Selina Solutions Concise Biology Class 10 Chapter 4 Absorption by Roots – The Processes Involved, are available in pdf format. Our professional tutors answered these questions to help you with your exam preparation to attain good marks in Biology. Students aiming to score good marks in Biology practise Selina Solutions Class 10, which help them to gain more knowledge. This book is one of the top materials when it comes to providing a question bank to practice.
These Absorption by Roots solutions are available for download in pdf format and offer answers to all the questions provided in Class 10 Biology Chapter 4, wherein questions are answered step by step with detailed explanations. Download pdf of Class 10 Chapter 4 in their respective links.
Download PDF of Selina Solutions Concise Biology Class 10 Chapter 4 Absorption by Roots – The Processes Involved
Access Answers of Selina Solutions Concise Biology Class 10 Chapter 4 Absorption by Roots – The Processes Involved
Review questions Page: 51
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
(Select the most appropriate option in each case)
1. Absorption of water by the plant cells by surface attraction is called:
(a) Diffusion (b) Osmosis
(c) Imbibition (d) Endosmosis
Solution:-
c) Imbibition
2. A plant cell placed in a certain solution got plasmolysed. What was the kind of solution?
(a) Isotonic sugar solution (b) Hypotonic salt solution
(c) Hypertonic salt solution (d) Isotonic salt solution
Solution:-
(c) Hypertonic salt solution
3. The state of a cell in which the cell wall is rigid and stretched by the increase in volume due to the absorption of water is called
(a) Flaccidity (b) Turgidity
(c) Capillarity (d) Tonicity
Solution:-
(b) Turgidity
4. Which one of the following is a characteristic NOT related with the suitability of the roots for absorbing water?
a) Tremendous surface area
b) Contain cell sap at higher concentration than the surrounding water
c) Root hairs have thin cell walls
d) Grow downward into the soil
Solution:-
d) Grow downward into the soil
5. Movement of molecules of a substance from the region of their higher concentration to the region of their lower concentration without the involvement of a separating membrane, is called:
a) Osmosis b) Diffusion
c) Active transport d) Capillarity
Solution:-
b) Diffusion
6. Osmosis and diffusion are the same except that in osmosis there is
a) a freely permeable membrane
b) a cell wall in between
c) a selectively permeable membrane in between
d) an endless inflow of water into a cell
Solution:-
c) a selectively permeable membrane in between
7. The highest water potential (capacity to move out to higher concentrated solution) is that of
a) Pure water b) 10% salt solution
c) Honey d) 50% sugar solution
Solution:-
a) Pure water
8. The space between the cell wall and plasma membrane in a plasmolysed cell is filled with
a) isotonic solution b) hypotonic solution
c) hypertonic solution d) water
Solution:-
d) water
9. What is responsible for guttation?
a) Osmotic pressure b) Root pressure
c) Suction pressure d) Capillarity
Solution:-
b) Root pressure
10. The most appropriate characteristic of semi-permeable membrane is that
a) it has minute pores
b) it has no pores
c) it allows the solute to pass through but not the solvent
d) it allows a solvent to pass through freely but prevents the passage of the solute
Solution:-
d) it allows a solvent to pass through freely but prevents the passage of the solute
B. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
1. Name the following:
(a) The condition of a cell placed in a hypotonic solution.
Solution:-
Turgidity is the condition of a cell placed in a hypotonic solution
(b) The process by which intact plants lose water in the form of droplets from leaf margins.
Solution:-
Guttation is the process by which intact plants lose water in the form of droplets from leaf margins.
(c) Process by which water enters root hairs.
Solution:-
Osmosis is the process by which water enters root hairs.
(d) The tissue concerned with upward conduction of water in plants.
Solution:-
Xylem is the tissue concerned with upward conduction of water in plants.
(e) The term for the inward movement of solvent molecules through the plasma membrane of a cell.
Solution:-
Endosmosis is the term for the inward movement of solvent molecules through the plasma membrane of a cell.
(f) The process by which molecules distribute themselves evenly within the space they occupy.
Solution:-
Diffusion is the process by which molecules distribute themselves evenly within the space they occupy.
(g) The pressure which is responsible for the movement of water molecules across the cortical cells of the root.
Solution:-
Root pressure is responsible for the movement of water molecules across the cortical cells of the root.
