What is Tin Oxide?
The inorganic compound tin(IV) oxide, also known as stannic oxide, has the formula SnO2. Cassiterite is a tin oxide mineral, SnO2, and it is the most common tin ore. Tin metal is burned in the air to create synthetic tin(IV) oxide. The annual production is in the kilotons scale.
In a reverberatory furnace at 1200–1300 °C, SnO2 is reduced to metal with carbon. Tin(iv) oxide is a crystalline solid or powder that is white or off-white. Sublime: 1800-1900°C, mp: 1127°C, density: 6.95 g/cm3 Water doesn’t remove it. It can dissolve in hydrochloric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid.
Other names – Stannic oxide
| SnO2 | Tin Oxide |
| Density | 6.95 g/cm³ |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 150.71 g/mol |
| pH | (6–12) |
| Melting Point | 1,630 °C |
| Chemical Formula | SnO2 |
Table of Contents
- Tin Oxide Structure
- Physical Properties of Tin Oxide
- Chemical Properties of Tin Oxide
- Uses of Tin Oxide
- Frequently Asked questions
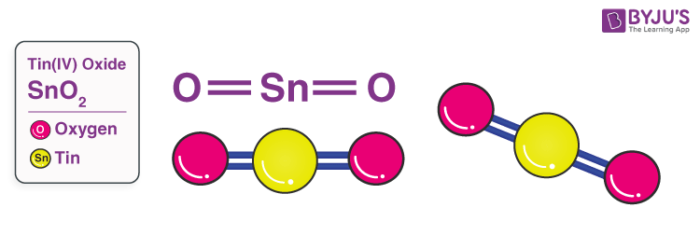
Tin Oxide Structure – SnO2
Physical Properties of Tin Oxide – SnO2
| Odour | Odourless |
| Appearance | Yellowish or light grey powder |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit | 2 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 2 |
| Solubility | insoluble in water |
Chemical Properties of Tin Oxide – SnO2
-
- Sulfate is formed when SnO2 dissolves in sulphuric acid. The chemical equation is given below.
SnO2 + 2 H2SO4 → Sn(SO4)2 + 2 H2O
-
- When tin(IV) oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide, stannate (IV) sodium and water are formed. At a temperature of 350-400°C, this reaction takes place. The chemical equation is given below.
Uses of Tin Oxide – SnO2
- Tin oxide, which has a +4 oxidation state, can be used to make ceramic bodies opaque, as a mild abrasive, and as a fabric weighting agent.
- The cosmetics ingredient review has determined that tin oxide is a healthy ingredient, based on the fact that it is not easily absorbed through the skin.
- Tin oxide is used in dentistry and to render a precious metal polishing paste for high polishing of amalgam and precious metals when combined with water.

Comments