 SMART CITY: places using technology, information and data to deliver services to its inhabitants efficiently and purposefully. Government play a vital role in envisioning and shaping cities in India WHY MAKE CITIES SMARTER: The lives of many depends on how cities are run – cities transform people 33%(420 million) of our population live in urban areas contributing to 66% GDP There is a need to accommodate people migrating from rural areas Statistics show that our cities are not smart enough Numbers: 33% population urban 420 million people living in urban areas 22% urban population poor 53 million+ cities 7936 cities and towns-4041 statutory towns,3894 census towns 66%GDP contributed by urban areas In 2001 – 2011, urban India grew faster than rural India in absolute terms-9.1 crore people added Projection(2031):600 million people in 2031/75%GDP/ 78 million+ cities Annual Exponential Growth rate in urban areas:2.76% in 2001-2011 Slum dwellers:65 million % with access to treated tap water:60% % with access to piped sewer system:33% % solid waste collected: 82% % solid waste processed:29% % contamination of surface water:75% % defecating in the open:19% % without access to toilet with flush system: 42% Primary mode of transportation(52%):walking Loss due to diseases in children under 12 because of poor sanitation -500 crore(UNICEF-2006) Investment required excluding land cost for improved infrastructure:54.3 lakh crore(Ahluwalia Committee)-not including cost of land By 2050- 64% developing world and86% of developed world would be urban Additional Info: census definitions
SMART CITY: places using technology, information and data to deliver services to its inhabitants efficiently and purposefully. Government play a vital role in envisioning and shaping cities in India WHY MAKE CITIES SMARTER: The lives of many depends on how cities are run – cities transform people 33%(420 million) of our population live in urban areas contributing to 66% GDP There is a need to accommodate people migrating from rural areas Statistics show that our cities are not smart enough Numbers: 33% population urban 420 million people living in urban areas 22% urban population poor 53 million+ cities 7936 cities and towns-4041 statutory towns,3894 census towns 66%GDP contributed by urban areas In 2001 – 2011, urban India grew faster than rural India in absolute terms-9.1 crore people added Projection(2031):600 million people in 2031/75%GDP/ 78 million+ cities Annual Exponential Growth rate in urban areas:2.76% in 2001-2011 Slum dwellers:65 million % with access to treated tap water:60% % with access to piped sewer system:33% % solid waste collected: 82% % solid waste processed:29% % contamination of surface water:75% % defecating in the open:19% % without access to toilet with flush system: 42% Primary mode of transportation(52%):walking Loss due to diseases in children under 12 because of poor sanitation -500 crore(UNICEF-2006) Investment required excluding land cost for improved infrastructure:54.3 lakh crore(Ahluwalia Committee)-not including cost of land By 2050- 64% developing world and86% of developed world would be urban Additional Info: census definitions  Unplanned urban development and inadequate infrastructure like roads, public transport, water and sanitation, affordable housing and system of service delivery have led to overcrowding. Problems: scarcity of clean drinking water, contamination of water, water logging and flooding, traffic congestion, pollution, irrational pricing of energy etc. Concerned ministry: Ministry of Urban Development]
Unplanned urban development and inadequate infrastructure like roads, public transport, water and sanitation, affordable housing and system of service delivery have led to overcrowding. Problems: scarcity of clean drinking water, contamination of water, water logging and flooding, traffic congestion, pollution, irrational pricing of energy etc. Concerned ministry: Ministry of Urban Development] 
 SMART CITIES MISSION 100 cities to be taken up 48000 crore to be spent+ 50 crore for intelligent transport for 5years period Retrofitting(improving existing infrastructure in 500 acres of area) Redevelopment( renewal of cities by new infrastructure creation>50 acres of area Green field Develpoment-development of vacant space>250 acres Pan city development: applying smart solutions to an entire city Implementation through: Special Purpose Vehicle with full time CEO and nominees from centre,state and local bodies. The SPV would be a limited company registered under the Companies Act, 2013 There would be a Smart City Advisory Forum for all 100 cities It would consist of the District Collector, MP, MLA, mayor, CEO of the SPV, local youth, Citizens and technical experts REQUIREMENTS – MAN, MONEY, MANAGEMENT Large infrastructure investments Integrated planning of land use and transportation Institutional structures(most census towns do not have Urban Local Bodies to govern them) AMRUT(Atal Mission for rejuvenation and Urban transformation) 500 cities with a population of 100000 or maore 50000 crore allocated 5years period States to formulate State Annual Action Plan(SAAP) HOUSING FOR ALL 2 lakh crore houses by 2022 1.5 lakh/house+interestsubsidy+land to be provided by state govt NATIONAL HERITAGE CITY DEVELOPMENT AND AUGMENTATION YOJANA(HRIDAY) revitalization of linked urban infrastructure for heritage assets such as monuments, Ghats, temples etc. 12 cities/500 crore/27 months OTHER SCHEMES THAT WOULD AID SMART CITY PROJECT SWACHH BHARAT ABHIYAN 4,041 statutory cities and towns / clean streets roads and infrastructure of the country(62000 crore including rural allocation) 300 urban clusters to be set up under Shyama Prasad Mukherji RURMAN MISSION BUDGET BOOST Swacch Bharat Abhiyan allocated Rs.9,500 crores. 