KVPY-SA 2020 Biology question paper is available here for free download. The question paper comes with solutions that have been specifically created by our subject-matter experts to facilitate easy learning and clear understanding of the concepts discussed in the paper. While students will be able to grasp the answers easily they will also get an overall idea of how the Biology paper is set, the types of questions asked and more.
Students can also use this paper as a practice study material and solve the questions without referring to the answers. They will not only be able to test their preparation level but they can revise the different topics properly before the main exam. All in all, working with the KVPY-SA 2020 Biology question paper as well as other subject papers will enable students to achieve a higher score in the actual exam.
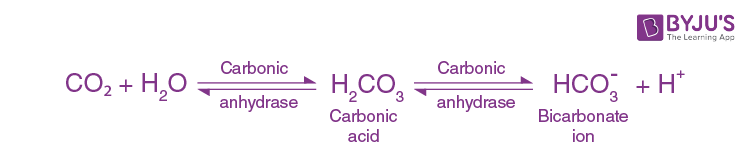
Question 1: Which one of the following chemicals serves as a substrate for carbonic anhydrase?
a. O2
b. CO2
c. NO2
d. CO
Answer: (b)
Large fraction of CO2 is transported in plasma in the form of bicarbonates. But the formation of bicarbonates from carbon dioxide occurs in RBC due to the presence of carbonic anhydrase enzyme. Carbonic anhydrase catalyzes the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into bicarbonates as shown below.
Question 2: Which one of the following is not a function of the small intestine?
a. Absorption of end products of digestion
b. Digestion of proteins
c. Digestion of lipids
d. Acidification of ingested food
Answer: (d)
The small intestine completes the digestion of food – protein, carbohydrates, fats and nucleic acid. It absorbs nutrients into the blood and lymph. It secretes certain hormones required for the absorption of the end product of digestion. The intestinal juice is slightly alkaline (pH 7.8).
Acidification of ingested food is completed by the stomach. Oxyntic cells of the stomach release HCl (hydrochloric acid) which activates various enzymes like pepsinogen.
Question 3: Insulin stimulates the conversion of glucose to
a. fructose
b. glycogen
c. sucrose
d. starch
Answer: (b)
Insulin is a peptide hormone, which plays a major role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis. Insulin acts mainly on hepatocytes and adipocytes (cells of adipose tissue) and enhances cellular glucose uptake and utilisation. As a result, there is a rapid movement of glucose from the blood to hepatocytes and adipocytes resulting in decreased blood glucose levels (hypoglycemia). Insulin also stimulates the conversion of glucose to glycogen (glycogenesis) in the target cells.
Question 4: Which one of the following statements about the ecosystem is incorrect?
a. The metabolic requirements of poikilotherms are higher than that of homeotherms
b.Autotrophs form the base of the food chain in natural ecosystems
c. In terrestrial ecosystems, most of the primary production is consumed by detritivores and not herbivores
d. Approximately 10% of the energy of one trophic level is transferred to the next level
Answer: (a)
Poikilotherms are animals whose body temperature adjusts depending on the environment. They are also known as conformers. Little energy is expended in order to maintain constancy.
Homeotherms are animals that have constant body temperature and a lot of energy is expended to maintain constancy.
So, the metabolic requirements of poikilotherms are lower than those of homeotherms.
Question 5: Proton motive force is created by pumping protons across the:
a. Trans-Golgi network
b. Endoplasmic reticulum
c. Mitochondrial inner membrane
d.Early endosomal membrane
Answer: (c)
Proton motive force (PMF) is the force that promotes the movement of protons across the membrane downhill the electrochemical potential.
During the electron-transport-system in the mitochondrial inner-membrane, oxidative phosphorylation occurs. NADH2 and FADH2 made in the citric cycle deposit their proton in peri mitochondrial space. Due to which proton gradient is created between peri mitochondrial and the inner membrane of mitochondria. ATP-synthase becomes active in ATP formation only where there is a proton gradient having a higher concentration of H+ on the F0 side as compared to F1 side.
Question 6: Which one of the following mendelian diseases is an example of X-linked recessive disorder?
a. Haemophilia
b. Phenylketonuria
c. Sickle cell anaemia
d. Beta thalassemia
Answer: (a)
Haemophilia is an example of X-linked recessive Mendelian disorder. In this disease, a single protein that is a part of the cascade of proteins involved in the clotting of blood is affected. Due to this, in an affected individual, a simple cut will result in non-stop bleeding.
Phenylketonuria, sickle cell anaemia and beta-thalassemia are all Mendelian autosomal disorders.
Question 7: Which one of the following pairs gives rise to fruit and seed, respectively, in a typical angiosperm plant?
a. Ovule and ovary
b. Ovary and Pollen
c. Pollen and anther
d. Ovary and ovule
Answer: (d)
After fertilization, the petals, stamens and style become dry and shed off. Endosperm develops or completely utilized by seed. The embryo develops after syngamy. Ovule converted into seed and ovary converted into a fruit.
