Diamonds are homogeneous, naturally-occurring, solid, and generally inorganic substances with a definable chemical composition and an orderly internal arrangement of atoms. Diamonds originate under extremely high pressure, 150 km deep in the upper mantle. Pure carbon is compressed into the diamond structure. Rifting causes deep mantle rock to move upward. Diamonds are found in kimberlite pipes.
Characteristics of a Diamond
The four main optical characteristics of diamonds are transparency, lustre, dispersion of light, and colour. In its pure carbon form, diamond is completely clear and transparent. As in all-natural substances, perfection is nearly impossible to find. Diamonds are the hardest substance known. And the only difference between an ugly piece of coal, and the beautiful diamond is pressure and heat. The beautiful diamond didn’t start out as it looks in its final form. As a matter of fact, uncut diamonds have greasy lustre and are not brilliant at all. But the same stones when cut exhibit a high lustre. The primary object of cutting a diamond is to bring out the fire and brilliance of the stone.
Geometry
- Diamond comprises the lowest mass element that can form a stable covalently bonded crystal lattice, and this lattice is highly symmetric and tightly bound.
- Geometric crystallography derives its significance from the fact that the external form of a crystal discloses the symmetry characters of its internal structure and, that these characters are in their turn closely related to the physical properties of the solid.
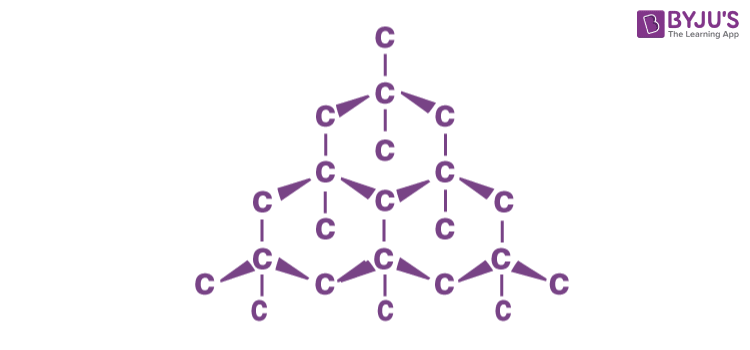
- Its resulting extreme properties, along with the recent developments in its synthesis, have led to an explosion of interest in the material for a diverse range of optical technologies including sensors, sources, and light manipulators.
- The study of the crystal forms of diamond thereby becomes a highly important first step towards an understanding of its many remarkable properties.
- A characteristic feature of a diamond is that it is generally found as single complete crystal, which is bounded on all sides by the natural faces.
- In diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. This makes it super strong, and it has a high melting and boiling point. With no electrons to spare, diamond can’t conduct electricity.
Material Properties
The presence of nitrogen as a major impurity in a diamond has been noted, as also has the occurrence of boron (< 20 ppm), which accounts for the semiconducting properties of Type IIb diamond. As a chemical sink for various elements, diamond is fairly poor with regard to concentration levels, although 58 elements have been recognized at the trace impurity level.
Colours in Diamonds
Nitrogen is by far the most common impurity found in gem diamonds and is responsible for the brown and colour in diamonds.
- In order of rarity, the yellow diamond is followed by brown, colourless, then blue, green, black, pink, orange, purple, and red.
- Colour diamonds contain impurities or structural defects that cause the colouration, while pure or nearly pure diamonds are transparent and colourless.
Diamonds can also be produced synthetically in a high-pressure high-temperature process, which approximately simulates the conditions in the Earth’s mantle. An alternative and completely different growth technique is chemical vapour deposition (CVD).
Applications
Diamonds have been adapted for many uses because of the material’s exceptional physical characteristics.
- Unlike many other gems, it is well-suited to daily wear because of its resistance to scratching, perhaps contributing to its popularity as the preferred gem in engagement or wedding rings, which are often worn every day.
- Diamond is the most important gemstone in the jewellery industry.
- The colourless stone is most often used for jewellery, although yellow and brown are also used.
- Diamond windows are made from thin diamond membranes and used to cover openings in lasers, x-ray machines and vacuum chambers.

Comments