The JEE Main 2022 July 29 – Shift 2 Maths Question Paper with Solutions is given on this page. Students can assess their performance by referring to the JEE Main 2022 answer keys. We also provide the question paper analysis videos along with the JEE Main 2022 question paper with solutions. Students can also download the PDF of the JEE Main 2022 July 29 – Shift 2 Maths Question Paper with Solutions for free.
JEE Main 2022 29th July Shift 2 Mathematics Question Paper and Solutions
SECTION – A
Multiple Choice Questions: This section contains 20 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (1), (2), (3) and (4), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Choose the correct answer :
1. If z ≠ 0 be a complex number such that \(\begin{array}{l}\left|z-\frac{1}{z}\right|=2,\end{array} \)
then the maximum value of |z| is
(A) √2
(B) 1
(C) √2 – 1
(D) √2 + 1
Answer (D)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\left|z-\frac{1}{z}\right|\ge \left||z| – \frac{1}{z}\right|\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow \left||z| – \frac{1}{|z|}\right|\le 2\end{array} \)
Let |z| = r
\(\begin{array}{l}\left|r-\frac{1}{r}\right|\le 2\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}-2\le r-\frac{1}{r}\le 2\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}r-\frac{1}{r}\ge -2 \text{ and } r -\frac{1}{r}\le 2\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}r^2 + 2r – 1 \geq 0 ~\text{and} ~r^2 – 2r – 1 \le 0 \end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}r\in [-\infty , -1 – \sqrt{2}]\cup [-1+\sqrt{2}, \infty] \text{ and } r \in [1-\sqrt{2}, 1+ \sqrt{2}]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Taking intersection}\ r \in [\sqrt{2}-1, \sqrt{2}+1]\end{array} \)
2. Which of the following matrices can NOT be obtained from the matrix \(\begin{array}{l}\begin{bmatrix} -1& 2 \\1 & -1 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
by a single elementary row operation?
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{A})\ \begin{bmatrix} 0& 1 \\1 & -1 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{B})\ \begin{bmatrix} 1& -1 \\-1 & 2\\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C})\ \begin{bmatrix} -1& 2 \\-2 & 7\\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D})\ \begin{bmatrix} -1& 2 \\-1 & 3\\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
Answer (C)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}(1) \text{By } R_1 \rightarrow R_1 + R_2, \begin{bmatrix}0 & 1 \\1 & -1 \\\end{bmatrix} \text{ is possible}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(2) \text{By } R_1 \leftrightarrow R_2, \begin{bmatrix}1 & -1 \\-1 & 2 \\\end{bmatrix} \text{ is possible}\end{array} \)
(3) This matrix can’t be obtained
\(\begin{array}{l}(4) \text{By } R_2 \rightarrow R_2 +2R_1, \begin{bmatrix}-1 & 2 \\-1 & 3 \\\end{bmatrix} \text{ is possible}\end{array} \)
3. If the system of equations \(\begin{array}{l}x + y + z = 6\\ 2x + 5y + \alpha z = \beta\\ x + 2y + 3z = 14\end{array} \)
has infinitely many solutions, then α + β is equal to
(A) 8
(B) 36
(C) 44
(D) 48
Answer (C)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\Delta = \begin{vmatrix}1 & 1 & 1 \\2 & 5 & \alpha \\1 & 2 & 3 \\\end{vmatrix} = 1(15-2\alpha) – 1 (6-\alpha)+1(-1)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}= 15 – 2\alpha – 6 + \alpha -1\\ = 8 – \alpha\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{For infinite solutions,~} \Delta = 0 \Rightarrow \alpha = 8\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Delta_x = \begin{vmatrix}6 & 1 & 1 \\\beta & 5 & 8 \\14 & 2 & 3 \\\end{vmatrix} = 6(-1)-1(3\beta – 112)+1(2\beta -70)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}= -6 – 3\beta + 112 + 2\beta – 70\\ = 36 – \beta\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Delta_x = 0 \Rightarrow for ~\beta = 36\\ \alpha + \beta = 44\end{array} \)
4. Let the function \(\begin{array}{l}f(x)= \left\{\begin{matrix}\frac{\log_e(1+5x)-\log_e(1+\alpha x)}{x} &; \text{if } x\in0 \\10 & ; \text{if } x=0 \\\end{matrix}\right.\end{array} \)
be continuous at x = 0. Then α is equal to
(A) 10
(B) –10
(C) 5
(D) –5
Answer (D)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\underset{x \to 0}{\text{It}}\frac{\ln(1+5x)-\ln(1+\alpha x)}{x}\\= 5 – \alpha = 10\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow \alpha = -5\end{array} \)
5. If [t] denotes the greatest integer ≤ t, then the value of \(\begin{array}{l}\int_{0}^{1}[2x-|3x^2 -5x + 2| + 1]dx \end{array} \)
is
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{A})\ \frac{\sqrt{37} + \sqrt{13}-4}{6}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{B})\ \frac{\sqrt{37} – \sqrt{13}-4}{6}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C})\ \frac{-\sqrt{37} – \sqrt{13}+4}{6}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D})\ \frac{-\sqrt{37} + \sqrt{13}+4}{6}\end{array} \)
Answer (A)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}I = \int_{0}^{1}[2x-|3x^2 – 5x + 2 |+1]dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}I = \int_{0}^{2/3} \left[ \underset{I_1}{\underbrace{-3x^2 + 7x -2}} \right]dx + \int_{2/3}^{1}\left[\underset{I_2}{\underbrace{3x^2-3x+2}} \right]dx + 1\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}I_1 = \int_{0}^{t_1}(-2)dx + \int_{t_1}^{1/3}(-1)dx + \int_{1/3}^{t_2}0.dx + \int_{t_2}^{2/3}dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=-t_1 – t_2 + \frac{1}{3}, \text{ where } t_1 = \frac{7-\sqrt{37}}{6}, t_2 = \frac{7-\sqrt{13}}{6}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}I_2=\int_{2/3}^{1}1dx =\frac{1}{3}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore I = \frac{1}{3}-t_1 -t_2 + \frac{1}{3} + 1 = \frac{5}{3}-\left[\frac{7-\sqrt{37}}{6}+ \frac{7-\sqrt{13}}{6}\right]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{\sqrt{37}+\sqrt{13}-4}{6}\end{array} \)
