According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 3.
What is Motion in a Plane?
Motion in a plane is the motion in 2 dimensions, for instance, projectile motion, circular motion and so on. The reference to analyze a 2 Dimensional motion will be the origin with two coordinate axes i.e., X and Y.
For more information on Motion in 2-Dimensions, watch the below videos


What are Scalar Quantities?
Scalar quantities are those physical qualities that can be specified completely by their magnitude alone. Examples of scalar quantities are mass, density, temperature, length, work, speed, etc.
What are Vector Quantities?
Vector quantities are specified by both magnitude and direction. Examples of vector quantities are displacement, acceleration, momentum, velocity, torque, force, etc. The direction of any vector quantity is specified by a unit vector. Vectors lying in the same or parallel to the same plane are called coplanar vectors.
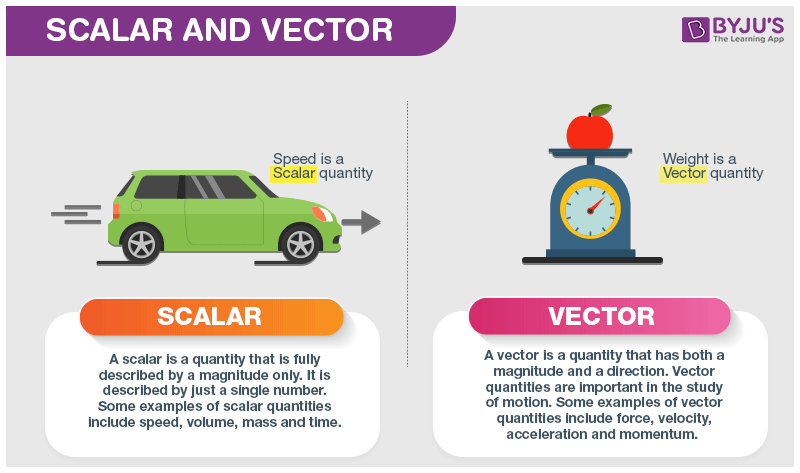
See also: Difference between scalar and vector
For more information on Unit Vectors, watch the below video.
Example of Motion in a Plane.
Projectile motion is one of the most common examples of motion in a plane. When an object moves in a circular path at a constant speed, then the object is said to be in a uniform circular motion.
Time Period
The time period of uniform circular motion is the time taken by an object to complete one complete revolution in its circular path. To maintain an object in its uniform circular motion, a radially inward acceleration must be maintained continuously, it is called centripetal acceleration.

| Also Access |
| NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 |
| NCERT Exemplar for Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 |
For more information on Projectile Motion, watch the below videos.

For more information on Basket Ball on Projectile Motion and Uniform Circular Motion, watch the below videos

Important Questions
- State, for each of the following physical quantities, if it is a scalar or a vector:
Volume, mass, speed, acceleration, density, number of moles, velocity, angular frequency, displacement, and angular velocity.
- Pick out the two scalar quantities in the following list:
Force, angular momentum, work, current, linear momentum, electric field, average velocity, magnetic moment, relative velocity.
- Pick out the only vector quantity in the following list:
Temperature, pressure, impulse, time, power, total path length, energy, gravitational potential, coefficient of friction, and charge.
Students can clear all their concepts related to this unit by referring to the motion in a plane class 11 notes from the links given below: Motion In A Plane Chapter 4(2 Dimensional Motion) Visualizing Circular Motion In A Vertical Plane Projectile Motion – Jumping off Cliffs.
Also, Read:
| Introduction to Motion | Motion in a Plane |
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 11 Physics Notes Chapter 4 Motion in a Plane
What does scalar quantity mean?
Scalar quantities are quantities that are described only by magnitude. They do not have a direction of action.
What does vector quantity mean?
A vector quantity is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
What is meant by ‘Non-uniform’ motion?
An object covers an unequal distance which is equal in intervals of time, then the object is said to have non-uniform motion.
Comments