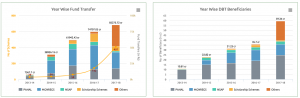
Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) Scheme
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) is Government’s major reform initiative to re-engineer the existing delivery processes, ensuring better and timely delivery of benefits using Information & Communication Technology (ICT).
- As a process, Centrally Sponsored Schemes are implemented through State Governments and granular level details are being maintained by the respective State Governments.
- DBT focuses on better targeting of beneficiary, timely disbursal of benefits and curbing of pilferage by de-duplication, elimination of ghost beneficiaries etc
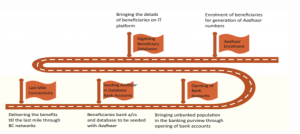
JAM Trinity
- DBT by leveraging the JAM (Jan Dhan, Aadhaar and Mobiles) trinity and the technological prowess offers to drastically improve the benefit delivery system in the country. The JAM Trinity will enable this novel system to transfer benefits in a leakage-proof, well targeted, cashless and timely manner.
Environment Ministry Launches a Regional Project to Tackle Stubble Burning
Background
- In another significant step to combat climate change, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has approved a regional project on ‘Climate Resilience Building among Farmers through Crop Residue Management’ under the National Adaptation Fund for Climate Change (NAFCC).
Issue Area
- The problem of crop residue burning has been intensifying over the years, with Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh being the major burning hotspots. Increased mechanization, declining number of livestock, long period required for composting and no economically viable alternate use of residues are some of the reasons for residues being burnt in field.
- This not only has implications for global warming, but also has an adverse impact on air quality, soil health and human health.
Details
- The project was approved at the meeting of the National Steering Committee on Climate Change
- The first phase of the project has been approved at a cost of approximately Rs. 100 Crore for the States of Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and Rajasthan. The project will leverage approximately three times the approved amount with contribution from the States as well as farmers.
- The project not only aims to mitigate climate change impacts and enhance adaptive capacity, but will also counter the adverse environmental impacts that arise from burning. The project will be implemented following a phased approach.
- A slew of technological interventions will be undertaken for timely management of crop residue in addition to effective utilisation of existing machineries. Implementable and sustainable entrepreneurship models will be created in rural areas through upscaling successful initiatives and innovative ideas
Comments