Students who are aiming to score high marks in Physics must solve the previous years ICSE Class 10 Physics Question Papers. So, to help them prepare efficiently for the exam, we have provided the ICSE Class 10 Physics Question Paper Solution 2018. Here, students will find the answer to each question along with the marking scheme. Also, these solutions will help students to understand how to handle numerical and theory problems in the exam.
The ICSE Class 10 Physics 2018 exam was conducted on 16th March 2018. The exam started at 11 am and students were allotted 2 hours of time duration to finish the paper. Students can download the ICSE Class 10 Physics Question Paper Solution 2018 PDF from the link below.
ICSE Class 10 Physics Question Paper 2018
Download ICSE Class 10 Physics Question Paper Solution 2018 PDF
Students can have a look at the ICSE Class 10 Physics Question Paper Solution 2018 below:
ICSE Class 10 Physics Question Paper 2018 With Solution
Question 1:
(a) (i) State and define the S.I. unit of power.
(ii) How is the unit horse power related to the S.I. unit of power?
(b) State the energy changes in the following cases while in use:
(i) An electric iron.
(ii) A ceiling fan.
(c) The diagram below shows a lever in use:

(i) To which class of levers does it belong?
(ii) Without changing the dimensions of the lever, if the load is shifted towards the fulcrum what happens to the mechanical advantage of the lever?
(d) (i) Why is the ratio of the velocities of light of wavelengths 4000Å and 8000Å in vacuum 1:1?
(ii) Which of the above wavelengths has a higher frequency?
(e) (i) Why is the motion of a body moving with a constant speed around a circular path said to be accelerated?
(ii) Name the unit of physical quantity obtained by the formula 2𝐾/𝑉 2 .
Where K: kinetic energy, V: Linear velocity.
Answer:
(a) (i) watt – If 1joule of work is done in 1 second then the power spent/developed / expended is 1watt.
(ii) 1H.P. = 746 W /750 W
(b) (i) Electrical energy to heat energy
(ii) Electrical energy to kinetic/mechanical energy.
(c) (i) Second order (or class) lever.
(ii) Mechanical advantage of the lever increases.
(d) (i) In vacuum their speed/velocity is the same.
(ii) 4000 Å has higher frequency.
(e) (i) Because on a circular path the direction of motion changes continuously which changes the velocity of the body continuously.
(ii) kg or kilogram/g/ any unit of mass can be accepted.
Question 2:
(a) The power of a lens is –5D.
(i) Find its focal length.
(ii) Name the type of lens.
(b) State the position of the object in front of a converging lens if:
(i) It produces a real and same size image of the object.
(ii) It is used as a magnifying lens.
(c) (i) State the relation between the critical angle and the absolute refractive index of a medium.
(ii) Which colour of light has a higher critical angle? Red light or Green light.
(d) (i) Define scattering.
(ii) The smoke from a fire looks white.
Which of the following statements is true?
- Molecules of the smoke are bigger than the wavelength of light.
- Molecules of the smoke are smaller than the wavelength of light.
(e) The following diagram shows a 60o, 30o, 90o glass prism of critical angle 42o. Copy the diagram and complete the path of incident ray AB emerging out of the prism marking the angle of incidence on each surface.

Answer:
(a) (i) 𝑓 = 1/𝑃 = 1/5 = 0.2m 20cm (substitution expressed with negative sign is also acceptable)
(ii) Concave/diverging lens
(b) (i) at 2F
(ii) Between the optical centre and principal focus.
(c) (i) 𝜇 = 1/sin 𝑐
(ii) Red
(d) Bending away at surface XZ
Angle of incidence = 30o
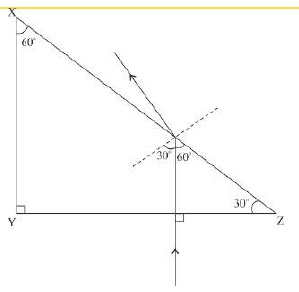
(e) (i) Scattering is the absorption and then reemission of light without the change in the wavelength.
(ii) Statement 1
Question 3:
(a) Displacement distance graph of two sound waves A and B, travelling in a medium, are as shown in the diagram below.

Study the two sound waves and compare their:
(i) Amplitudes
(ii) Wavelengths
(b) You have three resistors of values 2Ω, 3Ω and 5Ω. How will you join them so that the total resistance is more than 7Ω?
(i) Draw a diagram for the arrangement.
(ii) Calculate the equivalent resistance.
(c) (i) What do you understand by the term nuclear fusion?
(ii) Nuclear power plants use nuclear fission reaction to produce electricity. What is the advantage of producing electricity by fusion reaction?
(d) (i) What do you understand by free vibrations of a body?
(ii) Why does the amplitude of a vibrating body continuously decrease during damped vibrations?
(e) (i) How is the e.m.f. across primary and secondary coils of a transformer related with the number of turns of coil in them?
(ii) On which type of current do transformers work?
Answer:
(a) (i) Amplitudes of A and B are in the ratio 2:1.
(ii) Wavelengths of A and B are in the ratio 1:2.
(b) (i)

