TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS1 Related CULTURE 1. ‘Mud People’ festival B. GS2 Related INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS 1. India cuts export quotas for Maldives 2. Mongolia's Third Neighbor Policy Blooms 3. India, Bangladesh Navies to join hands GOVERNANCE 1. IAS officers to be judged on integrity POLITY 1. SC notifies new roster for judges C. GS3 Related SECURITY 1. NRC omissions raise fear in Assam ENVIRONMENT 1. Chilika Lake 2. Musi River AGRICULTURE-ECONOMY 1. Operation Sagar Rani D. GS4 Related E. Editorials FOOD SECURITY 1. State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World report F. Tidbits 1. Guns and death G. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions H. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
A. GS1 Related
1. ‘Mud People’ festival
- The annual tradition forms part of a joyous religious festival honouring Saint John they believed saved residents from execution by Japanese soldiers during Second World War.
- The “Mud People” festival, believed to have begun more than a century ago, became much more prominent after 1944 — during Japan’s wartime occupation of the former U.S. colony.
Details
- The event celebrates the feast of John the Baptist with devotees taking part in what they see as an act of humility and penance that imitates a saint who preached and lived a life of poverty in the desert.
B. GS2 Related
Category: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. India cuts export quotas for Maldives
Context
- India has lowered the limits on the export of certain essential commodities such as potatoes, onions, and eggs to the Maldives.
Details
- According to a bilateral pact that came into effect in 1981, India exports essential commodities by and large in line with the requirement as communicated by the government of Maldives.
- The Directorate General of Foreign Trade reduced these limits. Government sources said the calculations for 2018-19 were arrived at using a new methodology.
- Maldives usually sends the request for commodities but with no request an average of last three years has been decided.
2. Mongolia’s Third Neighbor Policy Blooms
Context
- India appreciates the ‘Third Neighbour’ policy of land-locked Mongolia.
What is it?
- The ‘Third Neighbour’ policy of Mongolia, a land-locked nation between Russia and China, refers to its building ties with countries other than these two.
- With this Ulaanbaatar to boost bilateral and multilateral diplomatic relations with countries around the world.
- the strategic policy framework intends to use a soft-power approach to international relations as a modus operandi to tackle developing vital sectors such as education, science and technology, mining, and energy infrastructure.
Details
- Rajnath Singh was on a three-day official visit to further strengthen bilateral relations and security cooperation as part of sustained high-level exchanges between Mongolia and India.
- Singh visited the Gandantsegchinlen Monastery.
- The relationship between India and Mongolia was upgraded to a ‘Strategic Partnership’ in 2015 during Modi’s visit, which coincided with the 60th anniversary of establishment of diplomatic relations between the two countries.
Agreements
- Mongolia broke ground for the construction of the landlocked country’s first oil refinery with the help of a $1 billion loan from India which Singh described as an important milestone in the bilateral ties.
Other economic Activities of Mongolia
- The most important goal of Mongolia’s foreign and domestic policy is to become a major energy source in the Far East. These agreements show significant progress in Mongolia’s influence in the region, demonstrating the strategic significance of the third neighbor policy. Landlocked Mongolia’s foreign policy now stretches out to many sectors, including oil and energy in the Persian Gulf.
- Mongolia’s third neighbor policy will play its part in the exploitation of crude oil resources, within the legal framework approved by parliament.
- the third neighbor policy is also creating transit transportation arrangements so products can be exported to or imported from third neighbors, changing Mongolia’s energy landscape.
Mongolia’s political stability, economic developments, non-traditional national security environment, and far-sighted foreign policy strategies are crucial for continuing its democratic transition and keeping up with new developments in the Asia-Pacific.
3. India, Bangladesh Navies to join hands
1. IAS officers to be judged on integrity
Context
- Top IAS officers at the level of secretary and additional secretary will soon be assessed on their attitude towards weaker sections of the society, among other qualities, according to draft appraisal forms finalised by the Personnel Ministry.
Details
- Besides this, their annual performance appraisal report will carry details on their ability to take timely and effective decision, especially in complex, ambiguous and critical situations.
- They will be asked to comment in not more than 50 words on their attributes like ‘ownership of responsibilities with courage to stand up for what is right, innovativeness, track record of delivery and ability to lead a team with coordination and collaboration’.
- The Personnel Ministry has written to chief secretaries of all the state governments and the Union territories suggesting changes in the annual performance appraisal forms for the officers of Indian Administrative Service (IAS).
- All the IAS officers, except at the level of secretary and additional secretary, will be appraised on their “integrity” in general.