2. Give the equivalent terms for the following:
(a) Pressure exerted by the cell contents on the cell wall.
Solution:-
Turgor pressure exerted by the cell contents on the cell wall.
(b) The condition in which the cell contents are shrunken.
Solution:-
Flaccidity is the condition in which the cell contents are shrunken.
(c) Loss of water through a cut stem.
Solution:-
Loss of water through a cut stem is called Bleeding.
3. Complete the following statements:
(a) Hypotonic solution is one in which the solution kept outside the cell has lower solute concentration than __________ the cell.
Solution:-
A hypotonic solution is one in which the solution kept outside the cell has lower solute concentration than the fluids inside the cell.
(b) Active transport is one in which the ions outside the roots move in with expenditure of energy __________.
Solution:-
Active transport is one in which the ions outside the roots move in with expenditure of energy from the region of their lower concentration outside to the region of their higher concentration inside.
(c) The bending movements of certain flowers towards the sun and the sleep movements of certain plants at night are examples of _____.
Solution:-
The bending movements of certain flowers towards the sun and the sleep movements of certain plants at night are examples of turgor movements.
4. Fill in the blanks by choosing the correct alternative from those given in brackets:
(a) When placed in a more concentrated solution, the cell contents will ……….. (Shrink/swell up)
Solution:-
When placed in a more concentrated solution, the cell contents will shrink.
(b) The pressure by which the …………. molecules tend to cross the semi-permeable membrane is called osmotic pressure. (Salt/water)
Solution:-
The pressure by which the water molecules tend to cross the semi-permeable membrane is called osmotic pressure
(c) Active transport is in a direction………….. to that of diffusion. (Opposite/same)
Solution:-
Active transport is in a direction opposite to that of diffusion.
5. Match the items in column I those in column II
Column I Column II
(a) Xylem (i) semi-permeable
(b) Phloem (ii) permeable
(c) Cell membrane (iii) downward flow of sap
(d) Root pressure (iv) upward flow of water
(e) Cell wall (v) guttation
Solution:-
Column I Column II
(a) Xylem (iv) upward flow of water
(b) Phloem (iii) downward flow of sap
(c) Cell membrane (i) semi-permeable
(d) Root pressure (v) guttation
(e) Cell wall (ii) permeable
C. SHORT ANSWER TYPE
1. Differentiate between the following:
(a) Plasmolysis and deplasmolysis
Solution:-
| Plasmolysis | Deplasmolysis |
| Plasmolysis is the contraction of cytoplasm from the cell wall caused due to the withdrawal of water when placed in a strong (hypertonic) Solution. | The recovery or the reversal of plasmolysis is called deplasmolysis |
(b) Turgor pressure and wall pressure
Solution:-
| Turgor pressure | Wall pressure |
| The pressure of the cell contents on the cell wall is called turgor pressure. | The pressure exerted by the wall on the cell content is called wall pressure. |
(c) Guttation and bleeding
Solution:-
| Guttation | Bleeding |
| The water appears as tiny drops along the margins or the tips of the leaves, especially in the early mornings. This loss of excessive water is called guttation. | Loss of water through a cut stem is called bleeding |
(d) Turgidity and flaccidity
| Turgidity | Flaccidity |
| When a cell reaches a state where it cannot accommodate any more water, i.e., it is fully distended, it is called turgid and the condition is called turgidity. | Flaccidity is the reverse of turgidity.
It is the condition in which the cell content is shrunken and the cell is not tight. |
2. (a) Mention whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F).
(b) Correct the false statements by altering the last word only.
(i) A plant cell placed in hypotonic solution gets plasmolysed. (T/F)
Solution:
(a)False
(b) A plant cell placed in a hypotonic solution gets turgid.
(ii) Addition of salt to pickles prevents growth of bacteria because they turn turgid. (T/F)
Solution:-
(a) False
(b) Addition of salt to pickles prevents the growth of bacteria because they turn flaccid.
(iii) Cells that have lost their water content are said to be deplasmolysed. (T/F)
Solution:-
(a) False
(b) Cells that have lost their water content are said to be plasmolysed.
(iv) Xylem is the water conducting tissue in plants. (T/F)
Solution:-
(a) True
(v) The shrinkage of protoplasm, when a cell is kept in hypotonic solution. (T/F)
Solution:-
(a) False
(b) The shrinkage of protoplasm, when a cell is kept in a hypertonic solution.
