The JEE Main 2022 July 25 – Shift 2 Maths Question Paper with Solutions is available on this page. The JEE Main 2022 answer keys are designed by expert faculties at BYJU’S. JEE Main 2022 question papers with solutions help students to analyse the question pattern and difficulty level. Students can solve and practise the JEE Main 2022 July 25 – Shift 2 Maths Question Paper with Solutions to crack the problems in a faster way.
JEE Main 2022 25th July Shift 2 Mathematics Question Paper and Solutions
SECTION – A
Multiple Choice Questions: This section contains 20 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (1), (2), (3) and (4), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Choose the correct answer :
1. For \(\begin{array}{l}z \in \mathbb{C}\ \text{if the minimum value of}\ \left(|z-3\sqrt{2}| + |z-p\sqrt{2}i|\right)\end{array} \)
is 5√2, then a value of p is _________.
(A) 3
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{B})\ \frac{7}{2}\end{array} \)
(C) 4
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D})\ \frac{9}{2}\end{array} \)
Answer (C)
Sol.
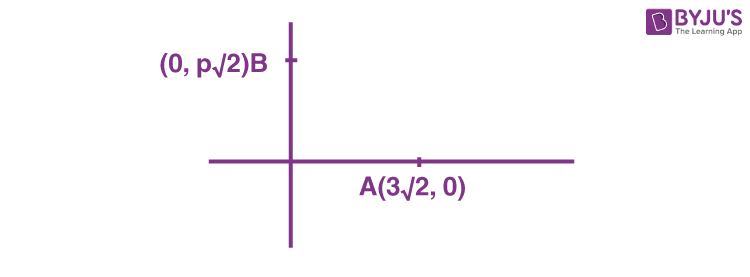
It is sum of distance of z from (3√2, 0) and (0, p√2).
For minimising, z should lie on AB and
\(\begin{array}{l}AB=5\sqrt{2}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(AB)^2=18+2p^2\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}p=\pm4\end{array} \)
2. The number of real values of λ, such that the system of linear equations
2x – 3y + 5z = 9
x + 3y – z = –18
3x – y + (λ2 – | λ |)z = 16
has no solutions, is
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) 2
(D) 4
Answer (C)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\Delta = \begin{vmatrix}2 & -3 & 5 \\1 & 3 & -1 \\3 & -1 & \lambda^2-|\lambda| \\\end{vmatrix} =2(3\lambda^2-3|\lambda|-1)+3(\lambda^2-|\lambda|+3)+5(-1-9)\end{array} \)
= 9λ2 – 9 | λ | – 43
= 9 | λ |2 – 9 | λ | – 43
Δ = 0 for 2 values of | λ | out of which one is –ve and other is +ve
So, 2 values of λ satisfy the system of equations to obtain no solution.
3. The number of bijective functions f : {1, 3, 5, 7, …, 99} → {2, 4, 6, 8, ….., 100} such that \(\begin{array}{l}f(3)\ge f(9)\ge f(15)\ge f(21)\ge … \ge f(99)\end{array} \)
is_____.
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{A})\ ^{50}P_{17}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{B})\ ^{50}P_{33}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C})\ 33!\times 17!\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D})\ \frac{50!}{2}\end{array} \)
Answer (B)
Sol. As function is one-one and onto, out of 50 elements of domain set 17 elements are following restriction
f(3) > f(9) > f(15) ….. > f(99)
So number of ways
\(\begin{array}{l}=^{50}C_{17}\cdot 1\cdot 33! = ^{50}P_{33}\end{array} \)
4. The remainder when (11)1011 + (1011)11 is divided by 9 is
(A) 1
(B) 4
(C) 6
(D) 8
Answer (D)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}Re\left( \frac{(11)^{1011}+(1011)^{11}}{9} \right) = Re\left(\frac{2^{1011}+3^{11}}{9}\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{For } Re \left(\frac{2^{1011}}{9}\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}2^{1011}=(9-1)^{337}=^{337}C_09^{337}(-1)^0 +^ {337}C_1 9^{336}(-1)^1+^{337}C_2 9^{335}(-1)^2 + … + ^{337}C_{337} 9^{0}(-1)^{337}\end{array} \)
so, remainder is 8.
and
\(\begin{array}{l}Re\left(\frac{3^{11}}{9}\right)=0\end{array} \)
So, remainder is 8.