- Those at the secretary and additional secretary level will be assessed on both “financial integrity” and “moral integrity”.
- All bureaucrats will have to indicate at least four domain assignments like social development, internal affairs and defence, industry and trade, public finance and financial management, natural resource management and personnel and general administration, governance reforms and regulatory system, among others.
- Barring those at the top levels, all other IAS officers will have to send an updated CV, including details of additional qualifications acquired/training programmes attended/ publications/special assignments undertaken, in a prescribed proforma, to the cadre controlling authority once in five years so that the records remain updated.
The changes have been proposed in two forms —
- form one, which is meant for all the IAS officers except those at the level of secretary and additional secretary.
- form two, that will be for secretary and additional secretary or equivalent officers.
1. SC notifies new roster for judges
- It will come into effect from July 2 when the top court reopens after summer vacation.
Details
- The new roster says that the Bench headed by Chief Justice of India Dipak Misra will hear all public interest litigation petitions, besides pleas on social justice, elections, habeas corpus and contempt of court.
- Justice Ranjan Gogoi, the seniormost judge after the Chief Justice, will deal with labour laws, indirect taxes, personal law and company law cases.
C. GS3 Related
1. NRC omissions raise fear in Assam
- June 30 is deadline for final draft
- This has created fear in many whether their names would be included in the list or not
- With many MLA’s and MP’s names also not in the list, this has raised the fear among common People
Read about the National Register of Citizens.
1. Chilika Lake
- It is a brackish water lagoon, spread over the Puri, Khurda and Ganjam districts of Odisha
- It is the largest coastal lagoon in India and the second largest coastal lagoon in the world
- Chilika Lake was designated the first Indian wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention
- It is the largest wintering ground for migratory birds on the Indian sub-continent. The lake is home to a number of threatened species of plants and animals
Proposed water aerodrome in Chilika Lake likely to face green hurdle
The Airports Authority of India has proposed to set up a water aerodrome in Chilika Lake for starting amphibious aircraft operations in Odisha.
The project will most likely face a green hurdle
- Chilika turns into a temporary habitat for lakhs of migratory and residential birds. If an aircraft flies at low height, there is every chance of the birds getting hit. While the bird population will be in danger, safety of passengers of amphibious aircraft will also be jeopardised.
- Noise pollution generated by close to 10,000 boats has already taken a toll on the endangered Irrawaddy dolphins in the lake. The amphibious aircraft operation would add to the woes.
- As many as 155 endangered Irrawaddy dolphins were spotted in Chilika, which is the single largest habitat of this species in the world. After clearing the lake of illegal man-made enclosures, dolphins have now started moving freely in all sectors.
2. Musi River
- It is a tributary of the Krishna River
- Himayat Sagar and Osman Sagar are dams built on it which used to act as source of water for Hyderabad.
- The river was known as Nerva during Qutub Shahi period.
Polluted Musi water used for irrigation affecting aquifers
- The continuous irrigation of agricultural and horticultural crops along the banks of the highly polluted Musi river is leading to the contamination of the city’s aquifers.
- The highly polluted river water seeps into the ground and contaminates the underground aquifers that sustain the state’s water table.
The problem is only compounded during the monsoon season, as percolation is higher. Chemicals present in the polluted river water also seep into the water table, changing its texture.

1. Operation Sagar Rani
- To ensure safety and hygiene at fish handling and distribution centres, Food Safety officials in Kerala launched an initiative named ‘Operation Sagar Rani’.
Context
- The State Food Safety wing officials during inspection seized 6,000 kg of fish preserved using formalin (formaldehyde) at the inter-State border check-post at Walayar in Palakkad.
D. GS4 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
E. Editorials
1. State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World report
- The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World is an annual flagship report jointly prepared by Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), the World Food Programme (WFP) and the World Health Organization (WHO) to inform on progress towards ending hunger, achieving food security and improving nutrition and to provide in-depth analysis on key challenges for achieving this goal in the context of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
- The report targets a wide audience, including policy-makers, international organizations, academic institutions and the general public.
For the first time, the report provides two measures of food insecurity.
- FAO’s traditional indicator of the extent of hunger, the prevalence of undernourishment, is complemented by the prevalence of severe food insecurity, which is estimated based on data collected from adult individuals worldwide using the Food Insecurity Experience Scale (FIES).
- The FIES is a new tool to measure people’s ability to access food, based on direct interviews.