2.87 lakh crore grants to gram panchayats and municipalities – a quantum jump of 228% 65 eligible habitats to be connected via 2.23 lakh kms of road Total allocation for road construction, including PMGSY, – Rs 97,000 crore Total outlay for infrastructure in Budget 2016 now stands at Rs. 2,21,246 crore New greenfield ports to be developed on east and west coasts Centre to Partner with States to revive small airports for regional connectivity Key infrastructure elements in a smart city Clean water Comfortable dwelling Access to sanitation &drainage(storm water drains) Effective waste management Efficient transport systems Sustainable and efficient energy systems Sustainable environment Smart delivery of services Robust IT connectivity and Digitization Smart and green buildings Knowledge of and Access to public utilities e-governance safety and security of citizens Good quality health and education services empowered local institutions
SMART CITIES MISSION 100 cities to be taken up 48000 crore to be spent+ 50 crore for intelligent transport for 5years period Retrofitting(improving existing infrastructure in 500 acres of area) Redevelopment( renewal of cities by new infrastructure creation>50 acres of area Green field Develpoment-development of vacant space>250 acres Pan city development: applying smart solutions to an entire city Implementation through: Special Purpose Vehicle with full time CEO and nominees from centre,state and local bodies. The SPV would be a limited company registered under the Companies Act, 2013 There would be a Smart City Advisory Forum for all 100 cities It would consist of the District Collector, MP, MLA, mayor, CEO of the SPV, local youth, Citizens and technical experts REQUIREMENTS – MAN, MONEY, MANAGEMENT Large infrastructure investments Integrated planning of land use and transportation Institutional structures(most census towns do not have Urban Local Bodies to govern them) AMRUT(Atal Mission for rejuvenation and Urban transformation) 500 cities with a population of 100000 or maore 50000 crore allocated 5years period States to formulate State Annual Action Plan(SAAP) HOUSING FOR ALL 2 lakh crore houses by 2022 1.5 lakh/house+interestsubsidy+land to be provided by state govt NATIONAL HERITAGE CITY DEVELOPMENT AND AUGMENTATION YOJANA(HRIDAY) revitalization of linked urban infrastructure for heritage assets such as monuments, Ghats, temples etc. 12 cities/500 crore/27 months OTHER SCHEMES THAT WOULD AID SMART CITY PROJECT SWACHH BHARAT ABHIYAN 4,041 statutory cities and towns / clean streets roads and infrastructure of the country(62000 crore including rural allocation) 300 urban clusters to be set up under Shyama Prasad Mukherji RURMAN MISSION BUDGET BOOST Swacch Bharat Abhiyan allocated Rs.9,500 crores. 2.87 lakh crore grants to gram panchayats and municipalities – a quantum jump of 228% 65 eligible habitats to be connected via 2.23 lakh kms of road Total allocation for road construction, including PMGSY, – Rs 97,000 crore Total outlay for infrastructure in Budget 2016 now stands at Rs. 2,21,246 crore New greenfield ports to be developed on east and west coasts Centre to Partner with States to revive small airports for regional connectivity Key infrastructure elements in a smart city Clean water Comfortable dwelling Access to sanitation &drainage(storm water drains) Effective waste management Efficient transport systems Sustainable and efficient energy systems Sustainable environment Smart delivery of services Robust IT connectivity and Digitization Smart and green buildings Knowledge of and Access to public utilities e-governance safety and security of citizens Good quality health and education services empowered local institutions  Urban Rejuvenation It should include fostering rural and urban linkages as urbanization is a pre condition for growth and employment generation. The AEGR of urban population is only 2.76%.Rural urban migration is also muted in spite of the hype. There must be a pro migrant policy Digitizing cities manual intervention where there can be digital can lead to inefficiencies ,underutilization and leakages In city governance it leads to fragmentation,duplication of institutional roles,lack of capacity,funding constraints,limited autonomy andweaklink with citizens Resource optimization applications and automated business processes can minimize human intervention Components of digitization: citizen centric online portals city performance dashboard for operations and maintenance Integrated command and operations centre Predictive analytics-maintenance cycles integrated asset management solutions multi-channel citizen interfaces – mobile, web, face to face kiosks, social media etc. for bill payment, tax payment etc Workforce and Resource Management Solutions to plan, forecast and schedule work Smart grid solutions for energy management