6. Let \(\begin{array}{l}\{a_n\}_{n=0}^\infty\ \text{be a sequence such that}\ a_0 = a_1 = 0\ \text{and}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}a_{n+2}=3a_{n+1}-2a_{n} + 1, \forall \ n \ge 0.\ \text{Then}\ a_{25}a_{23}-2a_{25}a_{22}-2a_{23}a_{24}+4a_{22}a_{24}\end{array} \)
is equal to
(A) 483
(B) 528
(C) 575
(D) 624
Answer (B)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}a_{n+2}=3a_{n+1}-2a_n+1, \forall \ n \ge 0 (a_0 = a_1 = 0)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(a_{n+2}-a_{n+1}\right)-2\left(a_{n+1}-a_n\right)-1 = 0\end{array} \)
Put n = 0
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(a_2-a_1\right)-2\left(a_1-a_0\right)-1=0\end{array} \)
n = 1
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(a_3-a_2\right)-2\left(a_2-a_1\right)-1=0\end{array} \)
n = 2
\(\begin{array}{l} \left(a_4-a_3\right)-2\left(a_3-a_2\right)-1=0\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\vdots \\n = n \end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(a_{n+2 } – a_{n+1}\right)-2\left(a_{a+1}-a_n\right)-1=0\end{array} \)
Adding,
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(a_{n+2 } – a_{1}\right)-2\left(a_{a+1}-a_0\right)-\left(n+1\right)=0\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore a_{n+2}-2a_{n+1}-\left(n+1\right)=0\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}n \rightarrow n – 2\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}a_n – 2a_{n-1}-n+1=0\end{array} \)
Now,
\(\begin{array}{l}a_{25}a_{23}-2a_{25}a_{22}-2a_{23}a_{24}+4a_{22}a_{24}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=a_{25}\left(a_{23}-2a_{22}\right)-2a_{24}\left(a_{23}-2a_{22}\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\left(a_{25}-2a_{24}\right)\left(a_{23}-2a_{22}\right) = 24 \cdot 22 = 528\end{array} \)
7. \(\begin{array}{l}\sum_{r=1}^{20}(r^2+1)(r!)\end{array} \)
is equal to
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(A\right) 22! – 21!\\ \left(B\right) 22! – 2(21!)\\ \left(C\right) 21! – 2(20!)\\ \left(D\right) 21! – 20!\end{array} \)
Answer (B)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\sum_{r=1}^{20}\left(r^2+1+2r-2r\right)r! = \sum_{r=1}^{20}\left((r+1)^2-2r\right)r!\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\sum_{r=1}^{20}\left[(r+1)(r+1)! -rr!\right]-\sum_{r=1}(r+1)r!=r!\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=(2\cdot 2! – 1!)+(3\cdot 3! – 2\cdot 2!)+…+ (21\cdot21! – 20\cdot 20!) -\left[(2!-1!)+(3! -2!)+…+(21!-20!)\right]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=(21\cdot 21! – 1)-(21! -1)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=20 \cdot 21! = (22-2)21! = 22! – 2(21!)\end{array} \)
8. For \(\begin{array}{l}I(x)=\int\frac{\sec^2 x – 2022}{\sin^{2022}x} dx,\ \text{if}\ I\left(\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=2^{1011},\end{array} \)
then
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{A}) \ 3^{1010}I\left(\frac{\pi}{3}\right)-I\left(\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=0\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{B}) \ 3^{1010}I\left(\frac{\pi}{6}\right)-I\left(\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=0\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C}) \ 3^{1011}I\left(\frac{\pi}{3}\right)-I\left(\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=0\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C}) \ 3^{1011}I\left(\frac{\pi}{6}\right)-I\left(\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=0\end{array} \)
Answer (A)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}I(x)=\int\frac{\sec^2x – 2022}{\sin^{2022}x}dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\int \left(\sec^2x \cdot \sin^{-2022}x – 2022\sin^{-2022}x\right)dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\sin^{-2022}x \tan x + \int 2022\sin^{-2023}x \cos x \cdot \tan x \ dx – \int2022 \sin^{-2022}x \ dx + c\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}I(x)=\sin^{-2022}x \tan x + c\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\because I\left(\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=2^{1011}\Rightarrow c = 2^{1011}-2^{1011}=0\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore I\left(\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=\left(\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}\right)^{2022}\sqrt{3},I\left(\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=2^{2022}\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{So, option (A)} : \frac{3^{1010}2^{2022}}{3^{1011}}\cdot \sqrt{3}-\frac{2^{2022}}{\sqrt{3}}=0\end{array} \)
∴ Option (A) is correct
9. if the solution curve of the differential equation \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{x+y-2}{x-y} \end{array} \)
passes through the points (2, 1) and (k + 1, 2), k > 0, then
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{A})\ 2\tan^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{k}\right)=\log_e(k^2+1)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{B})\ \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{k}\right)=\log_e(k^2+1)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C})\ 2\tan^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{k+1}\right)=\log_e(k^2+2k +2)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D})\ 2\tan^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{k}\right)=\log_e\left(\frac{k^2+1}{k^2}\right)\end{array} \)