(vi)The cell wall of the root cell is a differentially permeable membrane. (T/F)
Solution:-
(a)True
3. What is the difference between flaccid and turgid? Give one example of flaccid condition in plants.
Solution:-
| Flaccid | Turgid |
| Flaccidity is the condition in which the cell content in shrunken and the cell is no more “tight”.
The cell is then said to be flaccid. |
Turgidity is the state of a cell in which the cell wall is rigid and stretched by an increase in the volume of vacuoles due to the absorption of water.
The cell is then said to be turgid. |
| Example:- Salting of meat or addition of salt to pickles is a method of killing bacteria by plasmolysis – water is drawn out of the bacterial cells |
4. Give reasons for the following:
(a) If you sprinkle some common salt on grass growing on a lawn, it is killed at that spot.
Solution:-
If we sprinkle some common salt on grass growing on a lawn causes the Plasmolysis of grass cell finally leading them to death. Hence, after sprinkling some common salt on grass growing on a lawn, it is killed at the spot.
(b) If you uproot a plant from the soil, its leaves soon wilt.
Solution:-
This is because the turgidity of the leaf cells keeps the leaf straight and extended. If a plant is uprooted, the leaves continue losing water by transpiration, but there is no chance for absorbing water absorbed through the roots. This does not allow the compensation for the loss of water by transpiration; hence the leaves of the uprooted plant wilt soon.
(c) It is better to transplant seedlings in a flower-bed in the evening and not in the morning.
Solution:-
It is better to transplant seedlings in a flower-bed in the evening and not in the morning. Because in the morning heat is extensive which leads to high transpiration rate but the newly planted seedling needs some time to get accustomed to the surrounding environment thus leading to a low root pressure and thus leading to the wilting of the leaves and finally its death due to excessive transpiration.
(d) A plant cell when kept in a hypertonic salt solution for about 30 minutes turns flaccid.
Solution:-
When a living cell, such as the cell of a leaf of an aquatic plant, is placed in freshwater, it remains in a fully distended condition. Its plasma membrane remains in close contact with the cell wall and presses against it just like a rubber bladder of a football pushing against the leather casing. If this plant cell is now kept in a hypertonic solution for 30 minutes, it will lose its distended appearance, the cytoplasm will shrink and the plasma membrane will withdraw from the cell wall is called plasmolysis and the cells in this state are said to be limp or flaccid.
(e) Potato cubes when placed in water become firm and increase in size.
Solution:-
Potato cubes when placed in water become firm and increase in size because cubes contain an excess of salts and sugars as compared to the water in which the cubes are placed. Hence, due to endosmosis, water from the surrounding enters the potato cubes making them firm and increasing their size.
5. Mention whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F) and give explanation in support of your answer.
(a) Plasmolysis is reverse of deplasmolysis.
Solution:-
True.
Plasmolysis is the contraction of cytoplasm from the cell wall caused due to the withdrawal of water when placed in a strong (hypertonic) Solution.
Deplasmolysis is the result of the re-entry of water into the plasmolysed cell when placed in hypotonic solution due to which the protoplasm again swells up pressing tight against the cell wall.
(b) Guttation is another name for bleeding in plants.
Solution:-
False.
The water appears as tiny drops along the margins or the tips of the leaves, especially in the early mornings. This loss of excessive water is called guttation.
Loss of water through a cut stem is called bleeding.
(c) Soaked seeds burst three seed coats.
Solution:-
False.
Because, there is only one seed coat in a seed.
(d) If the phloem of a twig is removed keeping the xylem intact, the leaves of a twig wilt.
Solution:-
False.
Because, the leaves of the twig remain turgid since its xylem is intact and xylem is responsible for water conduction in plants.
(e) Guttation in plants occurs maximum at mid-day.
Solution:-
False.
The water appears as tiny drops along the margins or the tips of the leaves, especially in the early mornings or at night. This occurs due to excessive root pressure.
(f) Dry seeds when submerged in water swell up due to endosmosis.
Solution:-
False.
Because, dry seeds when submerged in water swell up due to imbibition.
