Due to the strain on the eye, eye-related or ophthalmological issues are now more prevalent. Hyperopia is one of the common eye problems that affect people of all age groups. Many infants and small children tend to have far-sightedness, but it gets normal once the babies reach the age of three. This article lets us know more about hyperopia, its causes and the ways it can be corrected.
| Table of Contents |
What is Hyperopia?
Farsightedness is also known as hyperopia. It is a refractive error in which distant objects are clearly seen, but close objects appear blurry. People experience farsightedness differently, and some people, more commonly when they are young, do not notice any problems with their vision. In addition, for people with significant farsightedness, vision can be blurry for objects at any distance, near or far.
What causes Hyperopia?
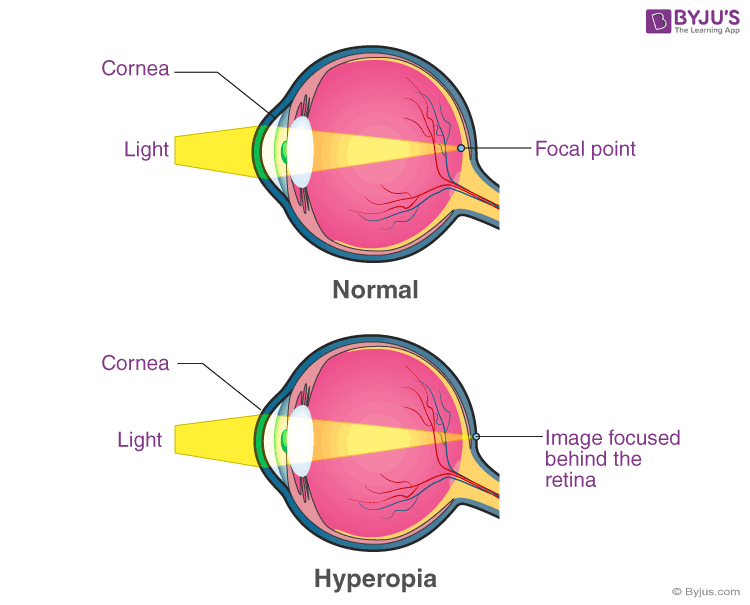
The human eye relies on two critical parts to focus on an image: the cornea, which is the clear front surface of the eye, and the crystalline lens, a clear structure inside the eye that changes shape in order to focus on objects.
In an eye without refractive error, these focusing elements have a smooth curvature, much like the surface of a smooth rubber ball, and bend incoming light to make a sharply focused image on the retina.
If the cornea is not smoothly curved, like, in the case of people with farsightedness, the light does not properly bend or refract light properly, and this results in a refractive error. Farsightedness occurs when light entering into the eye focuses behind or beyond the retina, instead of on it.
Both children and adults can be affected by farsightedness and it can even be hereditary. People whose parents are farsighted may likely also have the condition. An eye care professional (ECP) can diagnose farsightedness during a routine eye exam. Generally, at-school vision screenings are not effective in detecting farsightedness.
Hyperopia is generally classified into three types according to its clinical appearance –
- Simple hyperopia
- Pathological hyperopia
- Functional hyperopia
What are the Symptoms of Hyperopia?
- Blurred vision at night or later in the day
- Trouble focusing on near objects
- Aching eyes, eye strain, and headaches
- Squinting
- Difficulty maintaining a clear focus
- Eye fatigue
- Irritability or nervousness after sustained concentration
Farsightedness and its Correction
- Farsightedness or hyperopia is the inability of the eye to focus on nearby objects. The farsighted eye has no difficulty viewing distant objects. The lens can no longer presume the convex and curved shape lens that is needed to view the nearby objects. This vision problem can be corrected by using a converging lens.
- It will refract light before entering the eye and eventually decreases the distance of the image. By initializing the refraction process prior to light reaching the eye and the image of nearby objects is once again focused upon the retinal surface.
- Farsightedness is mostly seen among adults and occasionally in young people. If this vision problem happens among youth, the cause would rarely be related to the inability of the lens to assume a short focal length. The problem, in this case, is mostly related to an eyeball that is shortened.
- With the shortening of the eyeball, the retina lies closer than usual to the cornea and lens. This results in the formation of an image of nearby objects beyond the retina. To correct this problem, again the same converging lens is required for the adults.
Watch the video below to learn how and why spectacles/contact lenses are used to correct defects of vision and how exactly they affect the human eye.

Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is hyperopia also called?
What are the types of hyperopia?
What is hyperopia?
List five symptoms of hyperopia.
Farsightedness can be corrected using which type of lens?
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about Hyperopia, a human eye, and much more.


Comments