Amino acids have two functional groups present in one molecule which is of opposite nature. One is amino group shows basic nature and another is acidic carboxyl group. Therefore, amino acid molecule exists as a dipolar ion also called as zwitterion in which amino group converts in ammonium ion (NH4+) and carboxyl group changes to carboxylate ion (-COO–). The overall molecule is neutral in nature due to the presence of opposite charges.
During the electrolysis of amino acid solution, the movement of ions depends upon the pH of medium. In acidic medium, amino group converts to ammonium ion, and molecule converts to cation which moves towards the cathode. On the other hand, in basic medium carboxyl group convert into carboxylate ion and show the movement towards anode.
The presence of any other functional group in side chain decides the polarity and charge of amino acid molecules. The presence of non-polar side chain makes the molecule nonpolar and polar group like carboxyl and amino makes the molecule polar. For example, the presence of an additional carboxyl group in the side chain of aspartic acid is responsible for the polarity of molecules.
What is Aspartic Acid?
“Aspartic acid is a natural dibasic amino acid with two carboxyl groups (one on alpha carbon atom and another in side chain) and also called as amino succinic acid.”
Aspartic acid is also useful in culture media, detergents, dietary supplements, germicides, and fungicides. Aspartic acid is abbreviated as Asp or D. The main food sources for aspartic acid are sugar cane and beet molasses.
Some other food sources of aspartic acid are as follows.
| Animal sources | Vegetable sources | Other sources |
| Luncheon meat | Sprout seeds | Salts of aspartic acid like magnesium aspartate |
| Sausage meat | Oat flakes | Sweeter aspartame like canderel |
| Wild game | Avocado | Asparagus |
The aspartic acid plays a very vital role in the Krebs cycle or citric acid cycle, in which it involved in the formation of other biochemical and amino acids like asparagine, methionine, isoleucine and arginine, threonine, lysine , are synthesized.
This acidic amino acid is also involved in the treatment of chronic fatigue. Aspartic acid initiates the movement of the coenzyme NADH or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide molecules from the main cell body to its mitochondria and then use it to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) which acts as fuel powers for all cellular activity.
- Aspartic acid is also helpful in the transportation of minerals which are essential for healthy RNA and DNA to the cells.
- It also strengthens the overall immune system by helping in increasing the production of antibodies and immunoglobulins which are basically the immune system proteins.
- Aspartic acid helps in keeping the concentrations of NADH high in brain cells and also increase the mind sharpness leading to further production of neurotransmitters as well as chemicals needed for normal mental functioning.
It also involves in some of the biochemical reactions for the removal of excess toxins like ammonia from the cells, found to be very damaging to the brain, nervous system, and liver.
In the conditions of body stress, like other non-essential amino acids, the extra dose of aspartic acid will be helpful which is generally provided by protein supplements often marketed as energy boosters.
Aspartic Acid Structure
Aspartic acid is an acidic polar α-amino acid with one additional methylene group bonded with one carboxyl group. Hence aspartic acid is dicarboxylic amino acid. Because of the presence of second carboxyl group which makes the molecule very hydrophilic. The pKa of the second carboxyl group is about 3.85 and the overall molecule is negatively charged at neutral pH.
Due to the presence of negatively charged carboxyl group, it is found almost at the surface of proteins. The charged group can form an ionic bond with various metal ions as well as dipole interaction with water which is an important concept of solubility of amino acid in water. The isoelectric point of aspartic acid is 2.77 because of two carboxyl groups in the molecule.
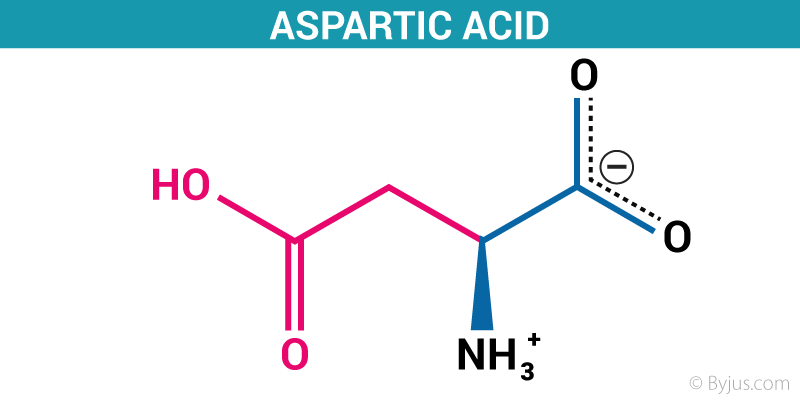
The pKa value of carboxyl group bonded on alpha carbon is 1.88, for -COOH group at the side chain is 3.65 and for amino group is 9.60.
The iso-electric point is equal to half of the sum of pKa1 and pKa3.
The neutral form of aspartic acid is dominant between pH 1.88 and 3.65, thus the isoelectric point is halfway between these two values, i.e. 1/2 (pKa1 + pKa3), so isoelectric point will be 2.77.
Aspartic Acid Hybridization
- The IUPAC name of aspartic acid is 2-Aminobutanoic acid with the molecular formula HOOCCH (NH2)CH2COOH.
- There are a total of four carbon atoms in the molecule. Out of which two are carbonyl carbon atoms of carboxyl group.
- The carbon atoms of both carboxyl groups (C1 and C4) are sp2 hybridized with trigonal planar geometry with 120o bond angle.
- C2 and C3 are sp3 hybridized and arranged in tetrahedral geometry with 109.28o bond angle.
- Both carbonyl carbon atoms of carboxyl group are sp2 hybridized with 120o bond angle.
- The nitrogen atom of the amino group is sp3 hybridized in which two hybridized orbital bonded with s-orbital of hydrogen atoms and one sp3 hybridized orbital overlap with sp3 hybrid orbital of C2 atom of parent chain