5. The sum \(\begin{array}{l}\sum_{n=1}^{21}\frac{3}{(4n-1)(4n+3)}\end{array} \)
is equal to
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{A})\ \frac{7}{87}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{B})\ \frac{7}{29}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C})\ \frac{14}{87}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D})\ \frac{21}{29}\end{array} \)
Answer (B)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\sum_{n=1}^{21}\frac{3}{(4n-1)(4n+3)}=\frac{3}{4}\sum_{n=1}^{21}\frac{1}{4n-1}-\frac{1}{4n+3}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{3}{4}\left[\left(\frac{1}{3}-\frac{1}{7}\right) + \left(\frac{1}{7}-\frac{1}{11}\right)+…+ \left(\frac{1}{83}-\frac{1}{87}\right)\right]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{3}{4}\left[\frac{1}{3}-\frac{1}{87}\right]=\frac{3}{4}~\frac{84}{3.87}= \frac{7}{29}\end{array} \)
6. \(\begin{array}{l}\displaystyle \lim_{ x\to \frac{x}{4}}\frac{8\sqrt{2}-(\cos x + \sin x)^7}{\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{2}\sin 2x}\end{array} \)
is equal to
(A) 14
(B) 7
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C})\ 14\sqrt{2}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D})\ 7\sqrt{2}\end{array} \)
Answer (A)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\displaystyle \lim_{ x\to\frac{x}{4} }\frac{8\sqrt{2}-(\cos x + sin x)^7}{\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{2}\sin 2x}~~~~~~~\left(\frac{0}{0} \text{ form}\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\displaystyle \lim_{ x\to\frac{x}{4} }\frac{-7(\cos x + \sin x)^6(-\sin x + \cos x)}{-2\sqrt{2}\cos 2x}\end{array} \)
using L–H Rule
\(\begin{array}{l}=\displaystyle \lim_{ x\to\frac{x}{4} }\frac{56(\cos x – \sin x)}{2\sqrt{2} \cos 2x} ~~~~~\left(\frac{0}{0}\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\displaystyle \lim_{ x\to\frac{x}{4} }\frac{-56(\sin x + \cos x)}{-4\sqrt{2} \sin 2x}\end{array} \)
using L–H Rule
\(\begin{array}{l}=7\sqrt{2}\cdot \sqrt{2}=14\end{array} \)
7. \(\begin{array}{l}\displaystyle \lim_{n \to \infty}\frac{1}{2^n}\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\frac{1}{2^n}}} + \frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\frac{2}{2^n}}} + \frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\frac{3}{2^n}}} + … + \frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\frac{2^n -1}{2^n}}}\right)\end{array} \)
is equal to
(A)
(B) 1
(C) 2
(D) –2
Answer (C)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}I = \displaystyle \lim_{n \to \infty}\frac{1}{2^n}\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\frac{1}{2^n}}} + \frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\frac{2}{2^n}}} + \frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\frac{3}{2^n}}} + … + \frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\frac{2^n -1}{2^n}}}\right)\end{array} \)
Let 2n = t and if n → ∞ then t → ∞
\(\begin{array}{l}I=\displaystyle \lim_{n \to \infty} \frac{1}{t}\left( \sum_{r=1}^{t=1}\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\frac{r}{t}}}\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}l=\int_{0}^{1}\frac{dx}{\sqrt{1-x}}=\int_{0}^{1}\frac{dx}{\sqrt{x}}~~~~~~~~ \int_{0}^{a}f(x)dx = \int_{0}^{a}f(a-x)dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\left[2x^{\frac{1}{2}}\right]_0^1=2\end{array} \)
8. If A and B are two events such that \(\begin{array}{l}P(A)=\frac{1}{3}, P(B)=\frac{1}{5}\ \text{and}\ P(A\cup B)=\frac{1}{2},\ \text{then}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}P(A|B’) + P(B|A’|)\end{array} \)
is equal to
\(\begin{array}{l} (\text{A})\ \frac{3}{4}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l} (\text{B})\ \frac{5}{8}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l} (\text{C})\ \frac{5}{4}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{D})\ \frac{7}{8}\end{array} \)
Answer (B)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}P(A)=\frac{1}{3}, P(B)=\frac{1}{5} \text{ and } P(A \cup B)=\frac{1}{2}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore P(A \cap B) = \frac{1}{3}+\frac{1}{5}-\frac{1}{2}=\frac{1}{30}\end{array} \)
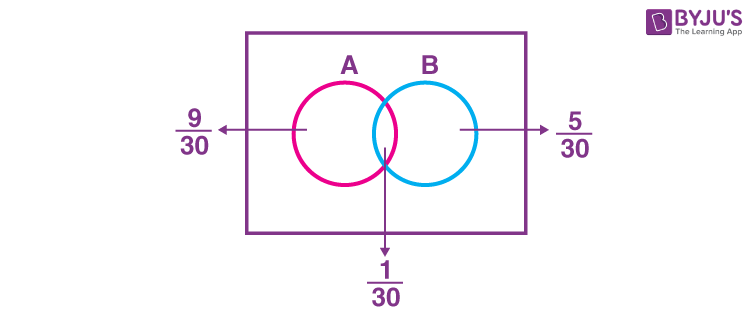
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Now, } P(A|B’) +P(B|A’)=\frac{P(A \cap B’)}{P(B’)}+\frac{P(B \cap A’)}{P(A’)}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{\frac{9}{30}}{\frac{4}{5}}+\frac{\frac{5}{30}}{\frac{2}{3}}=\frac{5}{8}\end{array} \)
9. Let [t] denote the greatest integer less than or equal to t. Then the value of the integral \(\begin{array}{l}\int_{-3}^{101}\left([\sin (\pi x)]+e^{[\cos(2\pi x)]}\right)dx\end{array} \)
is equal to
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{A})\ \frac{52(1-e)}{e}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{B})\ \frac{52}{e}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C})\ \frac{52(2+e))}{e}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D})\ \frac{104}{e}\end{array} \)
Answer (B)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}I = \int_{-3}^{101}\left(\left[sin(\pi x)\right]+e^{\left[cos(2\pi x)\right]}\right)dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\left[\sin \pi x\right]\ \text{is periodic with period 2}\end{array} \)
and \(\begin{array}{l}e^{\left[\cos 2\pi x\right]}\ \text{is periodic with period 1.}\end{array} \)
So,
\(\begin{array}{l}I = 52\int_{0}^{2}\left(\left[\sin(\pi x)\right]+e^{\left[\cos 2\pi x\right]}\right)dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=52\left\{\int_{1}^{2}-1dx + \int_{1/4}^{3/4}e^{-1}dx + \int_{5/4}^{7/4}e^{-1}dx + \int_{0}^{1/4}e^0 dx + \int_{3/4}^{5/4}e^0 dx + \int_{7/4}^{2}e^0 dx\right\} \end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{52}{e} \end{array} \)
10. Let the point P(α, β) be at a unit distance from each of the two lines L1 : 3x – 4y + 12 = 0 and L2 : 8x + 6y + 11 = 0. If P lies below L1 and above L2, then 100(α + β) is equal to
(A) –14
(B) 42
(C) –22
(D) 14
Answer (D)
Sol.