Answer (A)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{x+y-2}{x-y}=\frac{(x-1)+(y-1)}{(x-1)-(y-1)}\end{array} \)
Let x – 1 = X, y – 1 = Y
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{dY}{dX}=\frac{X+Y}{X-Y}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Let } Y = tX \Rightarrow \frac{dY}{dX}=t + X\frac{dt}{dX}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}t+X\frac{dt}{dX}=\frac{1+t}{1-t}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}X\frac{dt}{dX}=\frac{1+t}{1-t}-t=\frac{1+t^2}{1-t}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\int\frac{1-t}{1+t^2}dt = \int \frac{dX}{X}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\tan^{-1}t -\frac{1}{2}\ln (1+t^2)=\ln |X|+c\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\tan^{-1}\left(\frac{y-1}{x-1}\right)-\frac{1}{2}\ln \left(1+\left(\frac{y-1}{x-1}\right)^2\right)=\ln|x-1|+c\end{array} \)
Curve passes through (2, 1)
\(\begin{array}{l}0 – 0 = 0 + c \Rightarrow c = 0\end{array} \)
If (k + 1, 2) also satisfies the curve
\(\begin{array}{l}\tan^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{k}\right)-\frac{1}{2}\ln \left(\frac{1+k^2}{k^2}\right)=\ln k\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}2\tan^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{k}\right)=\ln(1+k^2)\end{array} \)
10. Let y = y(x) be the solution curve of the differential equation \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{dy}{dx}+\left(\frac{2x^2+11x+13}{x^3+6x^2+11x+6}\right)y = \frac{(x+3)}{x+1}, x > -1\end{array} \)
which passes through the point (0, 1). Then y(1) is equal to
(A) 1/2
(B) 3/2
(C) 5/2
(D) 7/2
Answer (B)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{dy}{dx}+\left(\frac{2x^2+11x+13}{x^3+6x^2+11x+6}\right)y = \frac{(x+3)}{x+1}, x > -1\end{array} \)
Integrating factor I.F
\(\begin{array}{l}=e^{\int \frac{2x^2 + 11x + 13}{x^3 + 6x^2 + 11 x + 6}dx}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Let } \frac{2x^2 + 11x + 13}{(x+1)(x+2)(x+3)}=\frac{A}{x+1}+\frac{B}{x+2}+\frac{C}{x+3}\end{array} \)
A = 2, B = 1, C = –1
\(\begin{array}{l}I.F. = e^{(2\ln|x+1|+\ln|x+2|-\ln|x+3|)}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{(x+1)^2(x+2)}{x+3}\end{array} \)
Solution of differential equation
\(\begin{array}{l}y\cdot\frac{(x+1)^2(x+2)}{x+3} = \int (x+1)(x+2)dx\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}y\cdot\frac{(x+1)^2(x+2)}{x+3} = \frac{x^3}{3}+\frac{3x^2}{2}+2x+c\end{array} \)
Curve passes through (0, 1)
\(\begin{array}{l}1\times \frac{1\times 2}{3}=0+c \Rightarrow c = \frac{2}{3}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{So, }y(1)=\frac{\frac{1}{3} + \frac{3}{2} + 2 + \frac{2}{3} }{\frac{(2^2 \times 3)}{4}} = \frac{3}{2}\end{array} \)
11. Let m1, m2 be the slopes of two adjacent sides of a square of side a such that \(\begin{array}{l}a^2 + 11a + 3(m_1^2 + m_2^2) = 220. \end{array} \)
If one vertex of the square is \(\begin{array}{l}\left(10\left(cos~\alpha – sin~\alpha\right),10\left(sin~\alpha + cos~ \alpha\right)\right),\ \text{where}\ \alpha \in \left(0, \frac{\pi}{2}\right)\end{array} \)
and the equation of one diagonal is \(\begin{array}{l}(\cos \alpha – \sin \alpha)x + (\sin \alpha + \cos \alpha)y = 10,\ \text{then}\ 72(\sin^4 \alpha + \cos^4 \alpha) + a^2 -3a + 13 \end{array} \)
is equal to :
(A) 119
(B) 128
(C) 145
(D) 155
Answer (B)
Sol. One vertex of square is
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(10\left(cos\alpha – sin\alpha\right), 10\left(sin\alpha + cos\alpha\right)\right) \end{array} \)
and one of the diagonal is
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(cos\alpha – sin\alpha\right) x + \left(sin\alpha + cos\alpha\right)y = 10\end{array} \)
So the other diagonal can be obtained as
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(cos\alpha + sin\alpha\right)x – \left(cos\alpha – sin\alpha\right)y = 0\end{array} \)
So, point of intersection of diagonal will be
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(5\left(cos\alpha – sin\alpha\right), 5\left(cos\alpha + sin\alpha\right)\right).\end{array} \)
Therefore, the vertex opposite to the given vertex is (0, 0).
So, the diagonal length
\(\begin{array}{l}=10\sqrt{2}\end{array} \)
Side length (a) = 10
It is given that
\(\begin{array}{l}a^2+11a+3\left(m_1^2 + m_2^2\right) = 220\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}m_1^2 + m_2^2 = \frac{220 – 100 -110}{3} = \frac{10}{3}\end{array} \)
and m1 m2 = – 1
Slopes of the sides are tanα and – cotα
\(\begin{array}{l}\tan^2 \alpha = 3 \text{ or } \frac{1}{3}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}72\left(sin^4\alpha + cos^4\alpha\right) + a^2 – 3a + 13 \end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=72 \cdot \frac{\tan^4 \alpha + 1}{(1+\tan^2 \alpha)^2} + a^2 -3a + 13 =128\end{array} \)
12. The number of elements in the set
\(\begin{array}{l}S=\left\{x \in \mathbb{R} : 2\cos \left(\frac{x^2 + x}{6}\right)=4^x + 4^{-x}\right\}\end{array} \)
(A) 1
(B) 3
(C) 0
(D) infinite
Answer (A)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}S=\left\{x \in \mathbb{R} : 2\cos \left(\frac{x^2 + x}{6}\right)=4^x + 4^{-x}\right\}\end{array} \)
LHS is less than or equal to 2 and RHS is greater than or equal to 2.
So equality holds only if LHS = RHS = 2
RHS is 2 when x = 0
and at x = 0, LHS is also 2.
So, only one solution exist.
13. Let A(α, -2), B(α, 6) and C(α/4, -2) be vertices of a ΔABC. If (5, α/4) is the circumcentre of ΔABC, then which of the following is NOT correct about ΔABC?
(A) Area is 24
(B) Perimeter is 25
(C) Circumradius is 5
(D) Inradius is 2
Answer (B)
Sol.
