An organism undergoes a series of changes throughout its life cycle. Gametogenesis (spermatogenesis and oogenesis), plays a crucial role in humans to support the continuance of generations.
Gametogenesis is the process of division of diploid cells to produce new haploid cells. In humans, two different types of gametes are present. Male gametes are called sperm and female gametes are called the ovum.
- Spermatogenesis: Sperm formation
- Oogenesis: Ovum formation
Spermatogenesis
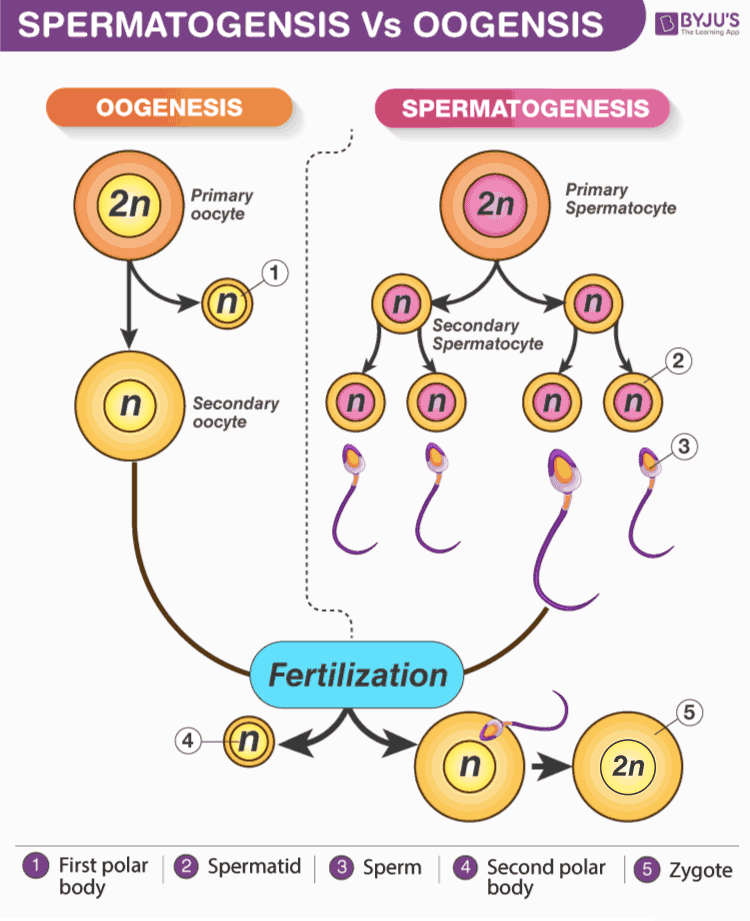
In the male, immature germ cells are produced in the testes. At puberty, in males, these immature germ cells or spermatogonia are converted into sperms by the process of spermatogenesis. Spermatogonia are diploid cells that undergo mitotic division and their number increases. Primary spermatocytes undergo meiosis and produce haploid cells- secondary spermatocytes. These secondary spermatocytes undergo the second meiotic division to produce immature sperms or spermatids. These spermatids undergo spermiogenesis to transform into sperms. Various hormones like GnRH, LH, FSH and androgens are involved in stimulating spermatogenesis.
Oogenesis
In females, the oogonia are converted to the mature ovum. This process is called oogenesis. In the female ovary, millions of oogonia or mother cells are formed during fetal development. These mother cells undergo the meiotic cell division, the meiotic division rests at the prophase-I and lead to the production of primary oocytes. Primary oocytes are embedded within the primary follicles on the outer layer. Primary follicles get surrounded by more granulosa cell layer and forms secondary follicles. Secondary follicles then turn into the tertiary follicle. At the stage of female puberty, the primary oocytes present in the tertiary follicles complete meiosis and form secondary oocytes (haploid) and the polar body by unequal division. The tertiary follicle undergoes some structural and functional changes and produces mature Graafian follicle. Secondary oocyte undergoes second meiotic division to form an ovum. Ovum is released from the Graafian follicle during the menstrual cycle. The release of an ovum from the Graafian follicle is called ovulation. Ovulation is controlled by the female reproductive hormone which is stimulated by the pituitary gland.
Also Read: Difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis
We have thus seen the basic introduction and common process involved in gametogenesis. For the complete understanding and illustrations of the topic, visit BYJU’S.


Comments