Question 8: The concept of vaccination arose from Edward Jenner’s observation that:
a. Injecting inactivated anthrax spores in sheep protected them from anthrax
b. Injecting humans with tuberculosis-infected lung extracts protected them from tuberculosis
c. Milk-maids previously infected with cowpox did not contract smallpox
d. Injecting inactivated rabies virus in human protected them from rabies
Answer: (c)
Edward Jenner noticed that milkmaid did not suffer from smallpox but they had scabs of cowpox. He transported the material from the sore of the milkmaid who was suffering from cowpox to the young boy. After some time he injected live smallpox material into that boy. But symptoms of disease did not appear. He tried this procedure on another person and got success. He gave the term vaccination for this process.
Question 9: A plant genotype AABBCC is crossed with another plant with aabbcc genotype. How many different genotypes of pollens is possible in an F1 plant if these three loci follow an independent assortment?
a. 8
b. 4
c. 2
d. 1
Answer: (a)
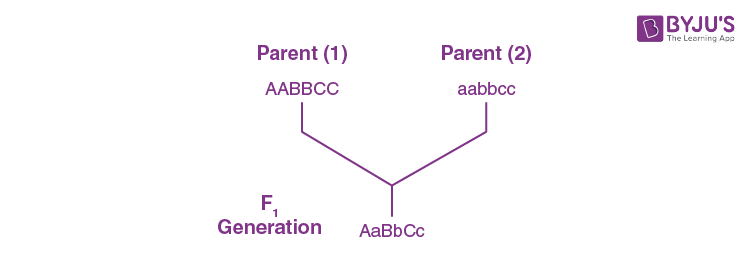
Gametes = 2n (here n = heterozygous locus)
= 23 (here n = 3)
= 2×2×2
= 8
Hence, 8 different genotypes of pollen are possible in F1 plants.
Question 10: Which one of the following sequences of events correctly represents mitosis?
a. Metaphase, Telophase, Prophase, Anaphase
b. Anaphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Telophase
c. Prophase, Anaphase, Metaphase, Telophase
d. Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
Answer: (d)
The type of cell division in which the number of the chromosome into the daughter cell is similar to the parent cell is called mitosis.
Division classified into two phases:-
(A)Interphase → G1, S, G2
(B)M phase → Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
Question 11: The amount of air that is left behind in the lungs after expiratory reserve volume has been exhaled is:
a. Inspiratory reserve volume
b. Tidal volume
c. Residual volume
d. Vital capacity
Answer: (c)
Residual Volume (RV): Volume of air remaining in the lungs even after a forcible expiration. This averages 1100 mL to 1200 mL.
Inspiratory Reserve Volume: Additional volume of air, a person can inspire by a forcible inspiration. This averages 2500 mL to 3000 mL.
Tidal Volume: Volume of air inspired or expired during normal respiration. It is approximately 500 mL.
Vital capacity: The maximum volume of air a person can breathe in after forced expiration.
Question 12: Match the species in column I with their respective feature in column II.

Choose the correct combination.
a.P-ii, Q-i, R-iv, S-iii
b. P-ii,Q-iv, R-i, S-iii
c. P-iii, Q-iv, R-i, S-ii
d. P-iv, Q-iii, R-ii, S-i
Answer: (b)
Mollusca: The mouth contains a file-like rasping organ for feeding, called a radula.
Annelida: Their body surface is distinctly marked out into segments or metameres (Latin, annulus: little ring) and, hence, the phylum name Annelida.
Aschelminthes/Nematoda: They may be free-living, aquatic and terrestrial or parasitic in plants and animals. Roundworms have an organ-system level of body organisation. They are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and pseudocoelomate animals.
Echinodermata: All are marine with an organ-system level of organisation. The adult echinoderms are radially symmetrical but larvae are bilaterally symmetrical.
Question 13: Who among the following scientists proposed the theory of natural selection independently of Charles Darwin?
a. Alfred Russel Wallace
b. Carl Linnaeus
c. Georges Cuvier
d. Jean Baptiste Lamarck
Answer: (a)
Alfred Wallace, a naturalist who worked in the Malay Archipelago had also come to similar conclusions around the same time and he sent his conclusions to Darwin. This theory was later on explained by Darwin in his book ‘On the origin of species by means of Natural Selection’ (1859).
Question 14: The maximum concentration of harmful chemicals is expected to be found in organisms:
a. At the bottom of a food chain
b. At the middle of a food chain
c. At the top of a food chain
d.At any level in a food chain
Answer: (c)
Heavy metals and persistent pesticides pass into the food chain and increase in the amount per unit weight of the organism with the rise in trophic level due to their accumulation. This is known as biomagnification. Hence, the maximum concentration of harmful chemicals is expected to be found in organisms at the top of a food chain.
Question 15: The genome of SARS-Co-V2 is composed of
a. double-stranded DNA
b. double-stranded RNA
c. single-stranded DNA
d. single-stranded RNA
Answer: (d)
SARS-COV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2), is composed of single-stranded RNA. It is an infectious disease that caused a global pandemic in 2020.