(ii) 𝑅 = 2 + 3 + 5 = 10 Ω
(Only 10 Ω can be accepted if the diagram is shown; else substitution is a must.)
(c) (i) Nuclear fusion – The process in which two lighter nuclei of lighter atoms combine to form a heavy and more stable nucleus with the liberation of large amount of heat.
(ii) The product formed is not radioactive hence less harmful to human/ energy produced per nucleon (for same mass of nuclear material) is more than fission.
(d) (i) Vibrations of a body in absence of any external periodic force with constant frequency and amplitude.
(ii) The energy is lost to the surrounding due to the friction of the surrounding medium.
(e) (i) e.m.f. and the number of turns of the coil are directly proportional.
(ii) A.C. or alternating current.
Question 4:
(a) (i) How can a temperature in degree Celsius be converted into S.I. unit of temperature?
(ii) A liquid X has the maximum specific heat capacity and is used as a coolant in Car radiators. Name the liquid X.
(b) A solid metal weighing 150 g melts at its melting point of 800 o C by providing heat at the rate of 100 W. The time taken for it to completely melt at the same temperature is 4 min. What is the specific latent heat of fusion of the metal?
(c) Identify the following wires used in a household circuit:
(i) The wire is also called as the phase wire.
(ii) The wire is connected to the top terminal of a three-pin socket.
(d) (i) What are isobars?
(ii) Give one example of isobars.
(e) State any two advantages of electromagnets over permanent magnets.
Answer:
(a) (i) oC + 273 = K
(ii) Water
(b) 𝑃 × t = mL => 100 × 4 × 60 = 150 × 𝐿 (both side correct substitutions.)
𝐿= 160 J g-1 (answer is accepted in any unit.)
(c) (i) Live wire
(ii) Earth wire
(d) (i) Elements of the same mass number but different atomic numbers are called isobars.
(ii)

(e)
|
Permanent Magnet |
Electromagnet |
|
Magnetic Strength cannot be easily altered |
Magnetic strength can be easily altered. |
|
Polarity cannot be reversed easily |
Polarity can be reversed easily. |
Question 5:
(a) (i) Derive a relationship between S.I. and C.G.S. unit of work.
(ii) A force acts on a body and displaces it by a distance S in a direction at an angle θ with the direction of force. What should be the value of θ to get the maximum positive work?
(b) A half metre rod is pivoted at the centre with two weights of 20 gf and 12 gf suspended
at a perpendicular distance of 6 cm and 10 cm from the pivot respectively as shown
below.

(i) Which of the two forces acting on the rigid rod causes a clockwise moment?
(ii) Is the rod in equilibrium?
(iii) The direction of 20 kgf force is reversed. What is the magnitude of the resultant moment of the forces on the rod?
(c) (i) Draw a diagram to show a block and tackle pulley system having a velocity ratio of 3 marking the direction of load(L), effort(E) and tension(T).
(ii) The pulley system drawn lifts a load of 150 N when an effort of 60 N is applied. Find its mechanical advantage.
(iii) Is the above pulley system an ideal machine or not?
Answer:
(a) (i) 1 J = 1 N x 1 m
1 J = 105 dyn x 100 cm
1 J = 107 ergs
(ii) 0°
(b) (i) 12 kg f
(ii) Yes
(iii) On reversing the direction of 20 kg f, the magnitude of the resultant forces on the
rod = 20 x 6 + 12 x 10 = 240
(c) (i)

Two pulleys in block and one pulley(movable) in tackle, their proper connection, marking directions of load(L) and effort(E) and at least one tension and the support. Strands should be stretched.
(ii) 𝑀.𝐴.= 𝐿/𝐸 = 150/60 = 2.5
(iii) No, it is not an ideal system.
Question 6:
(a) A ray of light XY passes through a right angled isosceles prism as shown below.

(i) What is the angle through which the incident ray deviates and emerges out of the prism?
(ii) Name the instrument where this action of prism is put into use.
(iii) Which prism surface will behave as a mirror?
(b) An object AB is placed between O and F1 on the principal axis of a converging lens as shown in the diagram.

Copy the diagram and by using three standard rays starting from point A, obtain an
image of the object AB.
(c) An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm.
Find:
(i) the position of the image
(ii) nature of the image
Answer:
(a) (i) 900
(ii) refracting periscope.
(iii) Surface AB
(b) Image of the object AB, using three standard rays starting from point A

(c) (i)

(ii) Real or inverted
(iii) Image is bigger than object.
Question 7:
(a) Draw the diagram of a right angled isosceles prism which is used to make an inverted
image erect.
(b)

The diagram above shows a wire stretched over a sonometer. Stems of two vibrating tuning forks A and B are touched to the wooden box of the sonometer. It is observed that the paper rider (a small piece of paper folded at the centre) present on the wire flies off when the stem of vibrating tuning fork B is touched to the wooden box but the paper just vibrates when the stem of vibrating tuning fork A is touched to the wooden box.
(i) Name the phenomenon when the paper rider just vibrates.
(ii) Name the phenomenon when the paper rider flies off.
(iii) Why does the paper rider fly off when the stem of tuning fork B is touched to the
box?
(c) A person is standing at the sea shore. An observer on the ship which is anchored in between a vertical cliff and the person on the shore fires a gun. The person on the shore hears two sounds, 2 seconds and 3 seconds after seeing the smoke of the fired gun. If the speed of sound in the air is 320 ms-1 then calculate:
(i) the distance between the observer on the ship and the person on the shore.
(ii) the distance between the cliff and the observer on the ship.