D. LONG ANSWER TYPE
1. Give two examples of turgor movements in plants.
Solution:-
(a) Mimosa pudica is an outstanding example of turgor movement. The rapid dropping of the leaves of the sensitive plants. If one of the leaves is touched, even lightly, the leaflets fold up and within 2 to 3 seconds, the entire leaf droops. If the leaf is touched somewhat strongly, the wave of folding and drooping spreads from the stimulated leaf to all neighbouring leaves.
(b)Similar turgor movements are found in insectivorous plants whose leaves close up to entrap a living prey. The bending movement of certain flowers towards the sun and the sleep movements of the leaves of certain plants at night are also due to turgor movements.
2. Explain the mechanism of the closing and opening of the stomata.
Solution:-
The closing and opening of stomata depend on the turgidity of guard cells. Each guard cell has a thicker wall on the side facing the stoma and a thin wall on the opposite side. Guard cells contain chloroplasts. As a result of the synthesis of glucose during photosynthesis and some other chemical changes, the osmotic pressure of the contents of the guard cells increases and they absorb more water from the neighbouring cells, thus becoming turgid. On account of turgor, the guard cells become more arched outwards and an aperture between them widens, thereby opening the stoma. At night, or when there is a shortage of water in the leaf, the guard cells turn flaccid and their inner rigid walls become straight, thus closing the stomatal aperture.
3. Concentration of mineral nutrient elements is higher inside the root-hairs than in the surrounding soil. How do roots take them in from the soil?
Solution:-
The concentration of mineral nutrient elements is higher inside the root-hairs than in the surrounding soil because the absorption of mineral elements from the soil involves active transport by the cells. Minerals may also be absorbed as ions rather than as salts. The dilute solution of water and mineral salts, absorbed from the soil by the roots, can be used for food manufacture in the leaves, only if it can travel up to the highest points of the plant. This upward flow occurs through the xylem.
4. Explain how soaked seeds swell up and burst their seed coats.
Solution:-
Imbibition is the passive absorption of water by substances such as cellulose (in the cell wall) and starch. Turgor is the pressure set up inside the plant cells due to hydrostatic pressure on the cell walls on account of incoming water as a result of endosmosis. The seeds swell up when soaked in water due to imbibition and endosmosis. The force generated by the water thus absorbed is strong enough to make the seed coats burst. Hence, soaked seeds when kept in a fully filled closed container burst it open with pressure.
5. Leaves of the sensitive plant wilt and droop down on a slight touch. What mechanism brings about this change?
Solution:-
The rapid drooping of the leaves of the sensitive plant (Mimosa pudica) is an outstanding example of turgor movement. If one of the leaves is touched, even lightly, the leaflets fold up and within 2 to 3 seconds, the entire leaf droops. If the leaf is touched somewhat strongly, the wave of folding and drooping spreads from the stimulated leaf to all neighboring leaves. Slowly, the leaves recover and again stand erect. In this plant, the stimulus of touch leads to loss of turgor at the base of petioles called a pulvinus.
6. What is transpiration pull? How is it caused?
Solution:-
As the water is lost from the leaf surface by transpiration, more water molecules are pulled up due to the tendency of water molecules to remain joined (cohesion), and thus to produce a continuous column of water through the stem is called transpiration pull. Transpiration pull is an important force which causes the ascent of sap. Negative pressure or tension is produced in the xylem that pulls the water from the roots and soil.
E. STRUCTURED/APPLICATION/SKILL TYPE
1. The following diagram represents a plant cell after being place in a strong sugar solution.

Guidelines 1 to 5 indicate the following:
(1) Cell Wall (2) Strong Sugar Solution
(3) Protoplasm (4) Large Vacuole
(5) Nucleus
(a) What is the state of the cell shown in the diagram?
Solution:-
The state of the cell is flaccid.
(b) Name the structure which acts as a selectively permeable membrane.
Solution:-
The plasma membrane is the structure which acts as a selectively permeable membrane.
(c) If the cell had been placed in distilled water instead of strong sugar solution, which feature would not have been seen?
Solution:-
Plasmolysis would not occur and flaccidity would not be seen.
(d) Name any one feature of this plant cell which is not present in an animal cell.
Solution:-
Absent of cell wall in an animal cell.
2. A leaf cell of a water plant was placed in a liquid other than pond water. After sometime, it assumed a shape as shown below:

(a) Give the term for the state of the cell it has acquired.
Solution:-
The term for the state of the cell it has acquired is a flaccid cell.