- In addition, the report assesses the trends for six nutrition indicators: anaemia in women of reproductive age, stunting, wasting, overweight, obesity and levels of exclusive breastfeeding.
India – Status of food security and nutrition
- India’s efforts at improving access to food and good nutrition are led by the National Food Security Act. There are special nutritional schemes for women and children operated through the States.
- In spite of such interventions, 14.5% of the population suffers from undernourishment, going by the UN’s assessment for 2014-16. At the national level, 53% of women are anaemic.
- In India, cereal production recovered markedly after two consecutive bad seasons.
- Country-level prevalence rates for stunting among children under five years of age for India is 38.4%.
- As with most developmental outcomes, stunting prevalence varies markedly between poor and rich households. The stunting rates for the poorest, middle and richest quintiles are 50, 38 and 30 respectively.
- India is on course and registered good progress towards achieving the target on reducing overweight in children under five years of age.
Global Trend
- In 2016 the number of chronically undernourished people in the world is estimated to have increased to 815 million, up from 777 million in 2015 although still down from about 900 million in 2000.
- The food security situation has worsened in particular in parts of sub-Saharan Africa, South-Eastern Asia and Western Asia, and deteriorations have been observed most notably in situations of conflict and conflict combined with droughts or floods.
- Globally, the prevalence of stunting fell from 29.5 percent to 22.9 percent between 2005 and 2016, although 155 million children under five years of age across the world still suffer from stunted growth.
- The number of conflicts is also on the rise. Exacerbated by climate-related shocks, conflicts seriously affect food security and are a cause of much of the recent increase in food insecurity.
- Conflict is a key driver of situations of severe food crisis and recently re-emerged famines, while hunger and undernutrition are significantly worse where conflicts are prolonged and institutional capacities weak.
- Addressing food insecurity and malnutrition in conflict-affected situations cannot be “business as usual”. It requires a conflict-sensitive approach that aligns actions for immediate humanitarian assistance, long-term development and sustaining peace.
- The 2017 report sends a clear warning signal that the ambition of a world without hunger and malnutrition by 2030 will be challenging – achieving it will require renewed efforts through new ways of working.
Challenges
- The Centre and State governments are woefully short on the commitment to end undernourishment.
- Institutions such as the State Food Commissions have not made a big difference either.
- Distributing nutritious food as a public health measure is still not a political imperative, while ill-conceived policies are making it difficult for many to do this.
Way Forward
- The report on nutritional deficiency should serve as an opportunity to evaluate the role played by the PDS in bringing about dietary diversity for those relying on subsidised food.
- In a report issued two years ago on the role played by rations in shaping household and nutritional security, the NITI Aayog found that families below the poverty line consumed more cereals and less milk compared to the affluent.
- Complementing rice and wheat with more nutritious food items should be the goal.
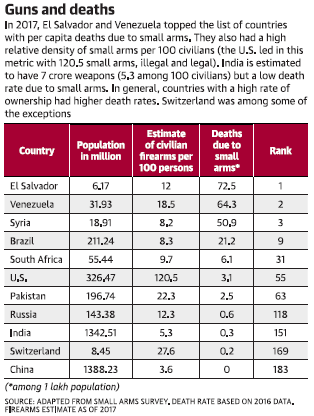
F. Tidbits
G. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
Question 1. The “Third Neighbour Policy”,recently in news
is with respect to which of the following country’s foreign policy?
- India
- Mongolia
- Bolivia
- China
See
Question 2. Consider the following statements about Coordinated Patrol (CORPAT)
- Indian and Bangladesh recently instituted the first edition of CORPAT.
- The Indian Navy regularly conducts CORPATs with Indonesia, Myanmar and Thailand.
Which of the above statement/s is/are correct?
-
-
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
-
See
Question 3. Consider the following statements about Chilika Lake:
- It is a Sweet Water Lake situated in Odisha
- Chilika Lake was designated the first Indian wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention
Which of the above statement/s is/are correct?
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
See
Question 4. Consider the following statements about “Musi River”
- It is a tributary of River Krishna
- It flows through Telangana
- The river was known as Nerva during the Qutub Shahi period
- 3 dams are built on River Musi
Which of the above statement/s is/are correct?
- 1 and 4 only
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
See
H. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
- Comment on India’s Status of Food Security and Nutrition. Discuss this with respect to National Food Security Act and National Nutrition Mission.
- Mongolia’s “Third Neighbour Policy” is an innovation in the development of diplomatic relations which can be followed by other land locked countries. Discuss.
Also, check previous Daily News Analysis
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Current Affairs Webinar’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series
Comments