
Human Eye, a precious gift from nature. Our eyes are the windows to the wonderful world, all we know and love, experience and discover, ponder and cherish. You can identify a flower by smelling and touching it, but you can’t identify the color without the sense of vision. Therefore vision is the most important sense organ out of five senses. Let’s peer into the structure and working of Human Eye.
Structure of Human Eye
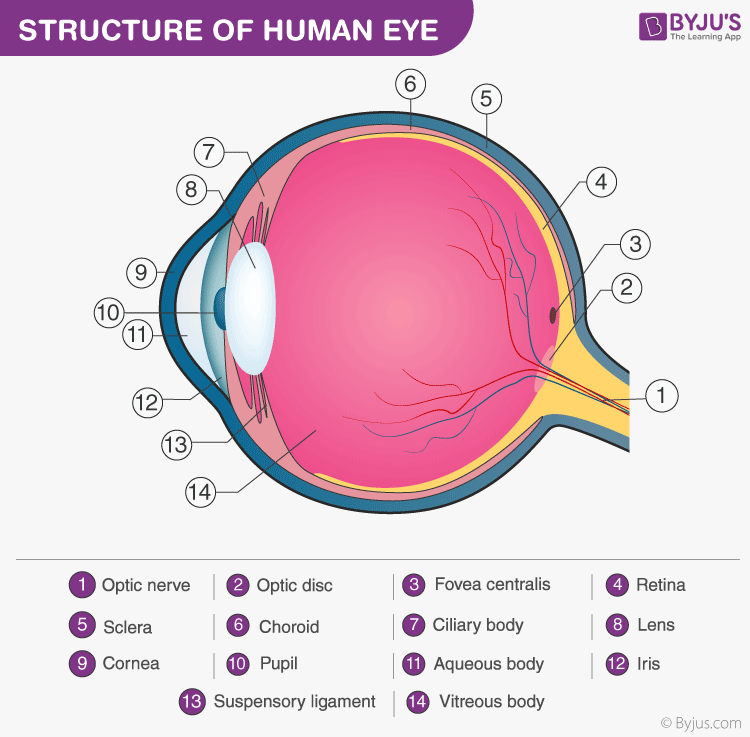
Nature has located eyes close to the brain so that its messages may be arrived there quickly. Eyeball owns a spherical shape and is completely surrounded by a layer of soft fatal tissue and placed within a bony orbit where eye is protected. A white colored stalk is known as Optic Nerve which connects the eye to the brain and also to the muscles which moves the eyeball.
Structure of eye seems to have three layers –
The first and outermost layer is known as Sclera which serves to protect the delicate structure within. The transparent bulging out portion is called Cornea and also crystalline lens which is one of the main parts of the human eye.
The second layer is called choroid which consists of three different zones-choroid proper that carries nourishment to the tissues of the eye. Another zone is called the ciliary body, a broad ring shaped band of thin muscles fiber which plays a very important role in vision adjustment of the eye. The third zone is called as Iris which expands and contracts the pupil much like the wi-frame of the camera.
The Third layer is called as Retina, a part of the optic nerve which transmit light impulses to the brain. It is the most important and complex structure in the eyeball, consists of complicated arrangements of rods and cones which convert light waves into nerve impulses.
Between the lense and the cornea is the Aqueous humor which consists of water and salt. The largest part in eye is called as Vitreous humor, consists of water mixed with salt and albumin. It is a highly transparent jelly like substance and plays an important role in visual adjustment.
The reflected light from outside enters through the crystal transparency of the cornea, pupil, Aqueous humor, lens and vitreous humor which is a clear gel-like substance that fills the middle of the eye and then projects on to the photoreceptor of the Retina, which is a photo sensitive tissue lying at the back of the eye.
The macula is a very small area at the centre of the Retina that gives a fine pin point centre of vision. The area of the Retina surrounding the macula gives a peripheral or sight vision. The retina convert the light rays into the signals that are sent to the optic nerve and then to the brain. Continuous adjustment of the pupil and lens regulates the entry and focusing light.
Learn more about the concept in depth through NCERT Solutions which is the latest edition from team Byju’s. Get detailed information for chapter Human Eye and Colorful World along with solutions to all questions of NCERT Books.
Comments