Students will find the KVPY-SX 2020 Biology question paper with solutions on this page. They can either view the question paper directly on the website or download it in the form of a PDF and use it to study for the exams. The questions asked in the KVPY-SX 2020 Biology question paper have been meticulously solved by our subject experts and students will benefit as they will be getting only the most accurate answers. This will further help students to understand the topics discussed more clearly and at the same time they will come to know about types of questions, difficulty level, and more.
Furthermore, as students engage in solving the questions, they will get to know their preparation level and in the end develop greater speed and accuracy for solving the different types of problems. In essence, by going through and solving the KVPY-SX 2020 Biology question paper students will be moving in the right direction to overcoming their shortcomings and clearing the final exam.
Question 1: Species with high fecundity, high growth rates, and small body sizes are typically
a. Endangered species
b. Keystone species
c. K-selected species
d. R-selected species
Answer: (d)
Endangered species are organisms whose number have reduced drastically and if not conserved will become extinct.
Keystone species are those which have an extremely high impact on a particular ecosystem relative to its population.
General features of K-selected species, and r-selected species
|
K-selected species
|
r-selected species
|
|
Live in predictable, stable environments |
Exploit rapidly changing environments |
|
Long-lived |
Short-lived |
|
Population size stable |
Population size highly variable |
|
Density-dependent mortality |
Density-independent mortality |
|
Competition intense |
Competition low |
|
Multiple reproductive events beginning later in life |
Single reproductive event at a young age |
|
Prolonged parental care of young |
Little or no parental care of young |
|
Modest numbers of offspring |
Very high number of offspring |
|
Tend to have an S-shaped population growth curve |
Tend to have a J-shaped population growth curve |
|
Large body size |
Small body size |
Question 2: When RNAse enzyme is denatured by adding urea, which one of the following combinations of bonds would be disrupted?
a. Ionic and disulphide bonds
b. Ionic and hydrogen bonds
c. Hydrogen and peptide bonds
d. Peptide and disulfide bonds
Answer: (b)
Denaturation is the process that causes a major phase change in proteins. Protein denaturation involves structural or conformational changes from the native structure without alteration of the amino acid sequence. These changes can be induced by pH, detergents, urea, and guanidine hydrochloride, as well as by heat. Protein denaturation is apparently a highly cooperative process accompanied by considerable enthalpy changes and disrupts hydrogen bonds.
Question 3: The function of aposematic colouration is to
a. Attract mates
b. Eamouflage
c. Scare off competitors
d. Warn predators
Answer: (d)
Aposematism is the correlation between conspicuous signals, such as bright colouration, and prey unprofitability. Aposematic, or warning, colouration is used by noxious organisms to signal their unprofitability to potential predators.
So, the correct answer is d
Question 4: Maize and rice genomes have diploid chromosome number of 20 and 24, respectively. In the absence of crossing over and mutations, which one of the following is correct about the genetic.
a. Maize < rice
b. Maize = rice > 0
c. Maize = rice = 0
d. Maize > rice
Answer: (a)
rennin is an enzyme found in the stomach of young mammals. In human babies, rennin is primarily associated with the coagulation of milk. This property assists in the digestion of milk in infants. At the base of the gland are the zymogenic (chief) cells, which are thought to produce the enzymes pepsin and rennin. (Pepsin digests proteins, and rennin curdles milk.)
Question 5: The exponent z of the species-area curve measured at continental scales is
a. Smaller than the value of z at regional scales
b. Equal to the value of z at regional scales
c. Greater than the value of z at regional scales
d. Unrelated to the value of z at regional scales
Answer: (c)
Alexander Von Humboldt has observed that within a region, species richness increased with the increased explored area, but only up to a limit. The relationship between species richness and area for a number of taxa like angiospermic plants, freshwater fishes and birds is found to be a rectangular hyperbola.