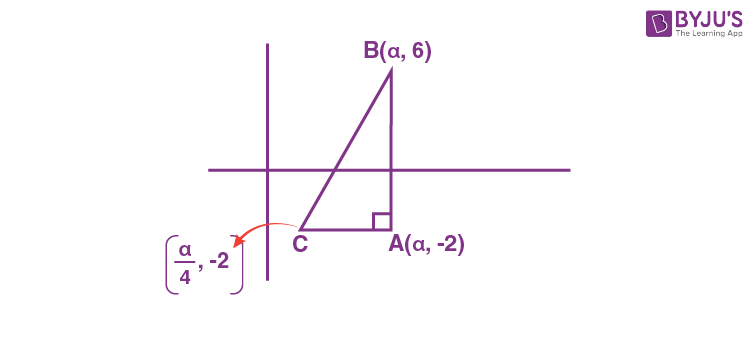
Circumcentre of ΔABC
\(\begin{array}{l}=\left(\frac{\alpha + \frac{\alpha}{4}}{2}, \frac{6-2}{2}\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\left(\frac{5\alpha}{8},2\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\left(5, \frac{\alpha}{4}\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow \alpha = 8\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}area(\Delta ABC)=\frac{1}{2}\cdot \frac{3\alpha}{4}\times 8 = 24~ \text{sq. units}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Perimeter } = 8 + \frac{3\alpha}{4}+\sqrt{8^2 + \left(\frac{3\alpha}{4}\right)^2}\\=8+6+10=24\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Circumradius} = \frac{10}{2}=5\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}r=\frac{\Delta}{s}=\frac{24}{12}=2\end{array} \)
14. Let Q be the foot of perpendicular drawn from the point P(1, 2, 3) to the plane x + 2y + z = 14. If R is a point on the plane such that ∠PRQ = 60°, then the area of ΔPQR is equal to :
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{A})\ \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{B})\ \sqrt{3}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C})\ 2\sqrt{3}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D}) 3\end{array} \)
Answer (B)
Sol.
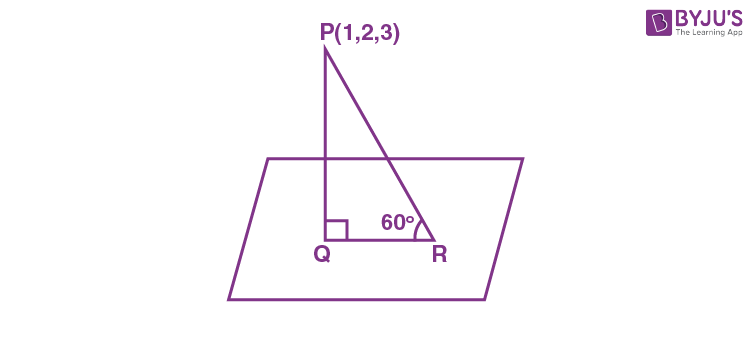
\(\begin{array}{l}PQ = \left|\frac{1+4+3-14}{\sqrt{6}}\right|=\sqrt{6}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}QR = \frac{PQ}{\tan 60^{\circ}} = \frac{\sqrt{6}}{\sqrt{3}}=\sqrt{2}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Area}(\Delta PQR) = \frac{1}{2}\cdot PQ \cdot QR = \sqrt{3}\end{array} \)
15. If (2, 3, 9), (5, 2, 1), (1, λ, 8) and (λ, 2, 3) are coplanar, then the product of all possible values of λ is :
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{A})\ \frac{21}{2}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{B})\ \frac{59}{8}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C})\ \frac{57}{8}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D})\ \frac{95}{8}\end{array} \)
Answer (D)
Sol. ∵ (2, 3, 9), (5, 2, 1), (1, λ, 8) and (λ, 2, 3) are coplanar.
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore \begin{vmatrix}\lambda – 2 & -1 & -6 \\-1 & \lambda-3 & -1 \\3 & -1 & -8 \\\end{vmatrix} =0\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore 8\lambda^2 – 67\lambda + 95 = 0\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore\text{Product of all values of }\lambda = \frac{95}{8}\end{array} \)
16. Bag I contains 3 red, 4 black and 3 white balls and Bag II contains 2 red, 5 black and 2 white balls. One ball is transferred from Bag I to Bag II and then a ball is drawn from Bag II. The ball so drawn is found to be black in colour. Then the probability, that the transferred ball is red, is :
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{A})\ \frac{4}{9}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{B})\ \frac{5}{18}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C})\ \frac{1}{6}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D})\ \frac{3}{10}\end{array} \)
Answer (B)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l} \text{Let} E \rightarrow \text{Ball drawn from Bag II is black.} \\ E_R \rightarrow \text{Bag I to Bag II red ball transferred.}\\ E_B \rightarrow \text{Bag I to Bag II black ball transferred.}\\ E_W \rightarrow \text{Bag I to Bag II white ball transferred.}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}P\left(E_R/E\right) =\frac{P(E/E_R)\cdot P(E_R)}{P(E/E_R)P(E_R) + P(E/E_B)\cdot P(E_B) + P(E/E_W)P(E_W)}\end{array} \)
Here,
\(\begin{array}{l}P(E_R)=\frac{3}{10},\ \ P(E_B)=\frac{4}{10}, \ \ P(E_W)=\frac{3}{10}\end{array} \)
and
\(\begin{array}{l}P\left(\dfrac{E}{E_R}\right)=\frac{5}{10}, P\left(\dfrac{E}{E_B}\right)=\frac{6}{10}, P\left(\dfrac{E}{E_W}\right)=\frac{5}{10}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore P\left(\dfrac{E_R}{E}\right)= \frac{\frac{15}{100}}{\frac{15}{100} + \frac{24}{100} + \frac{15}{100}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{15}{54}=\frac{5}{18}\end{array} \)