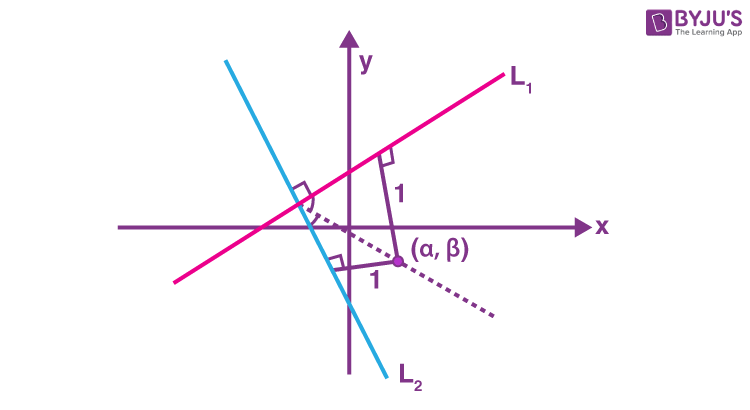
L1 : 3x – 4y + 12 = 0
L2 : 8x + 6y + 11 = 0
Equation of angle bisector of L1 and L2 of angle containing origin
2(3x – 4y + 12) = 8x + 6y + 11
2x + 14y – 13 = 0 …(i)
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{3\alpha – 4\beta + 12}{5}=1 \end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow 3\alpha -4 \beta + 7 =0~~~~~…(ii)\end{array} \)
Solution of 2x + 14y – 13 = 0 and 3x – 4y + 7 = 0 gives the required point \(\begin{array}{l}P\left(\alpha,\beta\right),\alpha = \frac{-23}{25},\beta = \frac{53}{50}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}100(\alpha +\beta) = 14\end{array} \)
11. Let a smooth curve y = f(x) be such that the slope of the tangent at any point (x, y) on it is directly proportional to (-y/x). If the curve passes through the points (1, 2) and (8, 1), then \(\begin{array}{l}\left|y\left(\frac{1}{8}\right)\right|\ \text{ is equal to}\end{array} \)
(A) 2 loge2
(B) 4
(C) 1
(D) 4 loge2
Answer (B)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{dy}{dx}\propto \frac{-y}{x}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{dy}{dx}= \frac{-ky}{x} \Rightarrow \int \frac {dy}{y}=-K\int\frac{dx}{x}\end{array} \)
ln | y | = -Kln | x | + C
If the above equation satisfies (1, 2) and (8, 1)
\(\begin{array}{l}ln2 = -K \times 0 + C \Rightarrow C = ln2\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l} \ln1 = -K \ln8+ \ln2 \Rightarrow K= \frac{1}{3}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{So, at } x= \frac{1}{8}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\ln \left|y\right| = -\frac{1}{3}\ln\left(\frac{1}{8}\right)+\ln2 = 2\ln2\end{array} \)
|y| = 4
12. If the ellipse \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{x^2}{a^2}+\frac{y^2}{b^2}=1\ \text{meets the line}\ \frac{x}{7}+\frac{y}{2\sqrt{6}} =1\end{array} \)
on the x-axis and the line \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{x}{7}-\frac{y}{2\sqrt{6}} =1\end{array} \)
on the y-axis, then the eccentricity of the ellipse is
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{A})\ \frac{5}{7}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{B})\ \frac{2\sqrt{6}}{7}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C})\ \frac{3}{7}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D})\ \frac{2\sqrt{5}}{7}\end{array} \)
Answer (A)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{x^2}{a^2}+\frac{y^2}{b^2}=1\ \text{meets the line}\ \frac{x}{7} + \frac{7}{2\sqrt{6}}=1\ \text{on the x-axis.}\end{array} \)
So, a = 7
and
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{x^2}{a^2} + \frac{y^2}{b^2}=1\ \text{meets the line}\ \frac{x}{7}-\frac{y}{2\sqrt{6}}=1\ \text{on the y-axis.}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{So, }b=2\sqrt{6}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore e^2 = 1- \frac{b^2}{a^2}=1-\frac{24}{49}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}e=\frac{5}{7}\end{array} \)
13. The tangents at the points A(1, 3) and B(1, –1) on the parabola y2 – 2x – 2y = 1 meet at the point P. Then the area (in unit2) of the triangle PAB is :
(A) 4
(B) 6
(C) 7
(D) 8
Answer (D)
Sol. Given curve : y2 – 2x – 2y = 1.