Answer:
(a)

(b) (i) Forced vibrations
(ii) Resonance.
(iii) Frequency of the tuning fork B matches the natural frequency of the stretched wire and vibrates with greater amplitude.
(c) (i) 𝑑 = 𝑣 × 𝑡 = 320 × 2
𝑑𝑑 = 640 m
(ii) 𝑑= (𝑣×𝑡)/2
2 = (320×1)/2
𝑑= 160 m
Question 8:
(a) (i) A fuse is rated 8A. Can it be used with an electrical appliance rated 5 KW, 200 V? Give a reason.
(ii) Name two safety devices which are connected to the live wire of a household electric circuit.
(b) (i) Find the equivalent resistance between A and B.

(ii) State whether the resistivity of a wire changes with the change in the thickness of the wire.
(c) An electric iron is rated 220V, 2kW.
(i) If the iron is used for 2h daily, find the cost of running it for one week if it costs ` 4.25 per kWh.
(ii) Why is the fuse absolutely necessary in a power circuit?
Answer:
(a) (i) 𝐼 = 𝑃/𝑉 = 5000/200 = 25𝐴 No, it cannot be used.
Maximum current drawn by the appliance is greater than the fuse rating.
(ii) M.C.B. Fuse, switch, ELCB
(b) (i)

(ii) No, it does not change.
(c) (i) E = P x t = 2 x 2 =4 kW h [Correct substitution]
Cost for running it for a week = 4 x 7 x 4.25 = ` 119/-
(ii) Power circuits draw large amount of current/
Electric shock in this circuit is very fatal hence to avoid it fuse is necessary in the power circuit/ to safeguard.
Question 9:
(a) (i) Heat supplied to a solid change it into liquid. What is this change in phase called?
(ii) During the phase change does the average kinetic energy of the molecules of the substance increase?
(iii) What is the energy absorbed during the phase change called?
(b) (i) State two differences between “Heat Capacity” and “Specific Heat Capacity”.
(ii) Give a mathematical relation between Heat Capacity and Specific Heat Capacity.
(c) The temperature of 170g of water at 50°C is lowered to 5°C by adding a certain amount of ice to it. Find the mass of ice added.
Given: Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg-1 ⁰C-1 and Specific latent heat of
ice = 336000 J kg-1
Answer:
(a) (i) Melting
(ii) No.
(iii) Latent heat of melting/fusion.
(b) (i)
|
Heat capacity |
Specific heat capacity |
|
Heat absorbed by the mass of a body to raise its temperature by 1oC. |
Heat absorbed by unit mass of a body to raise its temperature by 1oC. |
|
S.I. Unit is J K-1 |
S.I. unit is J kg-1 K-1 |
|
Depends on mass and (specific Heat capacity/material) |
Does not depend on mass (but depends on material) |
(ii) Heat capacity(C’) = mass of the body(m) x specific heat capacity (c)
(c)

Question 10:
(a)

The diagram shows a coil wound around a U shape soft iron bar AB.
(i) What is the polarity induced at the ends A and B when the switch is pressed?
(ii) Suggest one way to strengthen the magnetic field in the electromagnet.
(iii) What will be the polarities at A & B if the direction of current is reversed in the circuit?
(b) The ore of Uranium found in nature contains 92U238 and 92U235. Although both the isotopes are fissionable, it is found out experimentally that one of the two isotopes is more easily fissionable.
(i) Name the isotope of Uranium which is easily fissionable.
(ii) Give a reason for your answer.
(iii) Write a nuclear reaction when Uranium 238 emits an alpha particle to form a Thorium (Th) nucleus.
Answer:
(a) (i) South and south.
(ii) Increasing the strength of current through the coil.
(iii) The polarities at the two ends become North.
(b) (i) 92U235
(ii) Fission of 92U238 is possible only by fast neutrons while the fission of 92U235 can be
even possible by the slow neutrons.
(iii)

(c) (i) B (gamma)
(ii) C has less mass compared to A
(iii) A
(iv) C
We hope students found this information on “ICSE Class 10 Physics Question Papers Solutions 2018” helpful for their exam preparation. They can also access solutions of other subjects of ICSE Class 10 Previous Years Question Papers by clicking here. Stay tuned to BYJU’S for the latest update on ICSE/CBSE/State Boards/Competitive exams. Also, download the BYJU’S App and fall in love with learning.
























Comments