17. Let \(\begin{array}{l}S = \{z = x + iy : \left|z – 1 + i\right| \geq \left|z\right|, \left|z\right| < 2, \left|z + i\right| = \left|z – 1\right|\}.\end{array} \)
Then the set of all values of x, for which w = 2x + iy ∈ S for some y ∈ R is
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{A})\ \left(-\sqrt{2}, \frac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}\right]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{B})\ \left(-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}, \frac{1}{4}\right]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C})\ \left(-\sqrt{2}, \frac{1}{2}\right]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D})\ \left(-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}, \frac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}\right]\end{array} \)
Answer (B)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}S : \{z = x + iy : \left|z – 1 + i\right| \geq \left|z\right|, \left|z\right| < 2, \left|z – i\right| = \left|z – 1\right|\} \left|z – 1 + i\right| \geq \left|z\right| \end{array} \)
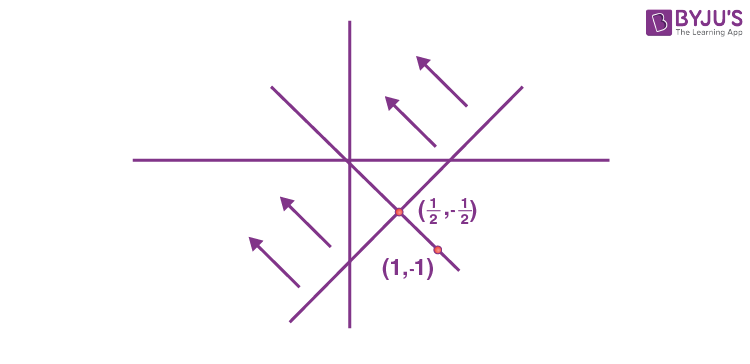
|z| < 2
\(\begin{array}{l}\left|z – i\right| = \left|z – 1\right|\end{array} \)
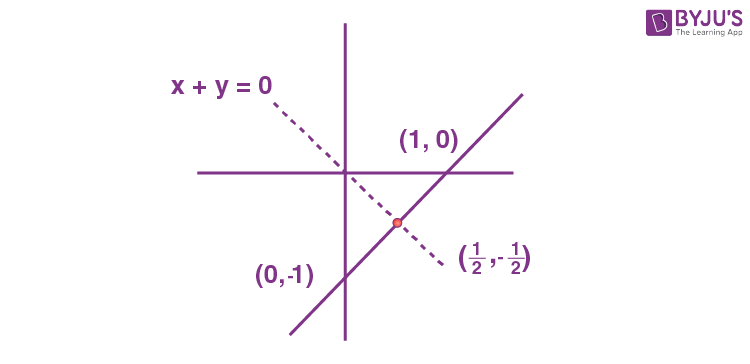
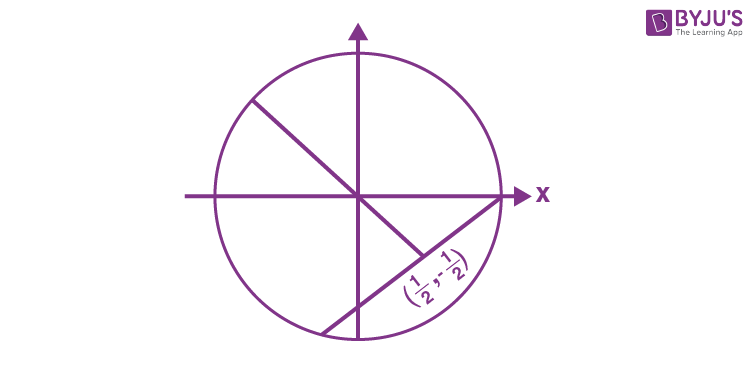
\(\begin{array}{l}\because w \in S ~\text{and} ~w = 2x + iy\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}2x< \frac{1}{2}\ \ \ \therefore x < \frac{1}{4}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(2x)^2 + (-2x)^2 < 4\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}4x^2 + 4x^2 < 4\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}x^2 < \frac{1}{2}\Rightarrow x \in \left(-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}, \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore x \in \left(-\frac{1}{2},\frac{1}{4}\right]\end{array} \)
18. Let \(\begin{array}{l}\vec{a},\vec{b},\vec{c} \end{array} \)
be three coplanar concurrent vectors such that angles between any two of them is same. If the product of their magnitudes is 14 and \(\begin{array}{l}(\vec{a}\times \vec{b}) \cdot (\vec{b} \times \vec{c}) + (\vec{b} \times \vec{c})\cdot (\vec{c} \times \vec{a}) + (\vec{c} \times \vec{a})\cdot (\vec{a} \times \vec{b}) = 168,\ \text{then}\ |\vec{a}| + |\vec{b}| + |\vec{c}|\end{array} \)
is equal to :
(A) 10
(B) 14
(C) 16
(D) 18
Answer (C)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}|\vec{a}| |\vec{b}| |\vec{c}| = 14\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\vec{a} \wedge \vec{b} = \vec{b} \wedge \vec{c} = \vec{c} \wedge \vec{a} = \theta = \frac{2\pi}{3}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b} = -\frac{1}{2}|\vec{a}||\vec{b}|\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\vec{b} \cdot \vec{c} = -\frac{1}{2}|\vec{b}||\vec{c}|\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\vec{c} \cdot \vec{a} = -\frac{1}{2}|\vec{c}||\vec{a}|\end{array} \)
Now,
\(\begin{array}{l}(\vec{a}\times\vec{b}) \cdot (\vec{b} \times \vec{c}) + (\vec{b} \times \vec{c})\cdot(\vec{c} \times \vec{a}) + (\vec{c} \times \vec{a})\cdot (\vec{a} \times\vec{b}) = 168\ \ \ …(i)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\vec{a}\times \vec{b}) \cdot (\vec{b} \times \vec{c}) = (\vec{a}\cdot \vec{b}) (\vec{b} \cdot \vec{c}) – (\vec{a} \cdot \vec{c})|\vec{b}|^2\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{1}{4}|\vec{b}|^2|\vec{a}||\vec{c}| + \frac{1}{2}|\vec{a}||\vec{b}|^2|\vec{c}|\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=\frac{3}{4}|\vec{a}||\vec{b}|^2|\vec{c}|\ \ \ …(ii)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Similarly } (\vec{b} \times \vec{c})\cdot (\vec{c} \times \vec{a}) = \frac{3}{4}|\vec{a}||\vec{b}||\vec{c}|^2\ \ \ …(iii)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\vec{c} \times \vec{a}) \cdot (\vec{a}\times \vec{b}) = \frac{3}{4}|\vec{a}|^2 |\vec{b}||\vec{c}|\ \ \ …(iv)\end{array} \)
Substitute (ii), (iii), (iv) in (i)
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{3}{4}|\vec{a}||\vec{b}||\vec{c}|\left[|\vec{a}|+|\vec{b}|+|\vec{c}|\right] = 168\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{3}{4}\times 14\left[|\vec{a}|+|\vec{b}|+|\vec{c}|\right] = 168\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}|\vec{a}|+|\vec{b}|+|\vec{c}|= 16\end{array} \)