(b) Comment on the nature (tonicity) of the liquid surrounding the cell.
Solution:-
The liquid is a hypertonic solution. It has higher solute concentration outside the cell than the fluids inside the cell.
(c) Redraw in the space provided, the diagram of the cell if it is soon placed in ordinary water for some time.
Solution:-

3. The diagram given below represents an experimental set-up to demonstrate a certain process. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:

(a) Name the process.
Solution:-
By observing the above figure we can say that the process is osmosis.
(b) Define the above-named process.
Solution:-
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from their region of higher concentration (dilute solution or with a lower solute concentration) to their region of lower concentration (concentrated solution or with a higher solute concentration) through a semi-permeable membrane.
(c) What would you observe in the experimental set-up after an hour or so?
Solution:-
After an hour so we would observe a gradual rise of the sugar solution in the thistle funnel from its initial level.
(d) What control experiment can be set up for comparison?
Solution:-
As a control, take another thistle funnel with plain water filled in it and suspend it in another beaker also containing water. Again mark the level on its stem.
(e) Keeping –hair, cell and its surroundings, name the parts that correspond to (1) concentrated sugar solution (2) parchment paper and (3) water in the beaker.
Solution:-
Keeping –hair, cell and its surroundings, name of the parts that correspond to:
1. Concentrated sugar solution: Cytoplasm of the root hair cell.
2. Parchment paper: Cell membrane, that is, the semi-permeable membrane.
3. Water in the beaker: water in the soil.
(f) Name any other substance that can be used instead of parchment paper in the above experiment.
Solution:-
The other substance that can be used instead of parchment paper in the above experiment is cellophane paper or animal bladder.
(g) Mention two advantages of the process to the plants.
Solution:-
Advantages of the osmosis process are,
1. Osmosis is the process during which the water moves from a higher concentration of the gradient to the lower concentration of the gradient.
2. Regulation of osmosis in the guard cells of the leaves helps in the opening and closing of stomata
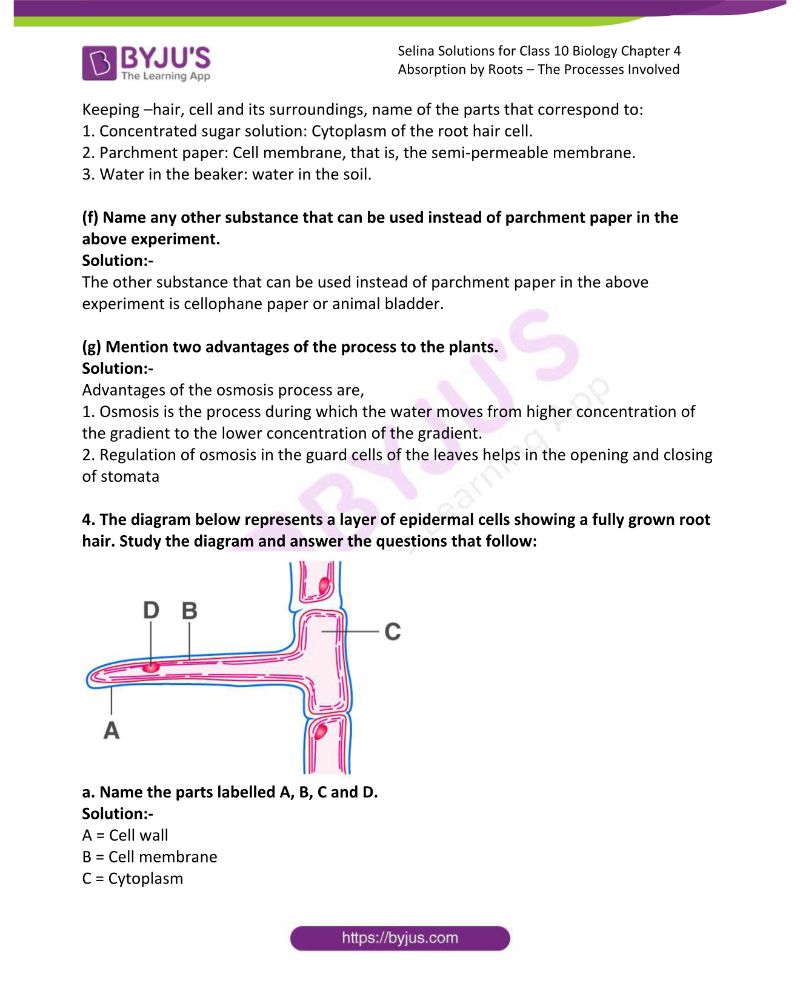
4. The diagram below represents a layer of epidermal cells showing a fully grown root hair. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:

a. Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D.