Intelligent Transport System Smart traffic policies Technology based optimization of space and energy use What’s the govt. doing about it? National e-Gov Plan: enquiry, registration(birth, death etc), form submission, payments and grievances can be processed online without having to travel to local offices. All departments must provide online servicing National Service Delivery Infrastructure AADHAR Mobile Service Delivery Gateway(m-governance) National Cloud-Meghraj State service delivery gateways, State Data centers (SDC), State Wide Area Network(SWAN) Common Service Centers(CSCs) Empowering Urban Local Bodies(ULBs) By 74th CAA, many functions of the state governments were transferred to ULBs but financial devolution did not happen Urban plans are mostly adhoc. Municipal bodies control over urban land Municipal bodies have to become more participative and have to interact with civil society actively ULBs should be empowered to levy taxes and collect user charges. There is no municipal budgeting There is financial potential hidden in the forms of unlocked land value, conversion charges, development charges, betterment fee etc. A new revenue model must be created for the repayment of loans, also to improve credit worthiness A municipal cadre must be created to meet the man power requirements of the ULBs Skilling functionaries and increasing capacity are the needs of the hour. Vertical and horizontal integration in governance alone can bring results on the ground Experts can be brought in by MoUs between other organisatiions PPP model is yet to be extensively explored Collaboration between city planners, developers, NGOs, IT System integrators, software providers, energy and utility providers, automotive industry experts, facility control and technology providers(mobile technology, cloud computing and networking) Peri urban areas and many census towns do not have any governance structure. Planning has to precede growth in these cities. It is impossible without proper institutional structures.
Urban Rejuvenation It should include fostering rural and urban linkages as urbanization is a pre condition for growth and employment generation. The AEGR of urban population is only 2.76%.Rural urban migration is also muted in spite of the hype. There must be a pro migrant policy Digitizing cities manual intervention where there can be digital can lead to inefficiencies ,underutilization and leakages In city governance it leads to fragmentation,duplication of institutional roles,lack of capacity,funding constraints,limited autonomy andweaklink with citizens Resource optimization applications and automated business processes can minimize human intervention Components of digitization: citizen centric online portals city performance dashboard for operations and maintenance Integrated command and operations centre Predictive analytics-maintenance cycles integrated asset management solutions multi-channel citizen interfaces – mobile, web, face to face kiosks, social media etc. for bill payment, tax payment etc Workforce and Resource Management Solutions to plan, forecast and schedule work Smart grid solutions for energy management Intelligent Transport System Smart traffic policies Technology based optimization of space and energy use What’s the govt. doing about it? National e-Gov Plan: enquiry, registration(birth, death etc), form submission, payments and grievances can be processed online without having to travel to local offices. All departments must provide online servicing National Service Delivery Infrastructure AADHAR Mobile Service Delivery Gateway(m-governance) National Cloud-Meghraj State service delivery gateways, State Data centers (SDC), State Wide Area Network(SWAN) Common Service Centers(CSCs) Empowering Urban Local Bodies(ULBs) By 74th CAA, many functions of the state governments were transferred to ULBs but financial devolution did not happen Urban plans are mostly adhoc. Municipal bodies control over urban land Municipal bodies have to become more participative and have to interact with civil society actively ULBs should be empowered to levy taxes and collect user charges. There is no municipal budgeting There is financial potential hidden in the forms of unlocked land value, conversion charges, development charges, betterment fee etc. A new revenue model must be created for the repayment of loans, also to improve credit worthiness A municipal cadre must be created to meet the man power requirements of the ULBs Skilling functionaries and increasing capacity are the needs of the hour. Vertical and horizontal integration in governance alone can bring results on the ground Experts can be brought in by MoUs between other organisatiions PPP model is yet to be extensively explored Collaboration between city planners, developers, NGOs, IT System integrators, software providers, energy and utility providers, automotive industry experts, facility control and technology providers(mobile technology, cloud computing and networking) Peri urban areas and many census towns do not have any governance structure. Planning has to precede growth in these cities. It is impossible without proper institutional structures.  