Can be written as
\(\begin{array}{l}(y-1)^2 = 2(x + 1)\end{array} \)
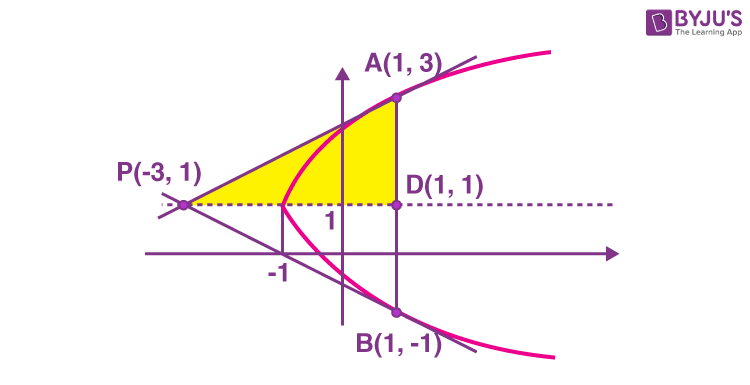
And, the given information can be plotted as shown in figure.
Tangent at A : 2y – x – 5 = 0 {using T = 0}
Intersection with y = 1 is x = –3
Hence, point P is (–3, 1)
Taking advantage of symmetry
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Area of } \Delta PAB = 2 \times \frac{1}{2}\times(1-(-3))\times(3-1)= 8 ~\text{sq. units}\end{array} \)
14. Let the foci of the ellipse \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{x^2}{16}+\frac{y^2}{7}=1\ \text{and the hyperbola}\ \frac{x^2}{144}-\frac{y^2}{\alpha}=\frac{1}{25}\end{array} \)
coincide. Then the length of the latus rectum of the hyperbola is :
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{A})\ \frac{32}{9}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{B})\ \frac{18}{5}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C})\ \frac{27}{4}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D})\ \frac{27}{10}\end{array} \)
Answer (D)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Ellipse} \colon \frac{x^2}{16}+\frac{y^2}{7}=1\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Eccentricity} =\sqrt{1-\frac{7}{16}}=\frac{3}{4}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Foci }\equiv(\pm ae, 0)\equiv(\pm 3, 0)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Hyperbola }\colon \frac{x^2}{\left(\frac{144}{25}\right)}-\frac{y^2}{\left(\frac{\alpha}{25}\right)}=1\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Eccentricity }=\sqrt{1+\frac{\alpha}{144}}=\frac{1}{12}\sqrt{144+ \alpha}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Foci } \equiv (\pm ae, 0)\equiv\left(\pm \frac{12}{5}\cdot \frac{1}{12}\sqrt{144 + \alpha},0\right)\end{array} \)
If foci coincide then
\(\begin{array}{l}3=\frac{1}{5}\sqrt{144+\alpha}\Rightarrow \alpha = 81\end{array} \)
Hence, hyperbola is \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{x^2}{\left(\frac{12}{5}\right)^2}-\frac{y^2}{\left(\frac{9}{5}\right)^2}=1\end{array} \)
Length of latus rectum
\(\begin{array}{l}=2\cdot \frac{\frac{81}{25}}{\frac{12}{5}}=\frac{27}{10}\end{array} \)
15. A plane E is perpendicular to the two planes 2x – 2y + z = 0 and x – y + 2z = 4, and passes through the point P(1, –1, 1). If the distance of the plane E from the point Q(a, a, 2) is 3√2, then (PQ)2 is equal to
(A) 9
(B) 12
(C) 21
(D) 33
Answer (C)
Sol. First plane, P1 = 2x – 2y + z = 0,
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{normal vector} \equiv \overline{n}_1=(2,-2,1)\end{array} \)
Second plane, P2 ≡ x – y + 2z = 4,
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{normal vector}\equiv \overline{n}_2=(1,-1,2)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Plane perpendicular to}\ P_1\ \text{and}\ P_2\ \text{will have normal vector}\ \overline{n}_3\end{array} \)
Where
\(\begin{array}{l}\overline{n}_3=(\overline{n}_1 \times \overline{n}_2)\end{array} \)
Hence,
\(\begin{array}{l}\overline{n}_3=(-3,-3,0)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Equation of plane E through}\ P(1,-1,1)\ \text{and}\ \overline{n}_3\ \text{as normal vector}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(x-1, y+1, z-1)\cdot(-3,-3,0)=0\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow x+y = 0 \equiv E\end{array} \)
Distance of PQ(a, a, 2) from E = |2a/√2|
as given,
\(\begin{array}{l}\left|\frac{2a}{\sqrt{2}}\right|=3\sqrt{2}\Rightarrow a = \pm 3\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Hence, }Q\equiv (\pm 3, \pm 3, 2)\end{array} \)
Distance PQ
\(\begin{array}{l}=\sqrt{21}\Rightarrow (PQ)^2 = 21\end{array} \)
16. The shortest distance between the lines \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{x+7}{-6}=\frac{y-6}{7}=z\ \text{and}\ \frac{7-x}{2}=y-2=z-6\end{array} \)
is
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{A})\ 2\sqrt{29}\end{array} \)
(B) 1
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C})\ \sqrt{\frac{37}{29}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D})\ \sqrt{\frac{29}{2}}\end{array} \)
Answer (A)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}L_1:\frac{x+7}{-6}=\frac{y-6}{7}=\frac{z-0}{1}\end{array} \)
Any point on it
\(\begin{array}{l}\vec{a}_1(-7,6,0)\end{array} \)
and L1 is parallel to
\(\begin{array}{l}\vec{b}_1(-6,7,1)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}L_2:\frac{x-7}{-2}=\frac{y-2}{1}=\frac{z-6}{1}\end{array} \)