Question 6: The pH of an aqueous solution of 10-8 M HCl is
a. 6.0
b. Between 6.9 – 7.0
c. Between 7.0 – 7.1
d. 8.0
Answer: (b)
Question 7: Which one of the following cannot cause eutrophication of lakes
a. Introduction of invasive floating plants
b. Discharge of fertilizer rich agricultural waste
c. Natural ageing of lakes
d. Discharge of industrial waste
Answer: (a)
Eutrophication is dominantly caused by human activity due to their dependence on using nitrate and phosphate fertilizers. Introduction in invasive floating plants is not the cause of eutrophication.
So, the correct answer is A
Question 8: Which one of the following polymerases transcribes 5S rRNA?
a. RNA Pol I
b. RNA Pol III
c. RNA Pol II
d. RNA Pol IV
Answer: (b)
5S-rRNA is a molecule of 120 nucleotides and transcribes by RNA polymerase III.
Question 9: Which one of the following statements about rennin is correct?
a. It is secreted by adrenal glands
b. It converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin
c. It is secreted by peptide cells of gastric glands into the stomach
d. It is a hormone
Answer: (c)
Rennin is a proteolytic enzyme that is useful in milk coagulation. It is present in the infant’s gastric juice produced by gastric glands.
Question 10: When one goes from a brightly lit area to a dimly lit room eyes adjusts slowly, thereby regaining the clarity of vision. Which one of the following explains this process?
a. Regeneration of rhodopsin in the rod cells
b. Bleaching of rhodopsin
c. Constriction of the pupil
d. Increase in the number of rod cells
Answer: (a)
When we enter into a dark room from a very bright place, we experience difficulty in vision. This change is due to the regeneration of rhodopsin, the pigment of the rods, which was earlier broken down due to bright light and even the size of the pupil is less in the bright light. After sometimes the vision gets restored by regeneration of rod cells and dilation of the pupil in the dark which permits more light to enter the eyes. Rod cells are the cell which helps in dim light vision.
Question 11: In a diploid population at Hardy-weinberg equilibrium, consider a locus with two alleles. The frequencies of these two alleles are denoted by p and q, respectively. heterozygosity in this population is maximum at
a. p=0.25, q = 0.75
b. p = 0.4, q = 0.6
c.p = 0.6, q = 0.4
d. p = 0.5, q = 0.5
Answer: (d)
Accordingly to hardy-weinberg principle
= p2 + q2 + 2pq = 1
P = 0.5 ; q = 0.5; 2pq = 0.50
In all option, only option (d) have heterozygosity in population is maximum.
Question 12: An enzyme with optimal activity at pH 2.0 and 370C is most likely to be
a. Lysozyme from hen egg white
b. Trypsin from cattle
c. DNA polymerase from Thermus aquaticus
d. Pepsin from humans
Answer: (d)
Pepsin is most active in acidic environments between pH 1.5 to 2.5. The optimum temperature of pepsin is between 370C and 420C. Accordingly, its primary site of synthesis and activity is in the stomach (pH 1.5 to 2).
Question 13: While adjusting to varying environmental temperature, plants incorporate in their plasma membrane
a. More saturated fatty acids in cold and more unsaturated fatty acids in hot environment
b. More unsaturated fatty acids in cold and more saturated fatty acids in hot environment
c. More saturated fatty acids in both cold and hot environment
d. More unsaturated fatty acids in both cold and hot environment
Answer: (b)
In high temperature, the cell membrane becomes more fluid. This gives a bigger chance for some materials to get in or out through the spaces made between the phospholipid molecules as a result of this increased fluidity.
A cold environment tends to compress membranes composed largely of saturated fatty acids making them less fluid. So in a cold environment, the proportion of unsaturated fatty acids shobe larger as kinks in the tail push adjacent phospholipid molecules away and maintains fluidity in the membrane.
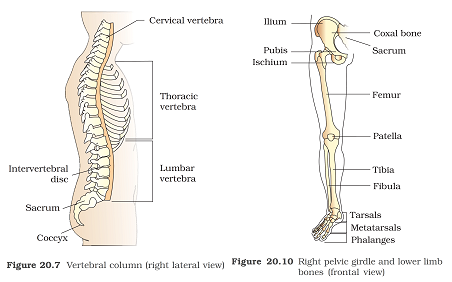
Question 14: Which one of the following terms is not used while describing human vertebra?
a. Lumbar
b. Sacral
c. Thoracic
d. Tarsal
Answer: (d)
In humans, the vertebral column usually consists of 33 vertebrae. The number of vertebrae can vary between 32 and 35. Usually, there are 7 cervicals, 12 thoracics, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral and 4 caudal (coccygeal) vertebrae.