Solution:-
A = Cell wall
B = Cell membrane
C = Cytoplasm
D = Nucleus
b. The root hair cell is in a turgid state. Name and explain the process that caused this state.
Solution:-
Absorption of water by the root is by means of root hairs. A root hair contains cell sap which has a higher concentration of salts as compared to the outside soil water. This difference sets of osmosis and the outside soil water diffuse into the root hair. Form the cell bearing root hair, water continues to pass to adjoining cells one after another to finally enter the xylem vessels. The turgidity acquired by the cells in the process also helps to push the water upwards through the xylem vessels.
c. Mention one distinct difference between the parts labelled A and B.
Solution:-
| Cell wall | Cell membrane |
| The cell wall is thin and permeable. It allows the movement of water molecules and dissolved substances freely in and out of the cell. | The cell membrane is very thin, and semi-permeable, which means that it allows water molecules to pass through, but not the larger molecules of the dissolved salts. |
d. Draw a diagram of the above root hair cell as it would appear when a concentrated solution of fertilizers is added near it.
Solution:-

5. Two potato cubes each 1 cm3 in size, were placed separately in two containers (A and B), the container A having water and the other (B) containing concentrated sugar solution. After 24 hours when the cubes were examined, those placed in water were found to be firm and had increased slightly in size and those placed in concentrated sugar solution were found to be soft and somewhat decreased in size. Use the above information to answer the questions that follow:
(a) Account for the firmness and increase in the size of the potato cubes placed in water.
Solution:-
In this condition, the solution outside the cell has a lower solute concentration than the fluids inside the cell. As a result, the water molecules from outside will move into the cell (endosmosis). This causes the firmness and increases in the size of the potato cubes when placed in water.
(b) Account for the softness and decrease in size of the potato cubes which were placed in sugar solution.
Solution:-
In this condition, the solution outside the cell has a higher solute concentration than the fluids inside the cell. Consequently, the water molecules from the interior of the cell will move out (exosmosis). This causes the softness and decrease in size of the potato cubes when placed in sugar solution.
(c) Name and define the physical process being investigated in this experiment.
Solution:-
Osmosis is the transport of water through a semi-permeable membrane from a solution of low concentration to a solution of high concentration.
6. Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow:

(a) Name the process being studied in the above experiment.
Solution:-
The process studied in the above experiment is water absorption by plant roots through osmosis.
(b) Explain the process mentioned in (a) above
Solution:-
Take a test tube (A) filled with water. Pull out a young leafy plant (such as balsam) from the soil with its roots intact. Insert the roots into the test tube soon. Put a few drops of oil in the test tube to prevent any loss of water by evaporation. Mark the level of water. In a day or two, you will find that the level of water in the test tube (A) falls, proving that water lost in the test tube was absorbed by the roots.
(c) Why is oil placed over water?
Solution:-
Oil is placed over water because in the test tube because to prevent any loss of water by evaporation.
(d) What do we observe with regard to the level of water when this set up is placed in (1) bright sunlight (2) humid conditions (3) windy day?
1. Bright sunlight: This set up is placed in bright sunlight, the water level in the test tube is seen to be less when compared to its initial marking. Because the rate of transpiration is very high.
2. Humid conditions: This set up is placed in humid condition, the water level in the test tube decreases from its initial mark, but at a very slow rate. Because the rate of transpiration is reduced.
3. Windy day: This set up is placed on the windy day the rate of transpiration highly increases thus the level of the water level in the test tube is seen to decrease fast from its initial marking.
(e) Mention any three adaptations found in plants to foster the process mentioned in (a) above
Solution:-
1. Large surface area provided by rootlets and root hairs
2. Loss of leaves
3. Root hairs with thin walls
7. Show by a series of diagrams, the change which a plant cell will undergo when placed in
(a) Hypertonic salt solution
Solution:-

(b) Hypotonic salt solution.