Any point on it,
\(\begin{array}{l}\vec{a}_2(7,2,6)\end{array} \)
and L2 is parallel to
\(\begin{array}{l}\vec{b}_2(-2,1,1)\end{array} \)
Shortest distance between L1 and L2
\(\begin{array}{l}=\left|\frac{(\vec{a}_2-\vec{a}_1)\cdot(\vec{b}_1\times\vec{b}_2)}{\left|\vec{b}_1 \times \vec{b}_2\right|}\right|=\left|\frac{(-14,4,-6)\cdot(3,2,4)}{\sqrt{9+4+16}}\right|\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=2\sqrt{29}\end{array} \)
17. Let \(\begin{array}{l}\vec{a}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+2\hat{k}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{and let}\ \vec{b}\ \text{be a vector such that}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\vec{a}\times \vec{b} =2\hat{i}-\hat{k}\ \text{and}\ \vec{a}\cdot\vec{b}=3\end{array} \)
Then the projection of \(\begin{array}{l}\vec{b}\ \text{on the vector}\ \vec{a}- \vec{b}\ \text{is}:\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{A})\ \frac{2}{\sqrt{21}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{B})\ 2\sqrt{\frac{3}{7}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C})\ \frac{2}{3}\sqrt{\frac{7}{3}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D})\ \frac{2}{3}\end{array} \)
Answer (A)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\vec{a}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+2\hat{k}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\vec{a}\times \vec{b}=2\hat{i}-\hat{k}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\vec{a}\cdot \vec{b}=3\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\left|\vec{a}\times \vec{b}\right|^2+\left|\vec{a}\cdot \vec{b}\right|^2=\left|\vec{a}\right|^2\cdot \left|\vec{b}\right|^2\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow 5 + 9 = 6 \left|\vec{b}\right|^2\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow \left|\vec{b}\right|^2 = \frac{7}{3}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\left|\vec{a} – \vec{b}\right|=\sqrt{\left|\vec{a}\right|^2 + \left|\vec{b}\right|^2-2\vec{a}\cdot\vec{b}} = \sqrt{\frac{7}{3}} \end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{projection of}|\vec{b}| \text{ on } \vec{a}-\vec{b}=\frac{\vec{b}\cdot(\vec{a}-\vec{b})}{|\vec{a}-\vec{b}|}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{\vec{b}\cdot \vec{a}-|\vec{b}|^2}{|\vec{a}-\vec{b}|}=\frac{3-\frac{7}{3}}{\sqrt{\frac{7}{3}}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{2}{\sqrt{21}}\end{array} \)
18. If the mean deviation about median for the number 3, 5, 7, 2k, 12, 16, 21, 24 arranged in the ascending order, is 6 then the median is
(A) 11.5
(B) 10.5
(C) 12
(D) 11
Answer (D)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Median } = \frac{2k+12}{2}=k+6\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Mean deviation}=\sum\frac{|x_i-M|}{n}=6\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow \frac{(k+3)+(k+1)+(k-1)+(6-k)+(6-k)+(10-k)+(15-k)+(18-k)}{8}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore \frac{58-2k}{8}= 6\\k = 5\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Median } = \frac{2\times 5 + 12 }{2}=11\end{array} \)
19. \(\begin{array}{l}2\sin\left(\frac{\pi}{22}\right)\sin\left(\frac{3\pi}{22}\right)\sin\left(\frac{5\pi}{22}\right)\sin\left(\frac{7\pi}{22}\right)\sin\left(\frac{9\pi}{22}\right)\end{array} \)
is equal to :
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(A\right)\frac{3}{16}\\\left(B\right)\frac{1}{16}\\\left(C\right)\frac{1}{32}\\\left(D\right)\frac{9}{32}\end{array} \)
Answer (B)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}2\sin\left(\frac{\pi}{22}\right)\sin\left(\frac{3\pi}{22}\right)\sin\left(\frac{5\pi}{22}\right)\sin\left(\frac{7\pi}{22}\right)\sin\left(\frac{9\pi}{22}\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=2\sin\left(\frac{11\pi-10\pi}{22}\right)\sin\left(\frac{11\pi-8\pi}{22}\right)\sin\left(\frac{11\pi-6\pi}{22}\right)\sin\left(\frac{11\pi-4\pi}{22}\right)\sin\left(\frac{11\pi-2\pi}{22}\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=2\cos\frac{\pi}{11}\cos\frac{2\pi}{11}\cos\frac{3\pi}{11}\cos\frac{4\pi}{11}\cos\frac{5\pi}{11}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{2\sin\frac{32\pi}{11}}{2^5\sin\frac{\pi}{11}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{1}{16}\end{array} \)
20. Consider the following statements :
P : Ramu is intelligent.
Q : Ramu is rich.
R : Ramu is not honest.
