Table of Contents
Introduction
The lungs are primary, complicated respiratory organ which functions by expanding and relaxing thousands of times every day by bringing in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. It is the vital organ for our respiration; hence it is important to care for our lungs. Lung diseases are one of the leading causes of death in the world as the lungs are susceptible to various infections and diseases.
Types of Lung Diseases
Some of the infections are mentioned below.
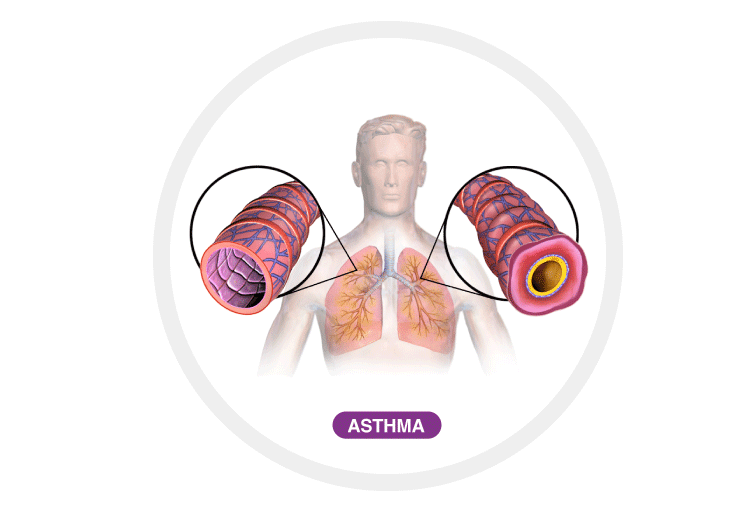
Asthma
It is a chronic disease of the airways that makes breathing difficult. It causes inflammation of the air passages that results in a temporary narrowing of the airways which carry oxygen to the lungs.
Causes: Genetics play an essential role in the development of this disease. It could be inherited from either of the parents. This is called genetic susceptibility. It could also be triggered by substances called allergens in the environment, including cockroaches, pets, moulds, fungi and pollen.
Symptoms: Most symptoms will start emerging from a younger age. The symptoms vary from person to person and can change over time. People who have asthma have these symptoms- wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing, and alsoresulting in decreased activity and inability to talk.
Treatments: The treatment range from inhalers to oral medication or asthma nebulizers to breathing machines. Early treatment is key to preventing Asthma attacks and symptoms.
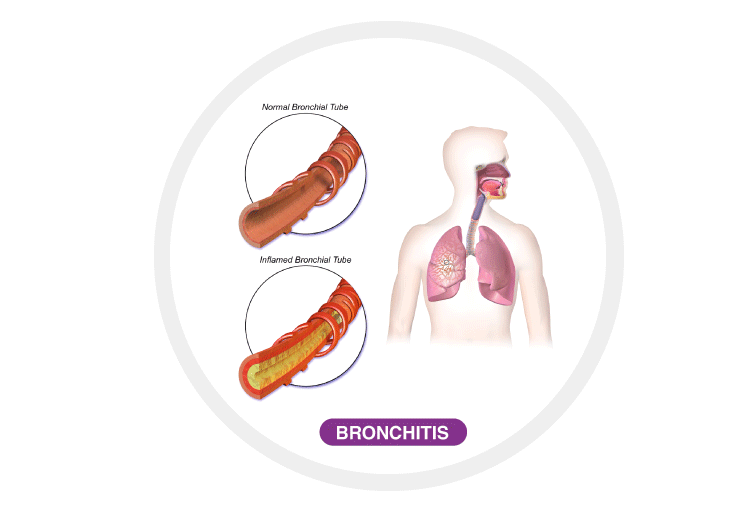
Bronchitis
Bronchitis is a viral infection which occurs when the mucous membrane in the bronchial passage becomes inflamed. Bronchi are the air passages that connect the windpipe (trachea) with air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs. It can last from six weeks to two years; it is most commonly seen in heavy smokers. There are two kinds of Bronchitis, Acute Bronchitis, and Chronic Bronchitis. Acute bronchitis does not last long and gets better after two or three weeks. Chronic Bronchitis lasts longer from three months up to a year.
Causes: Bronchitis is caused by basic viruses typically that cause cold and flu. It can also be caused by bacterial infection or exposure to tobacco, smoke, dust, and fumes which irritate the lungs.
Symptoms: These may include – a hacking cough which lasts for 4 – 5 days with more clear yellow or white phlegm, low-grade fever, soreness or tenderness in the chest with coughing and thick and dark mucus.
Treatments: Bronchitis can be treated by a simple contemporary measures such as rest, drinking lots of water, and avoiding smoke, dust, fumes, and pollution. Vaporization and hot showers also help in treating this syndrome.
