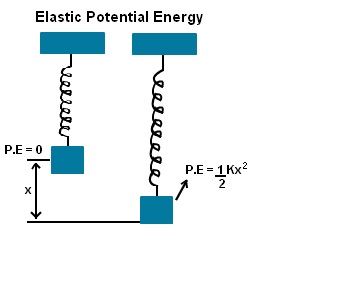
Elastic potential energy is the potential energy stored by stretching or compressing an elastic object by an external force such as the stretching of a spring. It is equal to the work done to stretch the spring which depends on the spring constant k and the distance stretched.
According to Hooke’s law, the force applied to stretch the spring is directly proportional to the amount of stretch.
 In other words,
In other words,
Force required to stretch the spring is directly proportional to its displacement. It is given as
F =kx
Wherein,
k = spring constant
x = displacement
The Elastic Potential Energy Formula of the spring stretched is given as
Where,
P.E = elastic potential energy and it’s expressed in Joule.
Example 1
A compressed spring has the potential energy of 20 J and its spring constant is 200 N/m. Calculate the displacement of the spring.
Solution:
Given:
Potential energy P.E = 40 J,
Spring Constant k = 200 N/m,
The Potential energy formula is given by
the displacement is given by
x = √2P.E / k
= √2×40 / 200
= 0.632 m
Example 2
The vertical spring is linked to a load of mass 5 kg which is compressed by 10m. Determine the force constant of the spring.
Solution:
Given: Mass m = 5kg
Distance x = 10 m
Force formula is given by
F = ma
= 5 kg × 9.8 m/s2
= 49 N
Force in the stretched spring is
F = k x
Force Constant k is given by
= F / x
= 49 / 10
= 4.9 N/m
The video explains how a stretched rod is analogous to a stretched spring.

Comments