The negation of the statement “Ramu is intelligent and honest if and only if Ramu is not rich” can be expressed as :
(A) ((P ∧ (~ R)) ∧ Q) ∧ ((~ Q) ∧ ((~ P) ∨ R))
(B) ((P ∧ R) ∧ Q) ∨ ((~ Q) ∧ ((~ P) ∨ (~ R)))
(C) ((P ∧ R) ∧ Q) ∧ ((~ Q) ∧ (( ~ P) ∨ (~ R)))
(D) ((P ∧ (~ R)) ∧ Q) ∨ ((~ Q) ∧ ((~ P) ∧ R))
Answer (D)
Sol. P : Ramu is intelligent
Q : Ramu is rich
R : Ramu is not honest
Given statement, “Ramu is intelligent and honest if and only if Ramu is not rich”
= (P ∧ ~ R) ⇔ ~ Q
So, negation of the statement is
~ [(P ∧ ~ R) ⇔ ~ Q]
= ~ [{~ (P ∧ ~ R) ∨ ~ Q} ∧ {Q ∨ (P ∧ ~ R)}]
= ((P ∧ ~ R) ∧ Q) ∨ (~ Q ∧ (~ P ∨ R))
SECTION – B
Numerical Value Type Questions: This section contains 10 questions. In Section B, attempt any five questions out of 10. The answer to each question is a NUMERICAL VALUE. For each question, enter the correct numerical value (in decimal notation, truncated/rounded-off to the second decimal place; e.g. 06.25, 07.00, –00.33, –00.30, 30.27, –27.30) using the mouse and the on-screen virtual numeric keypad in the place designated to enter the answer.
1. Let A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}. Define \(\begin{array}{l}B=\{T \subseteq A :\text{ either } 1 \notin T\ or\ 2 \in T\}\end{array} \)
and \(\begin{array}{l}C=\{T \subseteq A : T\text{ the sum of all the elements of } T \text{ is a prime number} \}\end{array} \)
. Then the number of elements in the set B ∪ C is ______.
Answer (107)
Sol. ∵ (B ∪ C)′ = B′ ∩ C′
B′ is a set containing sub sets of A containing element 1 and not containing 2.
And C′ is a set containing subsets of A whose sum of elements is not prime.
So, we need to calculate number of subsets of
{3, 4, 5, 6, 7} whose sum of elements plus 1 is composite.
Number of such 5 elements subset = 1
Number of such 4 elements subset = 3 (except selecting 3 or 7)
Number of such 3 elements subset = 6 (except selecting {3, 4, 5}, {3, 6, 7}, {4, 5, 7} or {5, 6, 7})
Number of such 2 elements subset = 7 (except selecting {3, 7}, {4, 6}, {5, 7})
Number of such 1 elements subset = 3 (except selecting {4} or {6})
Number of such 0 elements subset = 1
n(B′∩C′) = 21 ⇒ n(B∪C) = 27 – 21 = 107
2. Let f(x) be a quadratic polynomial with leading coefficient 1 such that f(0) = p, p ≠ 0, and f(1) = 1/3 . If the equations f(x) = 0 and fo fo fo f(x) = 0 have a common real root, then f(–3) is equal to ______.
Answer (25)
Sol. Let f(x) = (x – α) (x – β)
It is given that f(0) = p ⇒ αβ = p
and
\(\begin{array}{l}f(1)=\frac{1}{3}\Rightarrow (1-\alpha)(1-\beta)=\frac{1}{3}\end{array} \)
Now, let us assume that α is the common root of f(x) = 0 and fofofof(x) = 0
fofofof(x) = 0
⇒ fofof(0) = 0
⇒ fof(p) = 0
So, f(p) is either α or β.
(p – α) (p – β) = α
(αβ – α) (αβ – β) = α ⇒ (β – 1) (α – 1) β = 1
So, β = 3 (∵ α ≠ 0)
\(\begin{array}{l}(1-\alpha)(1-3)=\frac{1}{3}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\alpha=\frac{7}{6}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}f(x)=\left(x-\frac{7}{6}\right)(x-3)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}f(-3)=\left(-3-\frac{7}{6}\right)(3-3)=25\end{array} \)
3. Let \(\begin{array}{l}A = \begin{bmatrix}1&a&a\\0&1&b\\0&0&1\\\end{bmatrix},a,b \in \mathbb{R}\end{array} \)
. If for some \(\begin{array}{l}n\in N, A^n = \begin{bmatrix}1 & 48 & 2160 \\0 & 1 & 96 \\0 & 0 & 1 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
then n + a + b is equal to __________.
Answer (24)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}A=\begin{bmatrix} 1& 0 & 0 \\0 & 1 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 1 \\\end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix}0 & a & a \\0 & 0 & b \\0 & 0 & 0 \\\end{bmatrix} = I + B\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}B^2=\begin{bmatrix} 0& a & a \\0 & 0 & b \\0 & 0 & 0 \\\end{bmatrix}+\begin{bmatrix}0 & a & a \\0 & 0 & b \\0 & 0 & 0 \\\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} 0& 0 & ab \\0 & 0 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 0 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
B3 = 0
∴ An = (1 + B)n = nC0I + nC1 B + nC2 B2 + nC3 B3 + ….