In the human ankle, there are seven tarsal bones. The talus (astragalus) articulates above with the bones of the lower leg to form the ankle joint.
Question 15: Assume a population that has reached immunity for an infectious disease. If an infected individual is introduced to this population, which of the following is most likely to occur?
a. The infection will spread exponentially across the population
b. The infection will spread linearly across the population
c. A few individuals may get infected, but the infection will not spread across the population
d. No other individual will be infected by the disease
Answer: (c)
In a completely naive population, a pathogen will propagate through susceptible hosts in an unchecked manner following effective exposure of susceptible hosts to infected individuals. However, if a fraction of the population has immunity to that same pathogen, the likelihood of effective contact between infected and susceptible hosts is reduced, since many hosts are immune and, therefore, cannot transmit the pathogen. If the fraction of susceptible individuals in a population is too few, then the pathogen cannot successfully spread, and its prevalence will decline. The point at which the proportion of susceptible individuals falls below the threshold needed for transmission is known as the herd immunity threshold
Question 16: Match the type of cells in column I with the organs they are part of, listed in column II

Choose the correct combination
a. P-iii, Q-i, R-ii, S-iv
b. P-ii, Q-i, R-iii, S-iv
c. P-iv, Q-iii, R-ii, S-i
d. P-iii, Q-ii, R-iv, S-i
Answer: (a)
Chondroblast is cells of cartilage
The osteoclast is responsible for aged bone resorption and the osteoblast are responsible for new bone formation.
Microglia are a type of neuroglia located throughout the brain and spinal cord.
Pneumuocyte one of the linings of the alveoli in the lung.
Question 17: A bacterial culture was started with an inoculum of 10 cells. What will be the number of cells at the end of 10 cycles of division, assuming that every progeny cell undergoes division in each cycle?
a. 100
b. 1024
c. 2048
d. 10240
Answer: (d)
When a bacterial according to given data culture started with an inoculums 10 cells are there.
End of 10 cycle of division
= 210 × 10
= 1024 × 10 = 10240
So, the correct option is (d)
Question 18: The following family tree traces the occurrence of a rare genetic disease. The filled symbols signify the individuals with the disease, whereas the open symbols signify healthy individuals.

Based on this information, the disease is most likely to be
a. Autosomal, dominant
b. Autosomal, recessive
c. X-linked, recessive
d. X-linked, dominant
Answer: (b)
Autosomal recessive is one of several ways that a trait, disorder, or disease can be passed down through families. An autosomal recessive disorder means two copies of an abnormal gene must be present in order for the disease or trait to develop and it not seen in every generation. Given family tree showing autosomal recessive disorder.
Question 19: Which one of the following statements is correct about the mechanism of action of penicillin?
a. In inhibits transcription
b. It hydrolyses cell wall
c. It inhibits cell wall biosynthesis
d.It inhibits translation
Answer: (c)
Penicillins have been shown to inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis, and interact with penicillin-binding proteins, leading to bacterial lysis. Penicillins and cephalosporins are the major antibiotics that inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis. They are called beta-lactams because of the unusual 4-member ring that is common to all their members.
Question 20: Leaf extract from an infected plant was passed through a filter with a pore size of 0.05 μm diameter. The infectious agent was detected in the filtrate. Which one of the following is the likely infectious agent?
a. Bacteria
b. Virus
c. Nematode
d. Fungus
Answer: (b)
The virus should be smaller than bacteria, that’s why it has come out in the filtrate, so the correct option is B.
