What is Propane?
C3H8 is a three-carbon alkane with the chemical name Propane.
Propane is also called n-Propane, Dimethylmethane, or Propyl hydride. It is a gas molecular entity and acts as a food propellant. Propane was discovered in the year 1857 by Marcellin Berthelot who was a French chemist.
n-Propane is a colourless gas which has a faint petroleum-like odour. It is soluble in ethyl ether, chloroform, and benzene. It is usually obtained as a by-product of two other processes viz petroleum refining and natural gas processing. It is widely used as a fuel.
Table of Contents
- Properties of Propane
- Propane Structure
- Uses
- Chemical reactions of Propane
- Propyne and Propene can be distinguished by
- Health Hazards
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Properties of Propane – C3H8
| C3H8 | Propane |
| Molecular weight of C3H8 | 44.097 g/mol |
| Density of Propane | 2.0098 kg/m3 |
| Boiling point of Propane | −42.25 to −42.04 °C |
| Melting point of Propane | −187.7 °C |
Propane Structure – C3H8
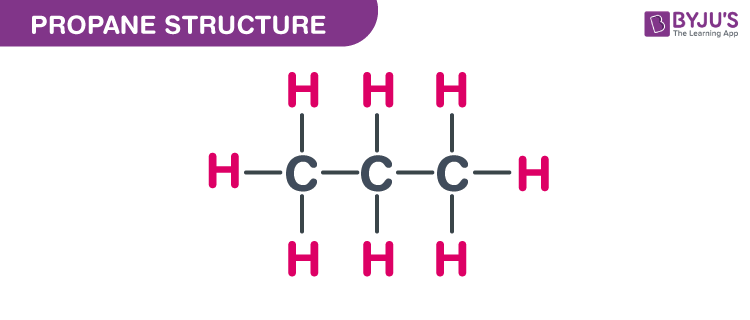
Propane Structure
The exact mass and the monoisotopic mass of Dimethylmethane is 44.063 g/mol. The number of hydrogen bond acceptors and the number of hydrogen bond donors equals to zero.
C3H8 Uses (Propane)
- Propane is used in food additives.
- Used as a component in liquid petroleum gas.
- Used in the manufacturing of propylene and ethylene.
- Used as a fuel in cutting and welding operations.
- Used as a primary component for chemical synthesis.
- Used as a source of energy in motor vehicles, and water heaters.
- Used as improvised explosive devices.
- Used in lawn movers.
- Used in refrigeration.
- Used in the campaign.
- Used as an industrial fuel.
Chemical reactions of Propane
Like other alkanes, Propane also undergoes combustion reactions in a similar manner. Propane burns in the presence of an excess amount of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.
C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O + heat
When too much or too less oxygen is available for the combustion reaction, incomplete combustion takes place, forming soot (carbon) and/or carbon monoxide.
2C3H8 + 9O2 → 4CO2 + 2CO + 8H2O + heat
C3H8 + 2O2 → 3C + 4H2O + heat
The hydrogen content of Propyl hydride is extremely high and therefore burns hotter when compared to diesel fuel or home heating oil. The presence of C–C bonds causes it to burn with a flame.
Propyne and Propene can be distinguished by
Propyne is terminal alkyne so it gives white precipitate with ammonical silver nitrate solution but alkene does not. Thus propene and propyne can be distinguished by ammonical silver nitrate solution. Terminal alkynes form silver salt with Tollen’s reagent while alkene does not react with Tollen’s reagent. Therefore, Tollen’s reagent can be used to distinguish a terminal alkyne like propyne from alkene as well as from internal alkynes.

Health Hazards
The vaporising liquid of propane may cause gangrene. It may cause dizziness if the concentration in air is greater than 10% and a higher dose causes asphyxiation. When heated it causes an explosion of containers. Its vapours are heavier when compared to air. This compound is extremely flammable.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is the use of propane?
Propane is widely used for space and water heating, cooking, and as a fuel for engine applications such as forklifts, farm irrigation engines, fleet vehicles, and buses; but, due to new technological advances, its applications are increasingly growing. The propane is known as propane autogas when used as vehicle fuel.
Where is propane found?
Propane is commonly found in deep underground rocks, mixed with natural gas and petroleum deposits. Propane is considered a fossil fuel because it was made from the remains of tiny animals and plants at sea millions of years ago.
What are the disadvantages of propane?
Propane is more compact than airborne. When there is a leak in a propane fuel tank, the gas may begin to sink into any enclosed area and thus pose a risk of fire and explosion.
What are the characteristics of propane?
It is non-toxic, colourless and nearly odourless. Like for natural gas, a distinguishing odour is applied so that the gas can be identified quickly. Propane exists as oil, as well as gas. It is a non-toxic, colourless and odourless gas at atmospheric pressure and temperatures above –44 F.
What is the condensed structural formula for propane?
Methane is the simplest alkane, with the molecular formula CH4. The carbon is the main atom and forms four single covalent bonds to the atoms of hydrogen. The condensed formula for propane will be C3H8.

Comments