Ideal gases are the gases which have elastic collisions between their molecules and there are no intermolecular attractive forces. In reality, there is no such thing as ideal gases. The gases just show ideal behaviour under certain conditions of temperature and pressure.
When we talk about ideal gases, the following assumptions are taken into consideration:
- The ideal gases are made up of molecules which are in constant motion in random directions.
- The molecules of an ideal gas behave as rigid spheres.
- All the collisions are elastic.
- The temperature of the gas is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of the molecules.
- Pressure occurs due to the collision between the molecules with the walls of the container.
The ideal gas law:
The gases which obey the three laws namely,
- Charles’ law – At constant pressure and number of moles, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature.
- Boyle’s law – At constant temperature and number of moles, the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure.
- Avogadro law – At constant pressure and temperature, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles.
Combining all the three laws we get,
Here R is the constant of proportionality. On rearranging the above equations we get,
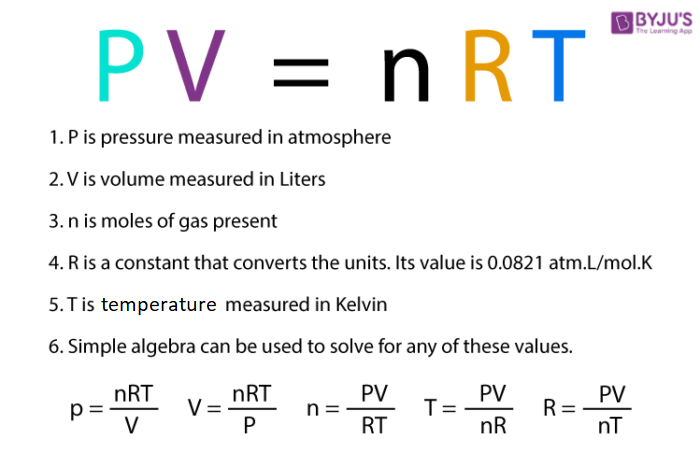
p V = n RT
R is known as the universal gas constant and is the same for all the gases. The above equation is called the ideal gas equation. So it can be said that at constant temperature and pressure n moles of any gas will have the same volume.
Here n, R, T, and p, all are constant so there will be a fixed volume for all the gases under these conditions. This equation is applicable to any gas which approaches the ideal behaviour. The ideal gas law is also known as the equation of the state because it determines the relation between the four variables and describes the state of a given gas.
If we consider a case in which the temperature, volume and pressure varies from T1, V1, p1 to T2, V2, p2 then the gas law can be written as:
Similarly,
This is a very useful equation and is known as the combined gas law. If five values are known then the sixth value can be calculated.
Recommended Videos
Ideal Gas Equation definitions, derivation

Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is an ideal gas equation and derive it mathematically?
What is meant by the ideal gas equation?
What is an ideal gas example?
What are ideal gas conditions?
We have seen what are ideal gases and the laws obeyed by them. For any further query on this topic, register with BYJU’S and get in touch with our mentor support team.

Comments