What is the Full form of WBC?
The full form of WBC is White Blood Cell. The WBC is also labelled as Leukocytes. They serve as a defence against all pathogens in the human body. WBC creates a different sort of protein called antibodies that recognise and counter the foreign agents like fungi, viruses and bacteria that infect the human body.
The WBC in the cells comprises recognisable granule-like structures. Thus their name is Granulocytes, and they do not contain agranulocytes. WBCs account for 1 per cent of the total quantity of blood, and they are colourless, since these lack haemoglobin.
Various types of WBC
The WBC is classified as five distinct types, which are categorised depending on the existence and absence of granules. The five kinds of WBC are described below with a diagram.
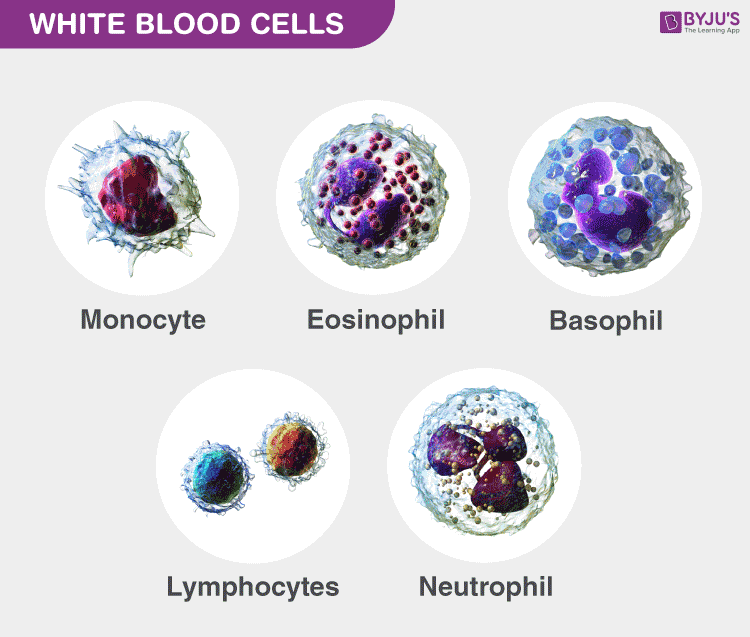
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes play a significant role in the development of antibodies and body protection, the size of which varies from 8 to 10 micrometres and is generally referred to as the natural killer cells. A human body comprises on average 10 to 12 cells of lymphocytes. WBC are colourless cells that develop in lymphoid tissue, hence called lymphocytes. These cells are quite significant in the immune system. The two main lymphocyte types are
- B lymphocytes
- T lymphocytes
Monocytes
Monocyte cells typically have a large bilobed nucleus with a diameter of 12 to 20 micrometres and the nucleus is usually half-moon or kidney-shaped and occupies 3 to 8% of WBCs. Monocytes are Immune System garbage vehicles. The primary functions of monocytes are,
- Migrating into tissues and removing dead cells
- Shielding towards bloodborne pathogens
- They travel very rapidly to tissue infection sites.
Neutrophils
Neutrophils generally found in the bloodstream, they are predominant cells, which are present in pus. About 60 to 70 per cent of WBCs are neutrophils of 10 to 12 micrometres in diameter. The nucleus is lobed with 2 to 5, and cytoplasm has tiny granules. Neutrophil assists with lysosomes in the degradation of bacteria and it serves as a potent oxidant. Neutrophils are only stained with neutral dyes. Neutrophils are often the first immune system cells to react to an invader, like a bacteria or a virus. The WBCs’ lifetime lasts up to 8 hours, and are formed in the bone marrow every day.
Eosinophils
Eosinophils are the leukocyte cells that are present in the immune system responsible for combating infections in vertebrate parasites and regulating processes associated with allergy & asthma. Eosinophilic cells are small agranulocytes that are formed in the bone marrow that make 2 to 4% of all WBCs and are present in the digestive tract at high concentrations.
Basophils
The least common of the granulocytes are basophils, ranging from 0.01 to 0.3 percent of WBC. They contain large cytoplasmic granules which play a vital role in mounting a non-specific immune response to pathogens, allergic reactions by releasing histamine and dilating the blood vessels. There are about 20 to 25 percent of basophils in WBCs. Such WBC has the capacity to stain when they are exposed to simple dyes, thus called basophilia, and they are best known for their function in asthma, and results in airway inflammation and bronchoconstriction.
Comments