Hydrohalic acids are commonly termed hydrogen halides when they dissolve in water to give acids. They are diatomic organic compounds with a formula HX, and X represents any of the halogens. Some of the halogens include iodine, chlorine, bromine and fluorine. Among these, hydrogen fluoride, chlorine and bromine fall under the category of volcanic gasses. Hydrogen chloride forms a primary component of gastric acid when present in the form of hydrochloric acid.
Volcanic gasses consist of dissolved gasses found in lava and gasses trapped in vesicles in volcanic rocks. These gases can be found in the Earth’s atmosphere, crust and mantle. Gastric acid is found in the stomach, which is a digestive fluid that comprises hydrochloric acid.
Physical Properties of Hydrogen Halides
At STP – Standard Temperature and Pressure, the hydrogen halides are colourless gas. Hydrogen fluoride is an exceptional case as it boils at nineteen-degree Celsius. Hydrogen fluoride can condense under cool conditions. They have an abnormal boiling point, and the reason for this is that they form a hydrogen bond. Each fluorine atom comprises three lone pairs of electrons representing highly charged recharge of space. Outer electrons are present at the n=2 level. The below figure illustrates the above concept.
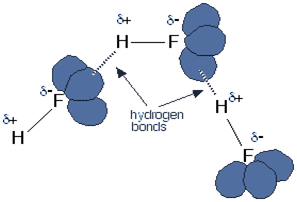
The concentrated hydrohalic acid produces white fumes that are caused by the small droplets of a concentrated aqueous solution of hydrohalic acid. The rest of the hydrogen halides do not form a hydrogen bond.
The Acidity of Hydrogen Halides
Let us consider the reaction of hydrogen chloride with water. Hydrogen chloride falls into the category of acid as it denotes protons to other species. When hydrochloric acid is dissolved in water, it forms hydrochloric acid. The fumes of hydrochloride are moist, and this is caused when hydrogen chloride reacts with water vapour in the presence of air resulting in a cloud of concentrated hydrochloric acid.
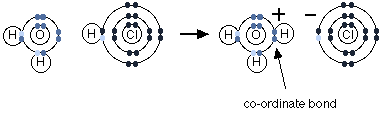
Hydrogen chloride denotes a proton to a lone pair of a water molecule. A dative covalent bond is formed between the transferred proton and oxygen.
Hydrochloric acid is the strongest acid as it fully ionises in water.

Comments