\(\begin{array}{l}=\begin{bmatrix} 1& 0 & 0 \\0 & 1 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 1 \\\end{bmatrix}+\begin{bmatrix}0 & na & na \\0 & 0 & nb \\0 & 0 & 0 \\\end{bmatrix}+\begin{bmatrix} 0& 0 & \frac{n(n-1)ab}{2} \\0 & 0 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 0 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\begin{bmatrix} 1& na & na+\frac{n(n-1)}{2}ab \\0 & 1 & nb \\0 & 0 & 1 \\\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}1 & 48 & 2160 \\0 & 1 & 48 \\0 & 0 & 1 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
On comparing we get na = 48, nb = 96 and
\(\begin{array}{l}na+\frac{n(n-1)}{2}ab=2160\end{array} \)
⇒ a = 4, n = 12 and b = 8
n + a + b = 24
4. The sum of the maximum and minimum values of the function f(x) = |5x – 7| + [x2 + 2x] in the interval [5/4, 2], where [t] is the greatest integer ≤ t, is ____.
Answer (15)
Sol. f(x) = |5x – 7| + [x2 + 2x]
= |5x – 7| + [(x + 1)2] – 1
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Critical points of}\ f(x)=\frac{7}{5},\sqrt{5}-1, \sqrt{6}-1, \sqrt{7}-1, \sqrt{8}-1,2\end{array} \)
∴ Maximum or minimum value of f(x) occur at critical points or boundary points
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore f\left(\frac{5}{4}\right)=\frac{3}{4}+4=\frac{19}{4}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}f\left(\frac{7}{5}\right)=0+4=4\end{array} \)
as both |5x – 7| and x2 + 2x are increasing in nature after x = 7/5.
∴ f(2) = 3 + 8 = 11
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore f\left(\frac{7}{5}\right)_{\text{min}}=4 \text{ and }f(2)_{\text{max}}=11\end{array} \)
Sum is 4 + 11 = 15
5. Let y = y(x) be the solution of the differential equation \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{4y^3+2yx^2}{3xy^2+x^3},y(1)=1.\end{array} \)
If for some n ∈ N, y(2) ∈ [n – 1, n), then n is equal to _________.
Answer (3)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{y}{x}\frac{(4y^2+2x^2)}{(3y^2+x^2)}\end{array} \)
Put y = vx
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow \frac{dy}{dx}=v+x\frac{dv}{dx}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow v+x\frac{dv}{dx}=\frac{v(4v^2+2)}{(3v^2+1)}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow x\frac{dv}{dx}=v\left(\frac{(4v^2+2-3v^2-1)}{3v^2+1}\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow \int (3v^2+1)\frac{dv}{v^3+v}=\int\frac{dx}{x}\end{array} \)
⇒ ln|v3 +v| = lnx + c
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow \ln \left|\left(\frac{y}{x}\right)^3+\left(\frac{y}{x}\right)\right|=\ln x + C\end{array} \)
↓ y(1) = 1
⇒ C = ln2
∴ for y(2)
\(\begin{array}{l}\ln \left(\frac{y^3}{8}+\frac{y}{2}\right)=2\ln 2 \Rightarrow \frac{y^3}{8}+\frac{y}{2}=4\end{array} \)
⇒ [y(2)] = 2
⇒ n = 3
6. Let f be a twice differentiable function on R. If f’(0) = 4 and \(\begin{array}{l}f(x)+\int_{0}^{x}(x-1)f'(t)dt=(e^{2x}+e^{-2x})\cos 2x + \frac{2}{a}x,\end{array} \)
then (2a + 1)5 a2 is equal to ________________.
Answer (8)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\because f(x)+\int_{0}^{x}(x-t)f'(t)dt=(e^{2x}+e^{-2x})\cos 2x + \frac{2x}{a}~~~~~…(i)\end{array} \)
Here f(0) = 2 …(ii)
On differentiating equation (i) w.r.t. x we get :
\(\begin{array}{l}f'(x)+\int_{0}^{x}f'(t)dt+xf'(x)-xf'(x)\\=2(e^{2x}-e^{-2x}) \cos 2x – 2(e^{2x}+e^{-2x})\sin 2x + \frac{2}{a}\end{array} \)
⇒ f′(x) + f(x) – f(0) = 2(e2x – e–2x)cos2x – 2 (e2x + e–2x) sin 2x + (2/a)
Replace x by 0 we get :
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow 4 = \frac{2}{a} \Rightarrow a = \frac{1}{2}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore (2a+1)^5 \cdot a^2 = 2^5 \cdot \frac{1}{2^2}=2^3=8\end{array} \)
7. Let \(\begin{array}{l}a_n=\int_{-1}^{n}\left(1+\frac{x}{2}+\frac{x^2}{3}+…+ \frac{x^{n-1}}{n}\right)dx\end{array} \)
for every n ∈ N. Then the sum of all the elements of the set {n ∈ N : an ∈ (2, 30)} is ________________ .
