 29 of them belonging to foreign countries — on board the PSLV-C38 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre.
- Satellites carried:
- Cartosat-2 series satellite, the main payload, weighing 712 kg
- NIUSAT, an Indian university/academic institute satellite from Noorul Islam University, Kanyakumari
- The other 29 nano satellites belonged to 14 nations — Austria, Belgium, Chile, Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Latvia, Lithuania, Slovakia, the U.K., and the U.S.
Cartosat-2 series satellite:
- The Cartosat-2 is a remote sensing satellite, and is the sixth in the series
- It will be used for cartographic applications, coastal land use and regulation, road network monitoring, water distribution, creation of land use maps, Land Information Systems (LIS) and Geographical Information System (GIS) applications.
Milestone achievement:
- With the launch of the PSLV-C38, ISRO now had the confidence to put a number of satellites into different orbits- Geo Synchronous, Sun Synchronous orbit or low inclination orbit, carrying multiple satellites, in a single mission.
Practice questions
1. The city liveability Index which was in news recently is intended
- To measure the quality of life in 116 major cities including capital cities and those with population over one million.
- To measure the quality of life in 116 major cities including capital cities and those with population over five million.
- To measure the quality of life in 116 major cities including capital cities and those with population over ten million.
- None of the above
2. Consider the following statement with reference to Cartosat-2 series satellite, which was launched recently by ISRO
- Cartosat-2 is a remote sensing satellite.
- Cartosat-2 will be used for Land Information Systems (LIS) and Geographical Information System (GIS) applications.
- Cartosat-2 is a weather forecasting satellite.
Identify the correct statement
- 1 only
- 2only
- 1and 3
- 1 and 2
3. Who among the following established the Bhil Seva Mandal in 1922?
- Narain Malhar
- Amritlal Vitthaldas Thakkar
- Jyotiba Phule
- Baba Amte
4. Which among the following temples of India is known as Black Pagoda?
- Sun Temple, Konark
- Brihadeeswara Temple, Tanjore
- Lord Jagannath Temple, Puri
- Meenakshi Temple, Madurai
Comments