Solution:-

8. Study the experimental setup in the figure and then answer the questions that follow.

(a) What phenomenon is being studied by this setup?
Solution:-
Osmosis phenomenon is being studied by this setup.
(b) Explain the phenomenon mention in (a) above.
Solution:-
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from their region of higher concentration (dilute solution or with a lower solute concentration) to their region of lower concentration (concentrated solution or with a higher solute concentration) through a semi-permeable membrane.
(c) What is meant by ‘semipermeable membrane’?
Solution:-
A semipermeable membrane is a membrane which means that it allows water molecules to pass through, but not the larger molecules of the dissolved salts.
(d) What will you observe in the setup after about half an hour? Give reasons for your answer.
Solution:-
Observing the setup after half an hour, water molecules will continue to pass from 10% sucrose solution to 15% sucrose solution through the semipermeable membrane due to osmosis. This will continue until the concentration of water molecules becomes the same in both ends of the setup.
9. A candidate in order to study the process of osmosis has taken 3 potato cubes and put them in 3 different beakers containing 3 different solutions. After 24 hours, in the first beaker the potato cube increased in size, in the second beaker the potato cube decreased in size and in the third beaker, there was no change in the size of the potato cube. The following diagram shows the result of the same experiment.

(a) Give the technical terms of the solutions used in the beakers 1, 2 and 3.
Solution:-
The technical terms of the solutions used in the bakers are
Solution 1 = Hypotonic solution
Solution 2 = Hypertonic solution
Solution 3 = Isotonic solution
(b) In beaker 3, the size of the potato cube remains the same. Explain the reason in brief.
Solution:-
In beaker 3, the size of the potato cube remains the same because the solution present in this baker 3 is an isotonic solution. The relative concentration of water molecules and the solute on either side of the cell membrane is the same. In such a solution there is no movement of water molecules from outside will move into the cell.
(c) Write the specific features of the cell sap of root hair which helps in absorption of water.
Solution:-
Root hairs are the extensions of the outer cells of the root. They also contain large vacuoles filled with a solution called sap.
(d) What is osmosis?
Solution:-
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from their region of higher concentration (dilute solution or with a lower solute concentration) to their region of lower concentration (concentrated solution or with a higher solute concentration) through a semi-permeable membrane
(e) How does a cell wall and a cell membrane differ in their permeability?
Solution:-
| Cell wall | Cell membrane |
| The cell wall is thin and permeable. It allows the movement of water molecules and dissolved substances freely in and out of the cell. | The cell membrane is very thin, and semi-permeable, which means that it allows water molecules to pass through, but not the larger molecules of the dissolved salts. |
Selina Solutions Concise Biology Class 10 Chapter 4 Absorption by Roots – The Processes Involved, the chapter contains some important topics, which are absorption by the roots, need of water and minerals for plants, characteristics of roots for absorbing water, absorption and conduction of water and minerals, use of turgidity to plants and some experiments on absorption and conduction of water in the plants. By practising Selina Solutions, students are able to score good marks in Biology.
List of subtopics covered in Selina Solutions Concise Biology Class 10 Chapter 4 Absorption by Roots – The Processes Involved
| Number | Subtopic |
| 4.1 | Absorption by the roots |
| 4.2 | Need of water and minerals for plants |
| 4.3 | Characteristics of roots for absorbing water |
| 4.4 | Absorption and conduction of water and minerals |
| 4.5 | Root pressure |
| 4.6 | Importance of root hairs and the upward movement of absorbed water and minerals |
| 4.7 | Some experiment on absorption and conduction of water in the plants |
| 4.8 | Forces contributing to ascent of sap |
Contents of Exercise
| Name of the exercise | Number of questions | Question Type | Page number |
| Review questions | 10 | MCQ | 51 |
| 5 | Very short | 51 and 52 | |
| 5 | Short | 52 | |
| 6 | Long | 52 | |
| 9 | Structured/Skill | 53 and 54 |
Key Features of Selina Solutions Concise Biology Class 10 Chapter 4 Absorption by Roots – The Processes Involved
- Selina solutions provide students step by step answers with detailed explanations.
- Related examples are used to explain the topics.
- Solutions have been given with the information provided in the textbook as per the CBSE syllabus.
- Tables are used in different questions and where ever necessary.
- Use of diagrams wherever required.





















Comments