Barium sulfate is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula BaSO4. It is a white crystalline, odourless solid that has many applications including medical uses. Barium sulfate occurs naturally as the mineral barite. Barium sulfate is obtained from barite after mining and processing. The processing of the impure barite requires heating it with coke to produce the water-soluble barium sulphide, which is then segregated from the impurities and is made to react with sulphuric acid to give barium sulfate product. In this article, let us learn more about the barium sulfate formula, its properties and chemical structure along with its uses.
Barium Sulfate Properties
| Properties of Barium Sulfate | |
| Name | Barium Sulfate |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Molecular Formula | BaSO4 |
| Melting Point Barium Sulfate | 1580 °C |
| Boiling Point of Barium Sulfate | 1600 °C |
| Density | 4.49 g/mL |
| Molar Mass | 233.38 g/mol |
| Solubility in Water | Poor solubility in water |
Barium Sulfate Chemical Structure
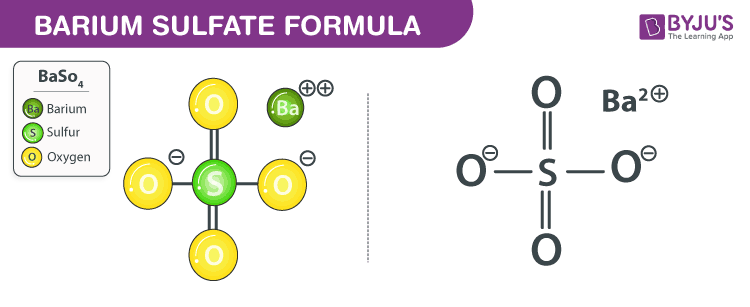
Barium Sulfate Uses
- Used as a radio-opaque agent to diagnose gastrointestinal medical conditions.
- It is used in concrete-based radiation shields and oil well drilling fluids.
- Has applications in root canal fillings, adhesives, paper coatings, textiles, rubber and catalyst supports.
To learn more about such chemistry topics register to BYJU’S now!
Comments