19. The domain of the function \(\begin{array}{l}f(x)=\sin^{-1}\left(\frac{x^2-3x+2}{x^2+2x+7}\right)\end{array} \)
is :
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(A\right) \left[1, \infty\right)\\ \left(B\right) \left[-1, 2\right]\\ \left(C\right) \left[-1, \infty\right)\\ \left(D\right) \left(-\infty , 2\right]\end{array} \)
Answer (C)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}f(x)=\sin^{-1}\left(\frac{x^2-3x+2}{x^2+2x+7}\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}-1\le \frac{x^2-3x+2}{x^2+2x+7}\le 1\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{x^2-3x+2}{x^2+2x+7}\le 1\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}x^2-3x+2 \le x^2+2x+7\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}5x \ge -5\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}x\ge -1\ \ \ …(i)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{x^2-3x+2}{x^2 +2x +7}\ge -1\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}x^2-3x+2\ge -x^2 -2x -7\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}2x^2- x + 9 \ge 0\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}x \in R\ \ \ \ …(ii) \end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(i\right)\cap \left(ii\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Domain} \in \left[-1, \infty\right) \end{array} \)
20. The statement \(\begin{array}{l}\left(p \Rightarrow q\right) \vee \left(p \Rightarrow r\right)\end{array} \)
is NOT equivalent to
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{A})\ (p \wedge (\sim r))\Rightarrow q\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{B})\ (\sim q)\Rightarrow ((\sim r)\vee p)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{C})\ p\Rightarrow (q\vee r)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}(\text{D})\ (p\wedge (\sim q))\Rightarrow r\end{array} \)
Answer (B)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(A\right) \left(p \wedge \left(\sim r\right)\right) \Rightarrow q\\ \sim \left(p \wedge \sim r\right) \vee q\\ \equiv \left(\sim p \vee r\right) \vee q \\ \equiv \sim p \vee \left(r \vee q\right)\\ \equiv p \rightarrow \left(q \vee r\right)\\ \equiv \left(p \Rightarrow q\right) \vee \left(p \Rightarrow r\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(C\right) p \Rightarrow \left(q \vee r\right)\\ \equiv \sim p \vee \left(q \vee r\right)\\ \equiv \left(\sim p \vee q\right) \vee \left(\sim p \vee r\right)\\ \equiv \left(p \rightarrow q\right) \vee \left(p \rightarrow r\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(D\right) \left(p \wedge \sim q\right) \Rightarrow r\\ \equiv p \Rightarrow \left(q \vee r\right)\\ \equiv \left(p \Rightarrow q\right) \vee \left(p \Rightarrow r\right) \end{array} \)
SECTION – B
Numerical Value Type Questions: This section contains 10 questions. In Section B, attempt any five questions out of 10. The answer to each question is a NUMERICAL VALUE. For each question, enter the correct numerical value (in decimal notation, truncated/rounded-off to the second decimal place; e.g. 06.25, 07.00, –00.33, –00.30, 30.27, –27.30) using the mouse and the on-screen virtual numeric keypad in the place designated to enter the answer.
1. The sum and product of the mean and variance of a binomial distribution are 82.5 and 1350 respectively. Then the number of trials in the binomial distribution is _______.
Answer (96)
Sol. Given np + npq = 82.5 … (1)
and np (npq) = 1350 … (2)
∴ Mean and Vairance be the roots of x2 – 82.5x + 1350 = 0
⇒ x2 – 22.5 x – 60x + 1350 = 0
⇒ x – (x – 22.5) – 60 (x – 22.5) = 0
Mean = 60 and Variance = 22.5
np = 60, npq = 22.5
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow q = \frac{9}{24}=\frac{3}{8}, p = \frac{5}{8}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore n\frac{5}{8}=60\\\Rightarrow n =96\end{array} \)
2. Let α, β(α > β) be the roots of the quadratic equation x2 – x – 4 = 0. \(\begin{array}{l}\text{If}\ P_n = \alpha^n – \beta^n, n \in \mathbb{N}\ \text{then}\ \frac{P_{15}P_{16} – P_{14}P_{16} – P_{15}^2 + P_{14}P_{15}}{P_{13}P_{14}}\end{array} \)
is equal to _______.
Answer (16)
Sol.
