According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been removed from NCERT Class 7 Science textbook.
Let’s Go Shopping
Fibres from Plants
- Plant fibre is mainly composed of cellulose and cellulose fibres. These are most commonly used to make paper and cloth.
- Cellulose generates long, often highly lustrous fibres when prepared appropriately.
- Plants, including cotton, jute, flax and hemp, are used to obtain plant fibres.
To know more about Plant Fibres, visit here.
Jute
- Jute fibre is obtained only from the stem of the jute plants. It is a soft, shiny and long fibre with a silky texture, which is grown in the rainy season.
- Jute mainly grows in regions having alluvial soil, which is found in the delta regions of the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers.
To know more about Jute Fibre, visit here.
Basics of Fabric
Fibres
- The finer part of the thread is referred to as fibre.
- Fibre is a thread-like structure that is spun into ropes, clothes and strings.
- Fabrics are made from fibres obtained from natural or artificial sources. For example, rayon, nylon, polyester, etc.
To know more about Fibres, visit here.
Fibre to Yarn to Fabric
The fabric consists of thin strands called yarn, which in turn consists of thinner strands called fibres.
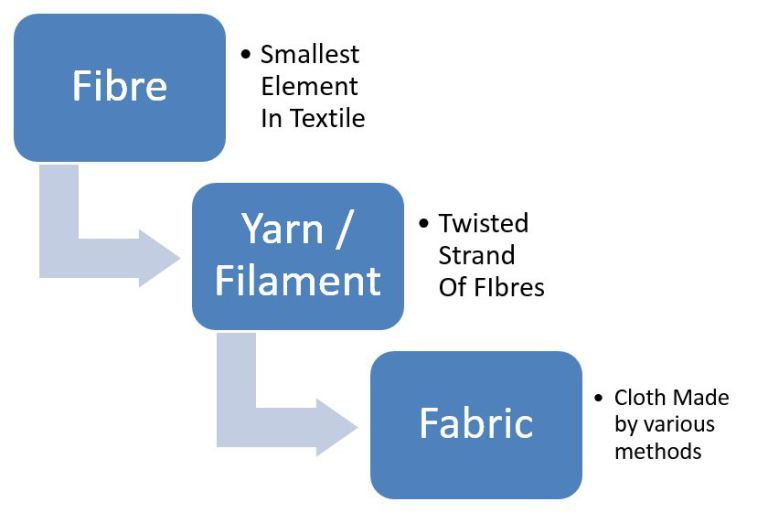
To know more about Fibre to Fabric, visit here.
Cotton and Its Processing
- Cotton is obtained from cotton bolls, which are directly from the surface of cotton seeds.
- It is grown in black clayey soil with a warm climate.
- The processing of cotton involves Ginning, Spinning, Weaving and Knitting.
Wool
Fibre from Animals
Wool
- The natural animal fibre is obtained from sheep, goats, yak, camel, etc.
- All these animals have an outer covering of hair, which is shaved off to obtain wool fibres.
To know more about Wool Fibre, visit here.

Silk
Natural protein fibre is cultivated from the cocoon of mulberry silkworm larvae.
For more information on Silk, watch the below video

To know more about Silk, visit here.
Wool from Animals
- The wool comes from sheep, goats, yak and some other animals. These wool-yielding animals bear hair on their body because hair keeps them warm, and wool is derived from these hairy fibres.
- Wool is used to make various wool fabrics like woollen clothes, carpets, woollen sweaters, saddle cloths etc.

Rearing and Breeding of Sheep for Wool
Rearing: It is a process of breeding, feeding and providing medical care to sheep. These animals are kept since they produce one or more useful products for human beings.
Breeding: Some special breeds of sheep are specially chosen to give birth to sheep which have only soft under hair. This process of selecting parents for obtaining special characteristics in their offspring is termed ‘selective breeding’.
To know more about “Extraction of Wool”, visit here.
Mary Had a Little Lamb
Processing Fibres into Wool
The skin of the sheep is hairy, having two types of fibres forming its fleece:
(i) the coarse beard hair
(ii) the fine soft under-hair near the skin is the fleece.
This fleece is the main source of fibres of wool.
The process of making fibre into wool follows a series of processes: Shearing → Scouring → Sorting → Dyeing → Straightening, Rolling and Combing.
Occupational Hazards of Fibre Production
Sometimes the sorters get infected by a bacterium, anthrax, which causes a fatal blood disease called sorter’s disease.
Silk
Silk from Animals
- Silk is a natural protein fibre which is obtained from silkworms and can be used as a textile fibre.
- The different types of silk are produced by different types of silkworms.
- It can be differentiated on the basis of lustre and texture. A few examples are Kosa, tassar, mooga, etc. They are produced by various types of silk moths. One of the common types is the mulberry silk moth.
Development of Silk Moth
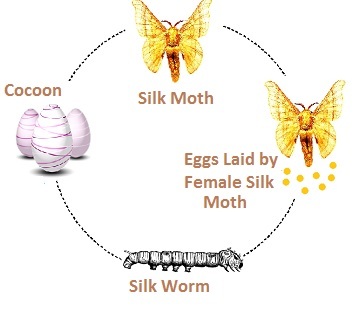
Sericulture
- The rearing of silkworms to produce raw silk is called sericulture.
- In this process, silkworms are reared at appropriate temperatures and humidity to get silk threads from cocoons.
Processing Silk Obtained from Cocoons
- Cocoons are collected and left under the sun or boiled to separate out the silk fibres.
- After that, the reeling of silk is done, the process of unwinding silk from a cocoon.
- Then, the spinning of silk fibres into threads is done.
- The silk threads obtained are woven into desired clothes.
Natural Fibres vs. Synthetic Fibres
Natural Fibres
- The naturally occurring fibres that humans derive from plants or animals are known as natural fibres.
- Animal fibres: These are the fibres that are acquired from animals. For example, wool and silk.
- Plant fibres: These are the ones that are obtained from plants. These fibres are extracted from the plants to make fabrics.
Synthetic Fibres
- Fibres that are made by humans using chemical substances are known as synthetic or man-made fibres.
- These are more durable than natural fibres.
- For example, Polyester, Nylon, Acrylic etc.
To know more about Natural and Synthetic Fibres, visit here.
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 7 Science Fibre-fabric
What are the uses of jute?
1. Pulp and paper 2. Household products 3. Geo-textiles 4. Replacing plastic covers in recent days
What is yarn?
Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres suitable for use in the production of textiles, sewing, crocheting, etc.
What is a natural fibre?
Natural fibres are the fibres that are obtained from plants, animals or mineral sources.
Comments