Answer (5)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\because a_n=\int_{-1}^{n}\left(1+\frac{x}{2}+\frac{x^2}{3 }+ … + \frac{x^{n-1}}{n}\right)dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\left[x+\frac{x^2}{2^2}+\frac{x^3}{3^2}+…+\frac{x^n}{n^2}\right]_{-1}^{n}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}a_n = \frac{n+1}{1^2}+\frac{n^2-1}{2^2}+\frac{n^3+1}{3^2}+\frac{n^4-1}{4^2}+…+\frac{n^n+(-1)^{n+1}}{n^2}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Here } a_1 =2, a_2 =\frac{2+1}{1}+\frac{2^2-1}{2}=3+\frac{3}{2}=\frac{9}{2}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}a_3=4+2+\frac{28}{9}=\frac{100}{9}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}a_4 = 5 + \frac{15}{4}+\frac{65}{9}+\frac{255}{16}>31\end{array} \)
∴ The required set is {2, 3}. ∵ an ∈(2, 30)
∴ Sum of elements = 5.
8. If the circles x2 + y2 + 6x + 8y + 16 = 0 and \(\begin{array}{l}x^2 + y^2 + 2(3-\sqrt{3})x + 2(4-\sqrt{6})y=k+6\sqrt{3}+8\sqrt{6},k > 0,\end{array} \)
touch internally at the point P(α, β), then \(\begin{array}{l}(\alpha + \sqrt{3})^2+(\beta + \sqrt{6})^2\end{array} \)
is equal to ______.
Answer (25)
Sol. The circle x2 + y2 + 6x + 8y + 16 = 0 has centre
(–3, –4) and radius 3 units.
The circle
\(\begin{array}{l}x^2 + y^2 + 2(3-\sqrt{3})x + 2(4-\sqrt{6})y = k + 6\sqrt{3}+8\sqrt{6}, k> 0\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{has centre}\ (\sqrt{3}-3, \sqrt{6}-4)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{and radius}\ \sqrt{k+34}\end{array} \)
∵ These two circles touch internally hence
\(\begin{array}{l}\sqrt{3+6}=\left|\sqrt{k+34}-3\right|\end{array} \)
Here, k = 2 is only possible (∵ k > 0)
Equation of common tangent to two circles is
\(\begin{array}{l}2\sqrt{3}x + 2 \sqrt{6}y+16+6\sqrt{3}+8\sqrt{6}+k =0\end{array} \)
∵ k = 2 then equation is
\(\begin{array}{l}x+\sqrt{2}y+3+4\sqrt{2}+3\sqrt{3}=0~~~~~~…(i)\end{array} \)
∵ (α, β) are foot of perpendicular from (–3, –4) to line (i) then
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{\alpha + 3}{1}=\frac{\beta + 4}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{-(-3-4\sqrt{2}+3+4\sqrt{2}+3\sqrt{3})}{1+2}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore \alpha + 3 = \frac{\beta + 4}{\sqrt{2}}=-\sqrt{3}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow (\alpha + \sqrt{3})^2= 9 \text{ and }(\beta + \sqrt{6})^2 = 16\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore (\alpha + \sqrt{3})^2 + (\beta + \sqrt{6})^2=25\end{array} \)
9. Let the area enclosed by the x-axis, and the tangent and normal drawn to the curve 4x3 – 3xy2 + 6x2 – 5xy – 8y2 + 9x + 14 = 0 at the point (–2, 3) be A. Then 8A is equal to _______.
Answer (170)
Sol. 4x3 – 3xy2 + 6x2 – 5xy – 8y2 + 9x + 14 = 0 differentiating both sides we get
12x2 – 3y2 – 6xyy’ + 12x – 5y -5xy’ – 16yy’ + 9 = 0
\(\begin{array}{l}\downarrow(-2, 3)\end{array} \)
⇒ 48 – 27 + 36y’ – 24 – 15 + 10y’ – 48y’ + 9 = 0
⇒ 2y’ = – 9
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow m_T = \frac{-9}{2}\ \& \ m_N = \frac{2}{9}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore \text{ Area } = \frac{1}{2}\times \text{ Base } \times \text{ Hight}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}A=\frac{1}{2}\times\left(\frac{-4}{3}+\frac{31}{2}\right)(3)=\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{85}{6}\right)\cdot 3 = \frac{85}{4}\\= 8A = 170\end{array} \)
10. Let x = sin(2tan–1 α) and \(\begin{array}{l}y=\sin\left(\frac{1}{2}\tan^{-1}\frac{4}{3}\right).\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{If}\ S=\{\alpha \in \mathbb{R} : y^2 = 1 -x \},\ \text{then}\ \sum_{a\in S}16\alpha^3\end{array} \)
is equal to _______.
Answer (130)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\because x = \sin(2\tan^{-1}\alpha)=\frac{2\alpha}{1+\alpha^2}~~~~~…(i)\end{array} \)
and
\(\begin{array}{l}y=\sin\left(\frac{1}{2}\tan^{-1}\frac{4}{3}\right)=\sin\left(\sin^{-1}\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\right)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\end{array} \)
Now,
\(\begin{array}{l}y^2 = 1 – x\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{1}{5}=1-\frac{2\alpha}{1+\alpha^2}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow 1 + \alpha^2 = 5 + 5\alpha^2-10\alpha\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow2\alpha^2 – 5\alpha + 2 =0\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore \alpha = 2, \frac{1}{2}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore \sum_{a\in S}16\alpha^3 = 16 \times2^3 + 16 \times \frac{1}{2^3}\end{array} \)
= 130
JEE Main 2022 July 25th Shift 2 Paper Analysis














Comments