The structure of atmosphere is an important topic in the geography section of the UPSC syllabus. It is important both for the prelims as well as the IAS mains exams. In this article, we discuss the structure of atmosphere including its different layers.
Our atmosphere is composed of many components. However, the structure of the atmosphere is a combination of various layers.
Structure of Atmosphere (UPSC Notes):- Download PDF Here
Structure of Atmosphere
The structure of the atmosphere is represented in a pictorial form below:
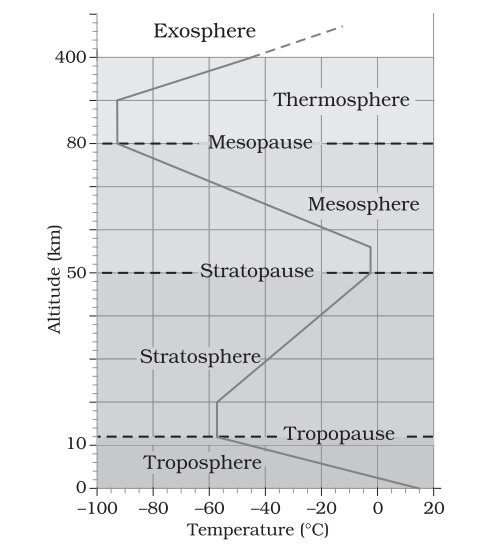
There are five layers in the structure of the atmosphere depending upon temperature. These layers are:
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermosphere
- Exosphere
This is an important topic in the Geography syllabus for the UPSC 2024 Exam.
Layers of Atmosphere
Troposphere
- It is considered as the lowest layer of Earth’s atmosphere.
- The troposphere starts at the surface of the earth and goes up to a height of 8 km (poles) to 18 km (equator). The main reason for higher height at the equator is due to the presence of hot convection currents that push the gases upward.
- All kinds of weather changes occur within this layer.
- This layer has water vapour and mature particles.
- Temperature decreases with increasing height of atmosphere at the rate of 1 degree Celsius for every 165 m of height. This is called the Normal lapse rate.
- Tropopause, the transitional zone, separates the Troposphere and Stratosphere.
Stratosphere
- It is the second layer of the atmosphere found above the troposphere.
- It extends up to a height of 50 km from the earth’s surface.
- This layer is very dry as it contains little water vapour.
- This layer provides some advantages for flight because it is above stormy weather and has steady, strong, horizontal winds.
- The ozone layer is found in this layer.
- The ozone layer absorbs UV rays and safeguards Earth from harmful radiation.
- Stratopause separates Stratosphere and Mesosphere.
Mesosphere
- The Mesosphere is found above the stratosphere.
- It is the coldest of the atmospheric layers.
- The mesosphere starts at 50 km above the surface of the Earth and goes up to 80 km.
- The temperature drops with altitude in this layer.
- By 80 km it reaches -100 degrees Celsius.
- Meteors burn up in this layer.
- The upper limit is called Mesopause which separates Mesosphere and Thermosphere.
Thermosphere
- This layer is found above Mesopause from 80 to 400 km.
- Radio waves that are transmitted from the earth are reflected by this layer.
- The temperature starts increasing again with increasing height in this layer.
- Aurora and satellites occur in this layer.
Ionosphere
- The lower Thermosphere is called the Ionosphere.
- The ionosphere consists of electrically charged particles known as ions.
- This layer is defined as the layer of the atmosphere of Earth that is ionized by cosmic and solar radiation.
- It is positioned between 80 and 400 km above the Mesopause.
Exosphere
- It is the outermost layer of the atmosphere.
- The zone where molecules and atoms escape into space is mentioned as the exosphere.
- It extends from the top of the thermosphere up to 10,000 km.
Structure of Atmosphere (UPSC Notes):- Download PDF Here
Also, See:
| General circulation of the atmosphere |
| Composition of the atmosphere |
| Heating and Cooling of Atmosphere |
Relevant Links

Comments