Human Eye
How do we see what we see? How do we perceive simple light rays as full-fledged images? Before getting into this, we should understand the important parts of the human eye and what their functions are.

The Cornea: Imagine this to be like a window to a human eye. The cornea contributes to the major refraction of light (bending of light rays) entering our eyes. It forms the clear front surface of a human eye. It also makes sure that foreign substances do not enter the eye.
The Iris: This lies right behind the cornea. It controls the circular opening called the pupil (aperture). It functions as an automatic camera shutter, controlling the amount of light entering a human eye.
The Crystalline Lens: The lens further focuses the light rays entering our eyes. Again, we can compare this to how an autofocus lens functions in a camera. This is called the accommodating power of the eye. Depending on where the object lies, the lens tries to focus on that object.
The Vitreous Humor: This is a jelly-like substance that fills most of the inner chamber of the eye. It helps the eye maintain its spherical nature. The light rays after passing through the opening, travel through the vitreous humour before striking the retina.
The Retina: It is a light-sensitive inner lining of the human eye. Ideally, light rays should focus on the retina, forming an image. It is the innermost lining of the inner tissue, which consists of the sclera and the choroid as well. When the light finally strikes the retina, an electric signal is sent to the brain (the visual cortex) via the optic nerve. The brain then processes the image and finally, we see what we see.
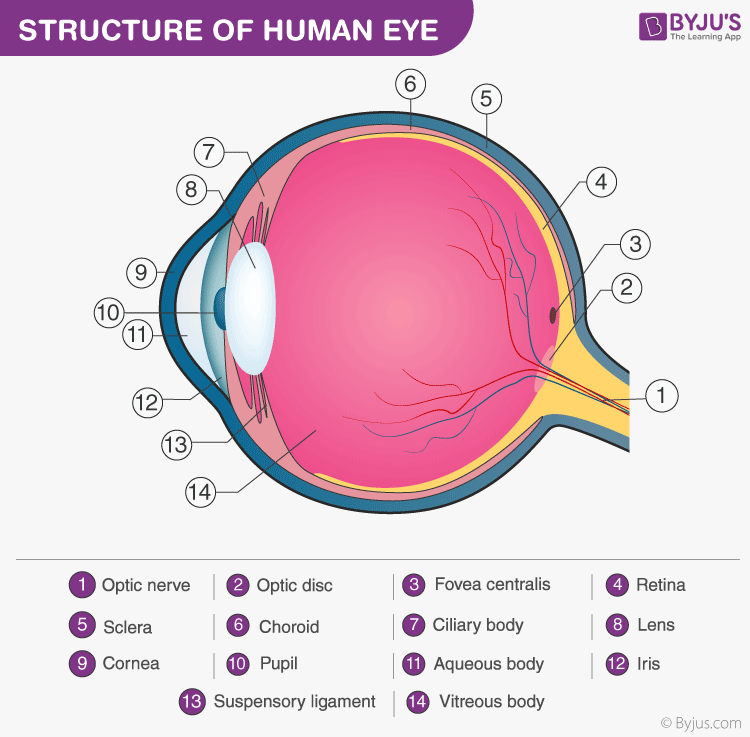
Obviously, there are other parts of the human eye with supporting functions like lubrication of the eye (tear formation) and muscles that allow eye movement. The eyelids play a very important role in protecting the eye from external damage. Apart from the optic nerves, there are other sensory nerves that relay information to the brain regarding pain and other abnormalities.
You now have a brief overview of how the human eye works.
Watch the video and learn more about rainbow

Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Define the human eye.
Define a blind spot.
It is the junction of the optic nerve and retina where no sensory nerve cells are present. Hence vision is not possible in the blind spot.
What is a retina?
What are the various parts of the human eye?
What are the types of optic nerves?
Stay tuned with BYJU’S for more such interesting articles. Also, register to “BYJU’S – The Learning App” for loads of interactive, engaging Physics-related videos and unlimited academic assistance.


its an very good app for education. it has helped me a lot in my 9th and 10th examinations.
BYJU’S provide the best study material.
A Byju’s student since I was in 7th standard now in 10th 😋
The Best App To Have Fun With Learning
Thankyou BYJU’S And Team.