A Co-ordinate bond is a type of alternate covalent bond that is formed by sharing of an electron pair from a single atom. Both shared electrons are donated by the same atom. It is also called a dative bond or dipolar bond.
Download Complete Chapter Notes of Coordination Compounds
Download Now
Co-ordinate covalent bonds are usually formed in reactions that involve two non-metals, such as a hydrogen atom or during bond formation between metal ions and ligands.
Characteristics of Coordinate Covalent Bond
- In this type of bonding, the atom that shares an electron pair from itself is termed as the donor.
- The other atom which accepts these shared pair of electrons is known as a receptor or acceptor.
- The bond is represented with an arrow →, pointing towards the acceptor from the donor atom.
- After sharing of electron pairs, each atom gets stability.
- This type of bonding is central to the Lewis theory.
- Getting a good understanding of co-ordinate covalent bonds can help in properly designing complex organic molecules.
Also Read: Chemical Bonding
Coordinate Bond Diagram
Below, we have given a simple diagram of a co-ordinate bond. The bond is shown by an arrow which points in the direction where an atom is donating the lone pair to the atom that is receiving it.
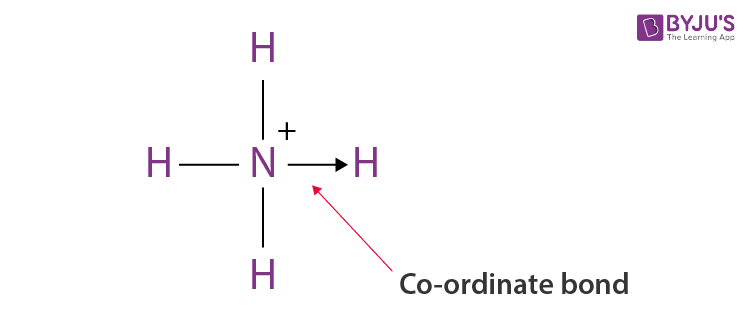
Co-Ordinate Bond Examples
Here are a few examples of the coordinate covalent bond.
Formation of Ammonium Ion
The nitrogen atom in Ammonia donates its electron pair to the empty orbital of the H+ ion; thus, nitrogen is the donor, H+ is the acceptor, and a co-ordinate bond is formed

Formation of Hydronium Ion
An oxygen atom in water donates its one pair of electrons to the vacant orbital of the H+ ion; thus, a dative bond is formed oxygen atom is the donor atom and the H+ is the acceptor atom.

Formation of Ammonia Boron Trifluoride
The nitrogen atom in Ammonia donates one pair of electrons to the vacant orbital of the Boron atom in the Boron trifluoride; thus nitrogen atom is the donor atom, and the boron atom is the acceptor.

Properties of Coordinate Compounds
- They have lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds.
- Some of these compounds exhibit isomerism.
- Sharing of electrons takes place in a definite direction; hence, it is a directional bond.
- It is weaker than Ionic bonding.
Also Read: Polar Covalent Bond
Important Questions
1. Why do atoms combine to form a molecule?
Answer:
Atoms combine to form molecules because atoms, in general, cannot exist on their own. Each atom is also unstable and therefore needs stability. Therefore, atoms also combine to achieve a stable electronic configuration.
2. What is dative bonding?
Answer:
Dative bonding, also known as co-ordinate bonding, is a type of covalent bond in which sharing of electrons takes place from the same atom.
3. Write an example of co-ordinate bonding.
Answer:
(1) Formation of ammonium ion
(2) Formation of ammonia boron trifluoride
(3) Formation of hydronium ion.
4. What is the major difference between ionic and co-ordinate bonding?
Answer:
Ionic bonding takes place between ions that are oppositely charged. Positive ions attract negative ions, or we can say that there is an electrostatic attraction between anions and cations. On the other hand, co-ordinate bonding is a type of covalent bonding where only one atom donates its electrons to form the bond. The other atom does not contribute anything.
5. Is co-ordinate bonding a strong bond?
Answer:
Co-ordinate covalent bonds are usually strong bonds. This is because the bonds are identical to any other interatomic bonds.

Comments