Table of Contents
Introduction
As we all know, photosynthesis is a biochemical process of producing carbohydrates using light energy. The whole process is carried out in two phases.
- Photochemical phase – In the photochemical phase, ATP and NADPH are produced
- Biosynthetic phase – In this phase, the final product glucose is formed.
Based on, how plants proceed in the biosynthetic phase, plants are further classified as C3 and C4 plants. Another factor which differentiates a C4 plant from C3 is photorespiration.
Photorespiration
Photorespiration is a wasteful respiratory process, which hinders the photosynthetic process in many higher plants.
The reaction in which carbon dioxide and water combine to give carbohydrates is termed carbon fixation. Calvin cycle is the first step of carbon fixation where CO2 combines with Ribulose-1 and 5-bisphosphate (RuBP) to form two molecules of 3 carbon acid called 3-phosphoglycericacid (PGA). The reaction is catalyzed by the most abundant enzyme in the world called RuBisCO (RuBP carboxylase-oxygenase). RuBisCO is the enzyme that has an affinity for both CO2 and O2 but has more affinity for CO2. Hence, the binding of CO2 and O2 are competitive in nature and the concentration of the molecules in the atmosphere determines the winner. This is the basis for photorespiration in plants.
Sometimes in C3 plants, RuBisCo instead of binding with CO2 binds with O2 which deviates the process from photosynthesis and instead of fixing carbon for photosynthesis, starts depleting the already fixed CO2 reserves. During this pathway, RuBP and oxygen together form one molecule each of phosphoglycerate and phosphoglycolate. This pathway is known as the photorespiration pathway, where energy formation takes place, instead, CO2 is wasted at the expense of energy.
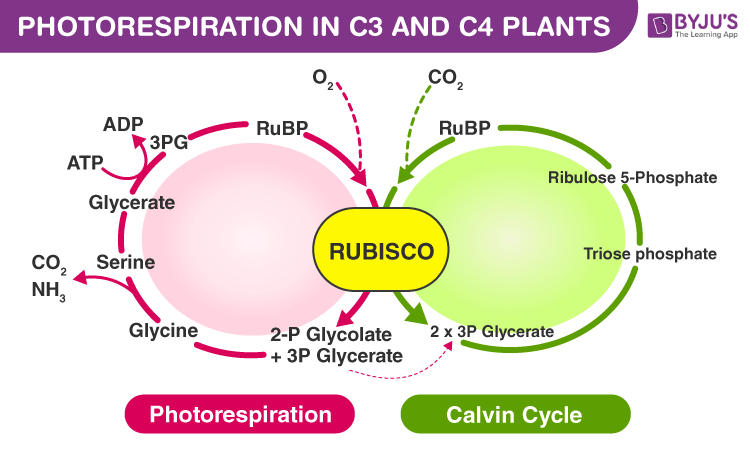
C4 plants have developed a special mechanism to avoid the wasteful photorespiration process and increase CO2 levels. C4 plants use the Hatch and Slack Pathway where CO2 is converted into oxaloacetic acid (C4 acid) which ensures that RuBisCo has a continuous and abundant supply of CO2. Therefore, RuBisCo works more as a carboxylase enzyme which helps in photosynthesis.
For more detailed information about photorespiration, visit BYJU’S.

nice it can help