α, β are the roots of x2 – x – 4 = 0 and
\(\begin{array}{l}P_n = \alpha^n – \beta^n, \end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore I = \frac{(P_{15}-P_{14})P_{16}-P_{15}(P_{15}-P_{14})}{P_{13}P_{14}} = \frac{(P_{16}-P_{15})(P_{15}-P_{14})}{P_{13}P_{14}}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow I = \frac{(\alpha^{16} – \beta^{16} – \alpha ^{15} + \beta^{15})(\alpha^{15} – \beta^{15} – \alpha ^{14} + \beta^{14})}{(\alpha^{13} – \beta^{13})(\alpha^{14} – \beta^{14})}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow I = \frac{(\alpha^{15}(\alpha – 1)-\beta^{15}(\beta -1))(\alpha^{14}(\alpha-1)-\beta^{14} (\beta-1))}{(\alpha^{13}-\beta^{13})(\alpha^{14}-\beta^{14})}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{As } \alpha^2 – \alpha = 4 \Rightarrow \alpha -1 = \frac{4}{\alpha} \text{ and } \beta -1 = \frac{4}{\beta}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow I = \frac{\left(\alpha^{15}\cdot \frac{4}{\alpha} – \beta^{15}\cdot \frac{4}{\beta}\right)\left(\alpha^{14}\cdot \frac{4}{\alpha} – \beta^{14}\cdot \frac{4}{\beta}\right)}{(\alpha^{13}-\beta^{13})(\alpha^{14}-\beta^{14})}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}= \frac{16(\alpha^{14}-\beta^{14})(\alpha^{13}-\beta^{13})}{(\alpha^{14}-\beta^{14})(\alpha^{13}-\beta^{13})} = 16\end{array} \)
3. Let \(\begin{array}{l}x=\begin{bmatrix}1 \\ 1\\1\end{bmatrix} and\ A = \begin{bmatrix}-1 & 2 & 3 \\0 & 1 & 6 \\0 & 0 & -1 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
For k ∈ N, if X’AkX = 33, then k is equal to _______.
Answer (10*)
Sol. Given
\(\begin{array}{l}A=\begin{bmatrix}-1 & 2 & 3 \\0 & 1 & 6 \\0 & 0 & -1 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}A^2=\begin{bmatrix}1 & 0 & 6 \\0 & 1 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 1 \\\end{bmatrix}, A^4 = \begin{bmatrix}1 & 0 & 12 \\0 & 1 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 1 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow A^k=\begin{bmatrix}1 & 0 & 3k \\0 & 1 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 1 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore X’A^kX=\begin{bmatrix}1 & 1 & 1 \\\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}1 & 0 & 3k \\0 & 1 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 1 \\\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}1 \\1 \\1\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}3k + 3\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
⇒ [3k + 3] = 33 (here it shall be [33] as matrix can’t be equal to a scalar)
i.e. [3k + 3] = 33
3k + 3 = [33] ⇒ k = 10
If k is odd and apply above process, we don’t get odd value of k
∴ k = 10
4. The number of natural numbers lying between 1012 and 23421 that can be formed using the digits 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 (repetition of digits is not allowed) and divisible by 55 is _______.
Answer (6)
Sol. Case-I When number is 4-digit number
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(\overline {a\ b\ c\ d}\right)\end{array} \)
here d is fixed as 5
So, (a, b, c) can be (6, 4, 3), (3, 4, 6), (2, 3, 6),
(6, 3, 2), (3, 2, 4) or (4, 2, 3)
⇒ 6 numbers
Case-II No number possible
5. If \(\begin{array}{l}\sum_{K=1}^{10}K^2\left(^{10}C_K\right)^2 = 22000L,\end{array} \)
then L is equal to _____.
Answer (221)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\sum_{K=1}^{10}K^2\left(^{10}C_K\right)^2 =1^2\ ^{10}C_1^2 + 2^2\ ^{10}C_2^2 + … + 10^2\ ^{10}C_{10}\end{array} \)
Let
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(1 + x\right)^{10} = ^{10}C_0 + ^{10}C_1 x + ^{10}C_2 x^2 + ….+ ^{10}C_{10} x^{10} \end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\Rightarrow 10\left(1 + x\right)^9 = ^{10}C_1 + 2\cdot ^{10}C_2 x +… + 10\cdot ^{10}C_{10} x^9 …\left(1\right)\end{array} \)
Similarly,
\(\begin{array}{l}10\left(x + 1\right)^9 = 10\cdot ^{10}C_0 x^9 + 9\cdot ^{10}C_1 x^8 + … + 1\cdot ^{10}C_9\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}100\left(1+ x\right)^{18}\text{has required term with coefficient of} ~x^9 \end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}i.e. ^{18}C_9 100 = 22000 L\\ \Rightarrow L = 221\end{array} \)
6. If [t] denotes the greatest integer ≤ t, then the number of points, at which the function \(\begin{array}{l}f(x)=4|2x+3|+9\left[x+\frac{1}{2}\right]-12[x+20]\end{array} \)
is not differentiable in the open interval (–20, 20), is ________.
Answer (79)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}f(x)=4|2x+3|+9\left[x+\frac{1}{2}\right]-12[x+20]\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}=4|2x+3|+9\left[x+\frac{1}{2}\right]-12[x]-240\end{array} \)
f(x) is non differentiable at x = -3/2
and f(x) is discontinuous at {–19, –18, ….., 18, 19}
as well as
\(\begin{array}{l}\left\{-\frac{39}{2}, -\frac{37}{2},…,-\frac{3}{2},-\frac{1}{2},\frac{1}{2},…,\frac{39}{2}\right\}\end{array} \)
,
at same point they are also non differentiable
∴ Total number of points of non differentiability
= 39 + 40
= 79
7. If the tangent to the curve y = x3 – x2 + x at the point (a, b) is also tangent to the curve y = 5x2 + 2x – 25 at the point (2, –1), then |2a + 9b| is equal to ________.
Answer (195)
Sol. Slope of tangent to curve y = 5x2 + 2x – 25
\(\begin{array}{l}=m=\left(\frac{dy}{dx}\right)_{\text{at}(2,-1)} = 22\end{array} \)
∴ Equation of tangent: y + 1 = 22(x – 2)
∴ y = 22x – 45
Slope of tangent to y = x3 – x2 + x at point (a, b) = 3a2 – 2a + 1
3a2 – 2a + 1 = 22
3a2 – 2a – 21 = 0
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore a = 3 \text{ or } -\frac{7}{3}\end{array} \)
Also b = a3 – a2 + a
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Then} \left(a, b\right) = \left(3, 21\right) or \left(-\frac{7}{3}, – \frac{151}{9}\right)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\left(-\frac{7}{3}, – \frac{151}{9}\right)\ \text{does not satisfy the equation of tangent}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore a = 3, b = 21\\ \therefore \left|2a + 9b\right| = 195\end{array} \)
8. Let AB be a chord of length 12 of the circle \(\begin{array}{l}(x-2)^2 + (y+1)^2=\frac{169}{4}.\end{array} \)
If tangents drawn to the circle at points A and B intersect at the point P, then five times the distance of point P from chord AB is equal to _______.