Meeting energy requirements Smart grids integrating renewable energy equipments for storing energy Smart building construction to conserve energy Energy installations to have sensors and controls to anticipate, detect and respond to problems quickly and to be disaster resistant Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED)- a US rating system can be used to evaluate the environmental performance of a building and encourage market transformation towards sustainable design There is a dire need save energy, materials, water and other natural resources and decrease emissions Smart and green neighbourhoods and buildings can save energy up to 30%,reduce emissions, provide higher efficiency and comfort Energy saving windows and panes can save on air conditioning cost, sensor controlled photo voltaic cells on roofs can make energy Making cities sustainable Decentralize power generation (too much dependence on a central grid is not recommendable) Low carbon public transport Disaster Risk Management Floods, earthquakes, fires, landslides. Anticipate and implement Changing citizen behaviour Citizens are central to any city. Participative development is the only possible way of development Citizens must be informed, educated and communicated with on a regular basis for meaningful change. Strict enforcement of laws and regulations are also a part of it Meeting housing requirements Budget housing to meet the requirements of middle and low income households is required. The possibilities of providing rental housing services are yet to be explored Recommendation of High Level Task Force(2008) Defined affordable housing as 300 to 600 sft carpet area housing for EWS/LIG(cost not > 4 times the gross household annual income and EMI/rent not > 30 % of gross monthly income); 1200 sft carpet area housing for MIG((cost not > 5 times the gross household annual income and EMI/rent not > 40% of gross monthly income) Requirements: Strong political will Active Development Mechanisms Clear Construction Strategies Innovative Financial Systems Use of technology What’s the govt. doing about it? Building Centres established Building Materials and Technology Promotion Council has been instituted WHAT CAN BE A GAMECHANGER? Industrialized house production Use of factory produced products to put together houses(pre fab housing) Modular Houses( 90% of housing components produced out situ, 1 day 1 house) Panelled homes-wall and roof panels are engineered and fabricated in a manufacturing plant Log homes Concrewall Houses –using reinforced concrete micro pillars for constructing houses Other Aspects That Should Be implemented in parallel High density land use Inclusive financial Intermediation Transport and connectivity Adequate water supply Employment for the semi skilled and unskilled Sanitation and Solid Waste Management in Indian Cities (Access to improved urban sanitation to at least half the urban population by 2015 and to all by 2025 is one of the MDGs) Requirements Attitudinal and behavioural changes among citizens Coordination across service providers Maintenance of reliable real time data National Urban Sanitation Policy was formulated to address the problems due to lack of sanitation Municipalities are responsible for solid waste management in India. PPP model is sometimes employed 100000 MT of waste is generated in India everyday 75% waste are taken to dump sites There are lot of laxities in the current system Waste is not segregated; there is no integrated institutional arrangement; lack of technical expertise There are serious implications to every resident Epidemics, health disorders, mortality High morbidity especially in low income households below poverty line What can be done: Create decentralized city wide sanitation plan with one command centre Construct toilets in every house and other commercial and public buildings 100% recycling in sanitation systems Discharge of only treated water to water bodies Access to information on available sanitation systems- use of GIS maps and GPS and real time updating of data Metered affordable water supply for optimal use( mobile water bill payment, meter reading via smartphone) Changes in the micro level F/B from users through social media and crowd sourcing of ideas GPS coordinates of bins and dumpsites to be maintained and status of bins picked/bins unpicked site capacity near breach to be automatically generated and monitored online GPS enabled vehicles to optimize the distances between collection points and dumping sites Number of collection points can also be optimised according to need CCTVs can be installed to discourage people from dumping non segregated waste Sensor based waste bins could send alerts when bins are full Automated waste collection system through chute system