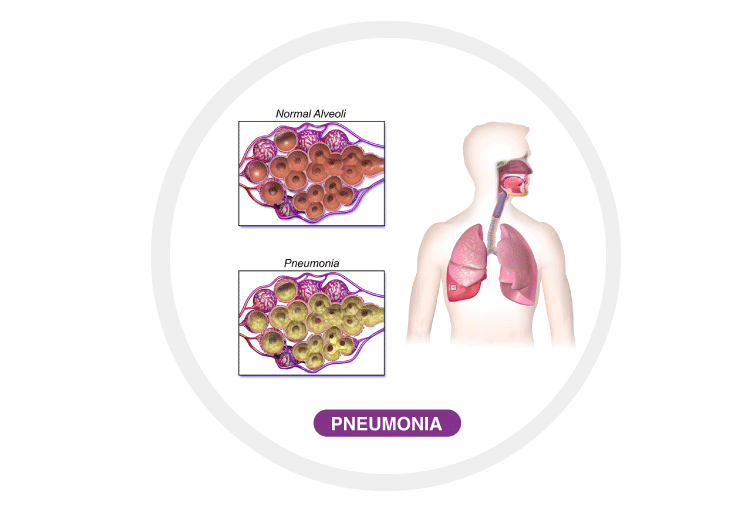
Pneumonia
It is a swelling of one or both the lungs that is usually caused by an infection. It could be triggered by fungi, bacteria or viruses—pneumonia results in fever and difficulty in breathing which could last up to 2-3 weeks. Pneumonia usually starts by breathing germs into the lungs. There are different kinds of Pneumonia like Bacterial Pneumonia, Viral Pneumonia, Mycoplasma Pneumonia and other kinds.
Causes: In most cases, it is caused by bacteria and viral infections. It is generally seen in people who have impaired immune systems. Pneumonia can also be caused by some forms of fungal infections.
Symptoms: The general symptoms of pneumonia can develop quickly and may include chest pain, shivering with chills, fever, dry cough, wheezing, muscle aches, and nausea.
Treatments: Treatments depend on the type and severity of pneumonia. General treatment includes using all prescribed medications and participating in follow-up care. Bacterial pneumonia can be treated by regularly taking antibiotics and stoppage will cause it to return. Antiviral drugs are prescribed for treating viral pneumonia symptoms.
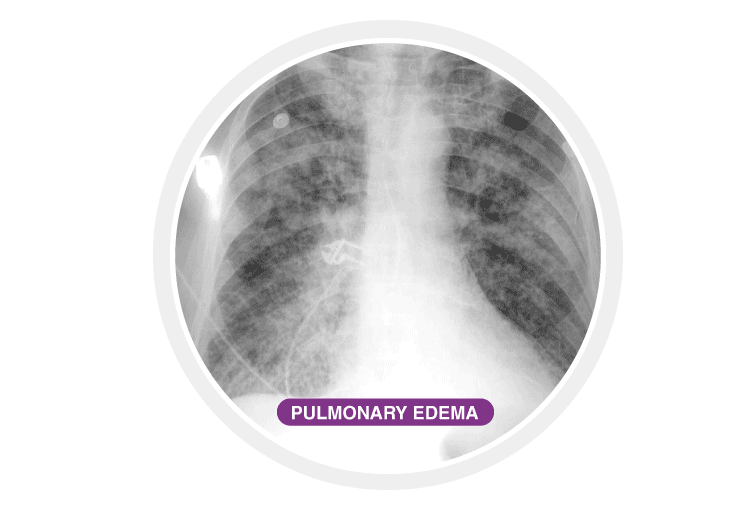
Pulmonary Oedema
This condition is caused by the excess collection of watery fluid in the lungs. As this fluid accumulates, it becomes difficult for the lungs to function and leads to the body struggling to get enough oxygen. The most common cause of pulmonary oedema is congestive heart failure resulting in failure of blood circulation throughout the body. There are two types of pulmonary – acute and chronic pulmonary oedema.
Acute pulmonary oedema is short-term, and Chronic oedema lasts longer.
Causes: Pulmonary oedema is often classified as a cardiogenic heart problem. When the heart muscle is not able to pump effectively, there is a backup of blood returning from the lungs to the heart. This causes pressure within the blood vessels.
Symptoms: Depending on the cause, the symptoms may appear suddenly or develop over time.
Acute oedema symptoms:
- A rapid and irregular heartbeat
- Wheezing or gasping for breath
- A feeling of suffocation or drowning
- Anxiety, restlessness or a sense of apprehension
- Chest pain if pulmonary oedema is caused by heart disease
- A cough that produces frothy sputum that may be tinged with blood
- Extreme shortness of breath or difficulty in breathing that worsens when lying down
Chronic oedema symptoms:
- Wheezing
- Swelling in lower extremities
- Difficulty in breathing with exertion
- Difficulty in breathing while lying flat
- Having more shortness of breath than usual when physically active
- Awakening at night with a breathless feeling that may be relieved by sitting up
Treatments: Doctors commonly prescribe diuretics and nitroglycerin, such as furosemide to treat pulmonary oedema.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Name a few lung diseases.
Asthma, bronchitis, pneumonia, pulmonary oedema, and acute oedema.
2. What are the causes of pulmonary oedema?
Pulmonary oedema is often classified as a cardiogenic heart problem. When the heart muscle is not able to pump effectively, there is a backup of blood returning from the lungs to the heart. This causes pressure within the blood vessels.

Comments