Answer (72)
Sol. Here AM = BM = 6
\(\begin{array}{l}OM = \sqrt{\left(\frac{13}{2}\right)^2-6^2}=\frac{5}{2}\end{array} \)
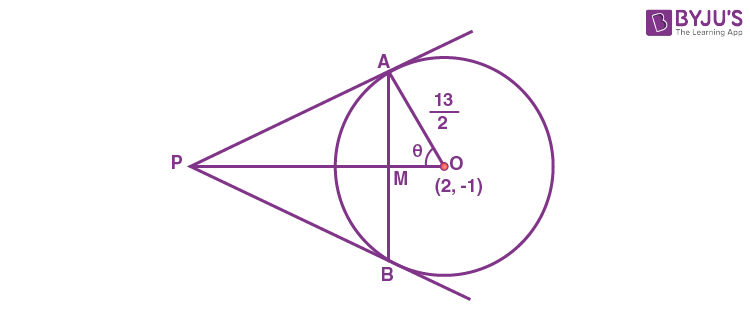
\(\begin{array}{l}\sin \theta =\frac{12}{13}\end{array} \)
In ΔPAO,
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{PO}{OA}=\sec \theta\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}PO = \frac{13}{2}\cdot \frac{13}{5}=\frac{169}{10}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore PM = \frac{169}{10}-\frac{5}{2}=\frac{144}{10}=\frac{72}{5}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore 5PM = 72\end{array} \)
9. Let \(\begin{array}{l}\vec{a}\ \text{and}\ \vec{b}\ \text{be two vectors such that}\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}|\vec{a} + \vec{b}|^2 = |\vec{a}|^2 + 2|\vec{b}|^2 , \vec{a}\cdot \vec{b}=3\ \text{and}\ |\vec{a} \times \vec{b}|^2 = 75.\ \text{Then}\ |\vec{a}|^2\end{array} \)
is equal to _____.
Answer (14)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}\because |\vec{a} + \vec{b}|^2 = |\vec{a}|^2+2|\vec{b}|^2\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{ or } |\vec{a}|^2 + |\vec{b}|^2 + 2\vec{a}\cdot \vec{b} = |\vec{a}|^2 + 2|\vec{b}|^2\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore |\vec{b}|^2 = 6 \ \ \ …(i)\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Now} |\vec{a}\times\vec{b}|^2 = |\vec{a}|^2 |\vec{b}|^2 -\left(\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b}\right)^2\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}75 = |\vec{a}|^2 \cdot 6-9\end{array} \)
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore |\vec{a}|^2 =14\end{array} \)
10. Let \(\begin{array}{l}S =\left\{(x,y)\in \mathbb{N}\times \mathbb{N} : 9(x-3)^2 + 16(y-4)^2 \le 144\right\}\end{array} \)
and \(\begin{array}{l}T =\left\{(x,y)\in \mathbb{R}\times \mathbb{R} : (x-7)^2 + (y-4)^2 \le 36\right\}.\end{array} \)
Then n(S ⋂ T) is equal to ______.
Answer (27)
Sol.
\(\begin{array}{l}S = \left\{(x,y) \in \mathbb{N} \times \mathbb{N}: \frac{(x-3)^2}{16} + \frac{(y-4)^2}{9}\le 1\right\}\end{array} \)
represents all the integral points inside and on the ellipse \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{(x-3)^2}{16} + \frac{(y-4)^2}{9}=1\end{array} \)
, in first quadrant.
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{and }T = \left\{(x,y) \in \mathbb{R}\times \mathbb{R} : (x-7)^2 + (y-4)^2 \le 36\right\}\end{array} \)
represents all the points on and inside the circle \(\begin{array}{l}(x-7)^2+(y-4)^2=36\end{array} \)
.
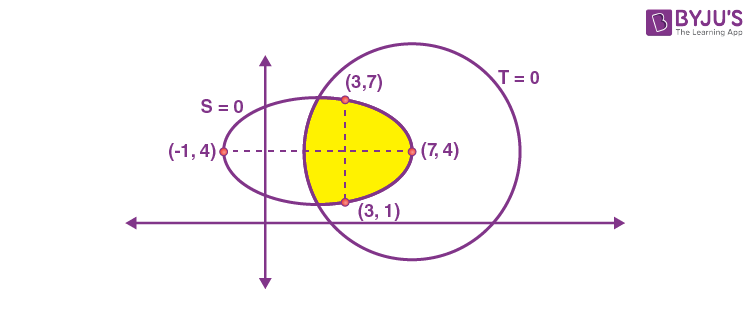
\(\begin{array}{l}\therefore \left(S\cap T \right)=\{\left(3,1\right)\left(2,2\right)\left(3,2\right)\left(4,2\right)\left(5,2\right)\left(2,3\right)……….\left(6,5\right)\}\end{array} \)
Total number of points = 27
JEE Main 2022 July 29th Shift 2 Paper Analysis
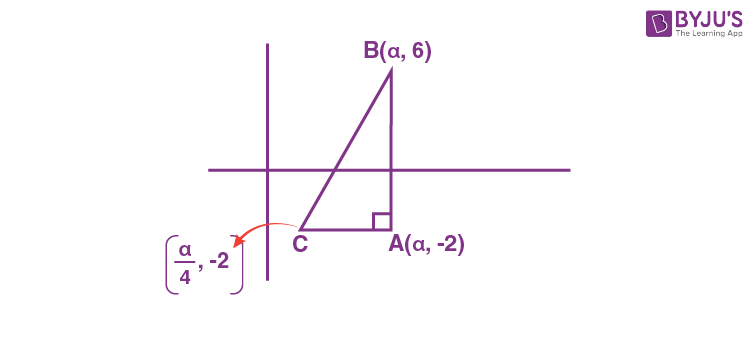

















Comments