Meeting energy requirements Smart grids integrating renewable energy equipments for storing energy Smart building construction to conserve energy Energy installations to have sensors and controls to anticipate, detect and respond to problems quickly and to be disaster resistant Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED)- a US rating system can be used to evaluate the environmental performance of a building and encourage market transformation towards sustainable design There is a dire need save energy, materials, water and other natural resources and decrease emissions Smart and green neighbourhoods and buildings can save energy up to 30%,reduce emissions, provide higher efficiency and comfort Energy saving windows and panes can save on air conditioning cost, sensor controlled photo voltaic cells on roofs can make energy Making cities sustainable Decentralize power generation (too much dependence on a central grid is not recommendable) Low carbon public transport Disaster Risk Management Floods, earthquakes, fires, landslides. Anticipate and implement Changing citizen behaviour Citizens are central to any city. Participative development is the only possible way of development Citizens must be informed, educated and communicated with on a regular basis for meaningful change. Strict enforcement of laws and regulations are also a part of it Meeting housing requirements Budget housing to meet the requirements of middle and low income households is required. The possibilities of providing rental housing services are yet to be explored Recommendation of High Level Task Force(2008) Defined affordable housing as 300 to 600 sft carpet area housing for EWS/LIG(cost not > 4 times the gross household annual income and EMI/rent not > 30 % of gross monthly income); 1200 sft carpet area housing for MIG((cost not > 5 times the gross household annual income and EMI/rent not > 40% of gross monthly income) Requirements: Strong political will Active Development Mechanisms Clear Construction Strategies Innovative Financial Systems Use of technology What’s the govt. doing about it? Building Centres established Building Materials and Technology Promotion Council has been instituted WHAT CAN BE A GAMECHANGER? Industrialized house production Use of factory produced products to put together houses(pre fab housing) Modular Houses( 90% of housing components produced out situ, 1 day 1 house) Panelled homes-wall and roof panels are engineered and fabricated in a manufacturing plant Log homes Concrewall Houses –using reinforced concrete micro pillars for constructing houses Other Aspects That Should Be implemented in parallel High density land use Inclusive financial Intermediation Transport and connectivity Adequate water supply Employment for the semi skilled and unskilled Sanitation and Solid Waste Management in Indian Cities (Access to improved urban sanitation to at least half the urban population by 2015 and to all by 2025 is one of the MDGs) Requirements Attitudinal and behavioural changes among citizens Coordination across service providers Maintenance of reliable real time data National Urban Sanitation Policy was formulated to address the problems due to lack of sanitation Municipalities are responsible for solid waste management in India. PPP model is sometimes employed 100000 MT of waste is generated in India everyday 75% waste are taken to dump sites There are lot of laxities in the current system Waste is not segregated; there is no integrated institutional arrangement; lack of technical expertise There are serious implications to every resident Epidemics, health disorders, mortality High morbidity especially in low income households below poverty line What can be done: Create decentralized city wide sanitation plan with one command centre Construct toilets in every house and other commercial and public buildings 100% recycling in sanitation systems Discharge of only treated water to water bodies Access to information on available sanitation systems- use of GIS maps and GPS and real time updating of data Metered affordable water supply for optimal use( mobile water bill payment, meter reading via smartphone) Changes in the micro level F/B from users through social media and crowd sourcing of ideas GPS coordinates of bins and dumpsites to be maintained and status of bins picked/bins unpicked site capacity near breach to be automatically generated and monitored online GPS enabled vehicles to optimize the distances between collection points and dumping sites Number of collection points can also be optimised according to need CCTVs can be installed to discourage people from dumping non segregated waste Sensor based waste bins could send alerts when bins are full Automated waste collection system through chute system  Next gen technology that can be used Simulation Robotics Nano technology Stereo lithography Providing smart utilities Satellite controlled parks, lawn micro irrigation SCADA(Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition ) for efficient water, gas and electricity supply at right prices Efficient drainage and sewerage system Intelligent community frameworks to provide health, education and recreation services to citizens
Next gen technology that can be used Simulation Robotics Nano technology Stereo lithography Providing smart utilities Satellite controlled parks, lawn micro irrigation SCADA(Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition ) for efficient water, gas and electricity supply at right prices Efficient drainage and sewerage system Intelligent community frameworks to provide health, education and recreation services to citizens  SCADA for water supply Providing Smart Mobility Seamless, safer, efficient and effective transport infrastructure is the need of the hour Travel smart cards Traffic simulation Providing Safety and Security Smart Buildings Embedding in built microchips on structures for self diagnosis and repair Emergency response Safety centres in every cities Crime, natural