Satellite communication is the method of transporting information from one place to another using a communication satellite in orbit around the earth. Watching the English Premier League every weekend with your friends would have been impossible without this. A communication satellite is an artificial satellite that transmits the signal via a transponder. It does so by creating a channel of communication between the transmitter and the receiver located at different places on Earth.
Satellite communications are used in telephone, radio, television, internet and military applications. Believe it or not, there are more than 2000 artificial satellites hurtling around in space right above your heads.
These satellites all have different purposes, and they’re all at different orbits. Orbit, in this case, is the path that a satellite follows while revolving around a planet. Let’s take a better look at the types of orbits.
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
Low Earth Orbit is usually a circular orbit at a height of 160 to 2000 km above the surface. Due to a low height and a circular orbit, they are able to revolve around the Earth in about 90 minutes. The line of sight of such a satellite is about 1000 km, and they are travelling at enormous speeds, (Around the World in 90 minutes!!). So for a station on Earth to have continuous connectivity, you need numerous Low Earth Orbit satellites. Such satellites though are very easy to launch and because they are close to the ground, Low Earth Orbit satellites do not require high signal strength which is an enormous advantage. Low earth orbit satellites can also form a satellite constellation, which is making and maintaining a specific arrangement with respect to other satellites.
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO)
Medium Earth Orbit satellite is a satellite in orbit around the earth somewhere between 2000 and 35786 km above the surface. These satellites take quite a bit longer than the ones in Low Earth orbit to go around the Earth and hence they are visible for longer durations. They make one revolution in about 3-12 hours. Also, since they are higher up than LEO, MEO Satellites have better coverage of the Earth’s surface. The disadvantage is that an MEO satellite is higher up which results in a long time for communication and weaker signal.
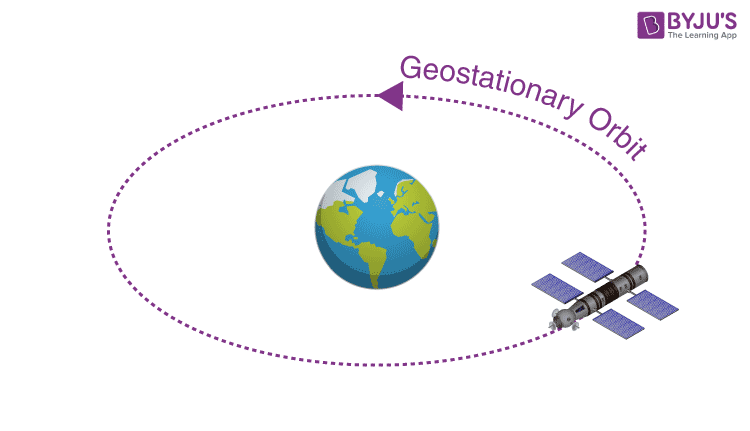
- Geostationary Orbit (GEO)
To a viewer on the ground, a satellite revolving around the Earth in a geostationary orbit at a height of 35786 km, would appear fixed in the sky. This is because the angular velocity of the satellite is synced with that of the Earth’s. Both the earth and the satellite cover 360o in 24 hours. Having a satellite fixed in space helps because you don’t have to track the satellite. You just point your equipment to the satellite once and you don’t have to bother again. Admittedly getting a satellite to the geostationary orbit is hugely expensive and the equipment is complex but in applications like television DTH service, the transmission can be scaled to a lot of people and the reception equipment is cheap.
These were some common orbits. Apart from these we also have orbits that address very specific problems. One such problem was faced by the Russians. GEO satellites worked perfectly for the equatorial regions but it had a very weak coverage near the Poles. To address this problem, the Russians designed an orbit with a very high inclination. The inclination is the angle between the satellite’s orbit and the equator. This orbit was called the Molniya orbit. The orbit had excellent coverage of the North Pole for a short time. Molniya had a period of 24 hours but out of that, it would be close to earth only for 6-9 hours. Russia launched some more satellites in the same orbit and soon they had uninterrupted coverage.
Do you know what a satellite city is?



Comments