What is Common Cold?
The cold or common cold is a disease diagnosed with a headache, runny nose, scratchy throat, fever and non-stop sneezing. It is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract, which primarily affects the nose and sometimes sinuses, ears, and bronchial tubes.

Causes of Common Cold
A common cold is caused by viruses. Some of them include –
- Rhinovirus – This one usually intrudes your system during early fall, spring, and summer. They are behind 10%-40% of colds. Even though these are the main common viruses which affect you, they would rarely make you seriously sick.
- RSV and parainfluenza – These tiny organisms are behind severe infections like pneumonia, in young children.
Pneumonia is a lung infection with symptoms of a cough, fever, and breathing problems. Some more symptoms would include –
- A cough viz. mucus (sputum) from your lungs, which could be rusty or green or tinged with blood
- Diarrhoea
- Fever
- Shaking and “teeth-chattering” chills
- Fast breathing and shortness of breath
- Fast heartbeat
- Chest pain that often feels worse when you cough or breathe in
- Vomiting and Nausea
- Feeling very weak or tired
You could get infected by a cold-infected person. When you touch surfaces or objects used by them, which contains germs and then to your nose or mouth, you are prone to get infected by the germs or virus.
You could get affected by it if you’re near a cold infected person, as their sneeze could contaminate the air that you breathe passively.
When a virus attaches to the lining of the nose or throat, the infection of cold initiates. The immune system of the body sends out white blood cells (WBC) to attack this invader and this is how cold gets demolished.
Signs and Symptoms of Common Cold
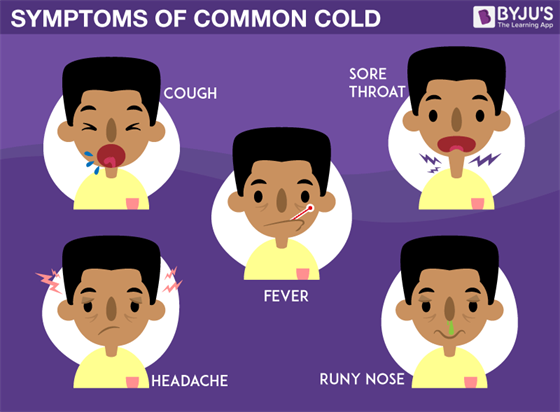
When cold strikes, the following symptoms are usually observed –
Primary Symptoms
- Scratchy or a sore throat
- Sneezing
- Stuffy nose
- Cough
- Runny Nose
- Watery eyes
- Mucus draining from your nose into your throat
Secondary Symptoms
- High fever
- Muscle aches
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
These symptoms indicate that you have flu rather than a common cold.
Prevention of Common Cold

It is practically impossible to completely prevent the spread of colds, but you can take certain measures to reduce the chances of getting cold.
- Wash your hands often – It is probably the best measure to prevent the transfer of a cold or any kind of infection. Use sanitiser while being in any public place and also make it a point to wash hands before eating. Teach the importance of hand-wash to kids also.
- Avoid touching your face – Try not to touch your face, mouth, nose & eye areas, when you are near a person infected with a cold.
- Control stress – People facing emotional stress regularly have a weaker immune system, which implies that they could catch a cold easily. So, reduce stress and live a healthy life.
- Cleanliness – Keep household surfaces like doorknobs, drawer pulls, keyboards, light switches, telephones, remote controls, countertops, and sinks clean. These are the places where viruses lie for hours after they are used by an infected person.
- Avoid Smoking – Cigarette smoke could raise the chances of susceptibility to colds and other infections. Avoid passive smoking as well.
- Drink a sufficient amount of water – Drink water, juice, clear broth, warm lemon water, chicken soup, and other warm fluids. These will help you to stay away from cold or flu.
Myths About Common Cold
Note that getting chilly or wet doesn’t trigger the cold sickness. You get infected with a cold only when you are more prone to it. When you are extremely tired, under emotional distress, or have allergies to nose and throat symptoms, you easily catch a cold.
Another myth states that your diet is the cause of such sickness or infection which is not true. Another hoax is when they say that you’re getting sick because your tonsils or adenoids are large.
For more detailed information about Common Cold, visit BYJU’S.

Very helpful 😁