disasters, accidents, terrorism, cyber crime and data breaches are potential safety and security concerns What can be done? Telesurveillance – real time communication of intelligence data between different agencies and response teams Collaborative Response Efforts- police stations have to work in tandem. When an ambulance is on the move the signals leading to the nearby hospital must automatically give it priority Data integrity has to be in place. Encryption solutions can be used to secure data transfer across unsecure lines Disaster resistant buildings have to be constructed and the entire city must function in such a way that there is minimum stress on natural resources Disaster resistant hubs with independent functioning capacity-solar power generation, rain water harvesting, waste composting etc within the community Data generated from implanted medical devices in human body can be amplified by smartphones to aid in rescue efforts Sensors can be embedded in infrastructure to detect tension, pressure etc Platforms that can sense overcrowding can be developed Virtual and physical links between persons, things and organisations can help in integrated and timely response Redesigning Roads The mode of transport for 52 % of urban population is walking. Also people walk to train stations and bus stops. There must be an Urban Road Agenda on how to build roads Multiply capacity of road networks, Build more roads to complete the existing network of roads Improve signal coordination and programme signals, Eliminate on street parking Maintain contiguous road width The National Urban Transport Policy says that the focus should be on movement of people not vehicles 1/3rd of the road must be used for public transport The Bus Rapid Transit system should be redesigned: level boarding ( boarding and alighting time minimized) Dedicated stations Safe pedestrian crossing Large, high capacity, comfortable buses Automated fare collection Signal priority to buses Pedestrian friendly features:(see pictures below) 40:40 principle(road width less than 40m for ease of crossing; speed limit of 40 km/hr) Smaller intersections Mid block crossing Erecting bollards Speed management not by sign boards but by road design itself-barriers, chicanes, lesser curb radii etc For Cyclers-Bicycle lanes , bicycle renting facility at various points
SCADA for water supply Providing Smart Mobility Seamless, safer, efficient and effective transport infrastructure is the need of the hour Travel smart cards Traffic simulation Providing Safety and Security Smart Buildings Embedding in built microchips on structures for self diagnosis and repair Emergency response Safety centres in every cities Crime, natural disasters, accidents, terrorism, cyber crime and data breaches are potential safety and security concerns What can be done? Telesurveillance – real time communication of intelligence data between different agencies and response teams Collaborative Response Efforts- police stations have to work in tandem. When an ambulance is on the move the signals leading to the nearby hospital must automatically give it priority Data integrity has to be in place. Encryption solutions can be used to secure data transfer across unsecure lines Disaster resistant buildings have to be constructed and the entire city must function in such a way that there is minimum stress on natural resources Disaster resistant hubs with independent functioning capacity-solar power generation, rain water harvesting, waste composting etc within the community Data generated from implanted medical devices in human body can be amplified by smartphones to aid in rescue efforts Sensors can be embedded in infrastructure to detect tension, pressure etc Platforms that can sense overcrowding can be developed Virtual and physical links between persons, things and organisations can help in integrated and timely response Redesigning Roads The mode of transport for 52 % of urban population is walking. Also people walk to train stations and bus stops. There must be an Urban Road Agenda on how to build roads Multiply capacity of road networks, Build more roads to complete the existing network of roads Improve signal coordination and programme signals, Eliminate on street parking Maintain contiguous road width The National Urban Transport Policy says that the focus should be on movement of people not vehicles 1/3rd of the road must be used for public transport The Bus Rapid Transit system should be redesigned: level boarding ( boarding and alighting time minimized) Dedicated stations Safe pedestrian crossing Large, high capacity, comfortable buses Automated fare collection Signal priority to buses Pedestrian friendly features:(see pictures below) 40:40 principle(road width less than 40m for ease of crossing; speed limit of 40 km/hr) Smaller intersections Mid block crossing Erecting bollards Speed management not by sign boards but by road design itself-barriers, chicanes, lesser curb radii etc For Cyclers-Bicycle lanes , bicycle renting facility at various points  smaller intersections
smaller intersections 

 mid block crossing
mid block crossing  chicane
chicane 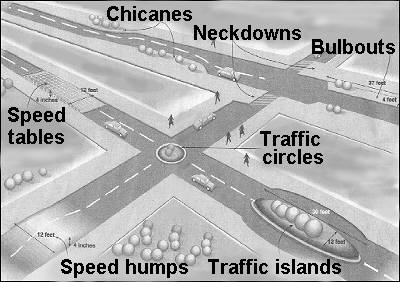 pedestrian safety and speed management design
pedestrian safety and speed management design  bicycle renting
bicycle renting  Bollards
Bollards 



Comments