Nucleus of an Atom
The nucleus of an atom is the central region of an atom where the majority of the mass is concentrated. Through the scattering of alpha particles experiment by Rutherford, we learned that the nucleus of an atom contains a majority of the mass of the atom. Numerically speaking, the nucleus of an atom occupies almost 10-14 times the volume of the atom but contains 99.99% of the atomic mass. The nucleus of an atom is so small that if you expanded an atom to fill up a room, the nucleus of an atom would still be no larger than a pinhead!
Nucleus of an Atom – atomic mass
An atom is tiny and therefore its mass is also proportionally minute. A regular unit of mass such as a Kilogram (Kg) cannot be used to weigh something as small as an atom and to address this issue, scientists have created a new unit of mass. It is called the Atomic Mass Unit (u). Its reference is taken as Carbon-12 and 1 Atomic Mass unit is equal to 1/12th the weight of one atom of Carbon 12.
| 1 u = one atom of C-12/ 12 = 1.992647 10-26/ 12 kg |
| 1 u = 1.660539 10-27 kg |
This is the mass of a hydrogen atom! Surprisingly except for a few elements, most of them are whole multiples of the weight of the Hydrogen atom.
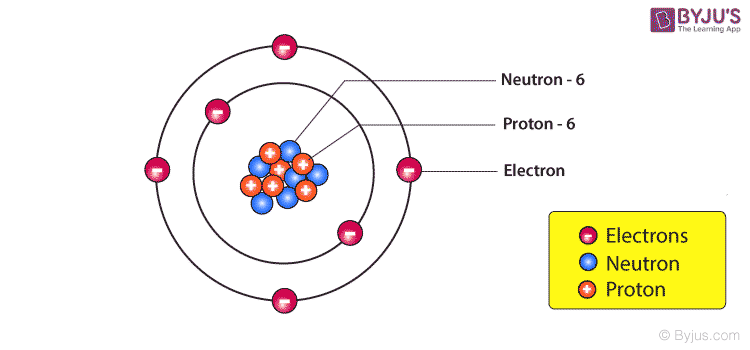
Nucleus of an Atom – Composition
The Nucleus of an atom consists of a tightly packed arrangement of protons and neutrons. These are the two heavy particles in an atom and hence 99.9% of the mass is concentrated in the nucleus. Of the two, the protons possess a net positive charge and hence the nucleus of an atom is positively charged on the whole and the negatively charged electrons revolve around the central nucleus. Since the mass concentration at the nucleus of an atom is immense the nuclear forces holding the protons and the neutrons together are also large. The protons are in such close vicinity to each other inside the tiny nucleus and therefore the electrostatic forces of repulsion also act inside the nucleus. Nuclear energy relies on nothing but releasing the energy trapped in the nucleus of an atom. The total number of protons in a nucleus is equal to the number of electrons revolving around the nucleus and hence the atom, on the whole, is electrically neutral.


This platform is very useful for preparation of any course.