Part 2
Question 16: Anthropocene refers to the geological age during which:
a. The earliest hominids radiated from their ancestral forms
b. Human activity significantly influenced the climate and environment
c. Arthropod radiation was highest
d. Arthropod radiation significantly influenced the climate and environment
Answer: (b)
Anthropocene refers to the geological age during which human activity significantly influenced Earth’s geology and ecosystems, including climate and environment.
Question 17: Match the vitamins listed in column I with the diseases caused due to their deficiency in column II.

Choose the correct combination
a. P-iv; Q-ii, R-iii, S-v
b. P-i, Q-ii, R-iv, S-iii
c. P-iv, Q-iii, R-ii, S-v
d. P-iii, Q-iv, R-v, S-i
Answer: (c)
The following are the vitamins with their respective deficiency diseases:
|
Vitamin
|
Deficiency Disease
|
|
Vitamin A |
Night blindness |
|
Vitamin B2 |
Ariboflavinosis |
|
Vitamin D |
Rickets |
|
Vitamin B12 |
Pernicious anaemia |
|
Vitamin B3 |
Pellagra |
Question 18: An adult mammal with a 50 kg body weight has the following functional parameters of its lungs.
Inspiratory reserve volume = 40ml/kg body weight
Expiratory reserve volume = 15 ml/ kg body weight
Vital capacity = 60 ml/kg body weight
Breathing rate = 20/min
The volume (in litre) of air that its lungs displaces in 24 hours is
a. 72,000
b. 7,200
c. 3,600
d. 1,200
Answer: (b)
Weight = 50 kg
IRV = 40 ml/kg
ERV = 15 ml/kg
VC = 60 ml/kg
Breathing rate = 20/min
Number of breath in 24 hrs = 24 × 60 × 20 = 28,800
Volume of air displaced by lungs = Tidal volume (TV)
Vital capacity = ERV + TV + IRV
60 = 15 + TV + 40
TV = 60 – 15 – 40 = 5 ml/kg
Volume displaced by body of 1 kg in 24 hrs = number of breaths in 24 hrs × TV
= 28,800 × 5 ml/kg = 14,4000 ml/kg
Volume displaced by body of 50 kg in 24 hrs = volume displaced by 1 kg body × 50 kg = 14,4000 × 50 = 72,00,000 ml = 7200 liter.
Question 19: In a breed of dog, the long-haired phenotype is recessive to short hair. In a litter, one pup is short-haired and its sibling is long-haired. Consider the following possible phenotypes of the parents.
i. Both parents are short-haired
ii. Both parents are long-haired
iii. One parent is short-haired, and one is long-haired
Choose the correct combination of the possible parental phenotypes.
a. i only
b. ii only
c. iii only
d. i or iii
Answer: (d)
Short hair dog = LL
Long hair dog = ll
Question given:
One pup is short-haired = LL or Ll
Sibling long-haired = ll
so,
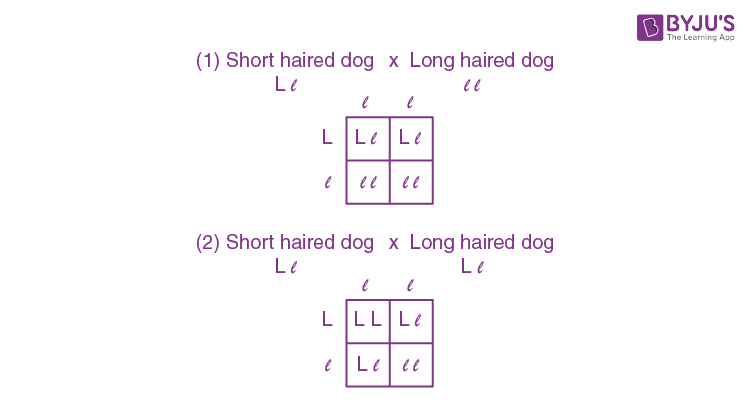
Hence, in both cases, the offspring will be either short hair or long hair. Both statements (i) and (iii) are possible.
Question 20: In medical diagnostics for a disease, sensitivity (denoted by a) of a test refers to the probability that a test result is positive for a person with the disease, whereas specificity (denoted by b) refers to the probability that a person without the disease test negative. A diagnostic test for COVID-19 has the values of a=0.99 and b=0.99. If the prevalence of COVID 19 in a population is estimated to be 10%, what is the probability that a randomly chosen person tests positive for COVID-19?
a. 0.099
b. 0.10
c. 0.108
d. 0.11
Answer: (c)
Lets total population = 100
Probability of person should pe positive =10% = 10/100=1/10
Probability of person whose sensitivity test result is positive = 0.99
= (99→Population correctly detected)/(100→Total population detected for disease)
Probability of person should be negative = ([100-10])/100=90/100
Probability of person with specificity = 0.99
Probability of person with wrong specificity = 1-0.99 = 0.01
Probability that a randomly chosen person tests positive for COVID-19
= Probability of a person to be positive X Sensitivity + Probability of a person to be negative X Probability of person with wrong specificity
= 10/100 × 0.99 + 90/100 x 0.01 = 0.099 + 0.009 = 0.108.
Comments