Part 2
Question 21: Which one of the following is the most likely ratio of blood groups (A : B : AB) among the progeny from heterozygous parents with B and AB blood groups?
a. 0.5 : 0.25 : 0.25
b. 0.25 : 0.25 : 0.5
c. 0.25 : 0.5 : 0.25
d. 0 : 0.25 : 0.75
Answer: (c)

IAIB = AB
IAI0 =A
IBIB = B
IBI0 = B
A : B : AB
1 : 2 : 1
Ratio of red blood groups (A : B : AB) in the progenies are = (1/4 : 2/4 : 1/4)
= 0.25 : 0.5 : 0.25
Question 22: Match the plants in column I with their features listed in column II, III & IV.
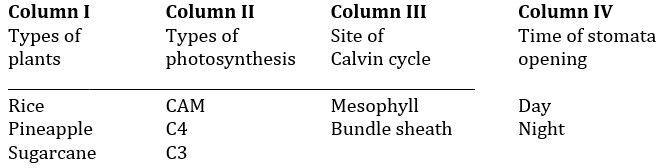
Choose the correct combination
a. Rice – C3- mesophyll-day, pineapple-CAM-mesophyll-night, Sugarcane-C4-Bundle sheath-day
b. Rice-C3-Mesophyll-day, pineapple-CAM-mesophyll-night, sugarcane-C4-mesophyll-day
c. Rice-C4-mesophyll-day, pineapple-C3-Bundle sheath-night, sugarcane-CAM-Bundle sheath-day
d. Rice-CAM-Mesophyll-Day, Pineapple-CAM-mesophyll-day, sugarcane-C4-bundle sheath-day
Answer: (a)
Rice – C3 – Mesophyll- Day
Pineapple – CAM – Mesophyll- Night
Sugarcane – C4- Bundle sheath – Day
Question 23: A bacteriophage T2 particle contains within its head a double-stranded B-form DNA with a molecular weight of 1.2 × 108Da. Assume that the head of a T2 phage particle is 210 nm in length and the average molecular weight of a nucleotide is 330Da. The length of the T2 genome is in the range of
a. 6 x 105 to 6.4 x 105 nm
b. 40 x 104 to 41 x 104 nm
c. 1.8 x 105 to 2 x 105 nm
d. 6 x 104 to 6.4 x 104 nm
Answer: (d)
In bacteriophage, double-stranded B form of DNA is present with molecular weight 1.2 ×108 Da.
Since average m.w. of a nucleotide = 330 Da
Therefore no. of bp = (1.2×108 Da)/330Da = 36.36 x 104
Hence no. of bases in single strand = (136.36 x 104)/2= =18.18 x 104
So, length of DNA will be = no. of base × distance between bp
= 18.18 x 104 x 0.34 nm
= 6.18 x 104 nm
Question 24: In the graph below, where N is the population size and is time, M represents
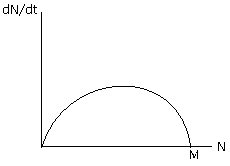
a. Specific growth rate
b. Median population size
c. Carrying capacity
d. Minimum population size without going extinct
Answer: (c)
In the given graph dN/dt represents the increasing/decreasing size of the population in a given time period, since curve increasing upside & than drop-down in previous population size it means after some time population size is the same as initially mentioned by carrying capacity (Specific for each habitat)
Question 25: Match the metabolic pathways in column I with their corresponding intermediate molecules listed in column II

Choose the correct combination
a. P-ii, Q-i, R-iii, S-iv
b. P-i, Q-v, R-iv, S-ii
c. P-v, Q-i, R-iii, S-iv
d. P-ii, Q-i, R-iii, S-v
Answer: (a)
P. Krebs cycle – Succinate
Q. Glycolysis – Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP)
R. Electron transport chain – Cytochrome c
S. Nitrogen fixation – glutamate
Question 26: By comparing mitosis and meiosis occurring in the same organism, which one of the following options is correct regarding the DNA content per cell?
a. Mitotic anaphase > Meiotic anaphase I = Meiotic anaphase II
b. Mitotic anaphase = Meiotic anaphase I > Meiotic anaphase II
c. Mitotic anaphase < Meiotic anaphase I = Meiotic anaphase II
d. Mitotic anaphase = Meiotic anaphase I < Meiotic anaphase II
Answer: (b)
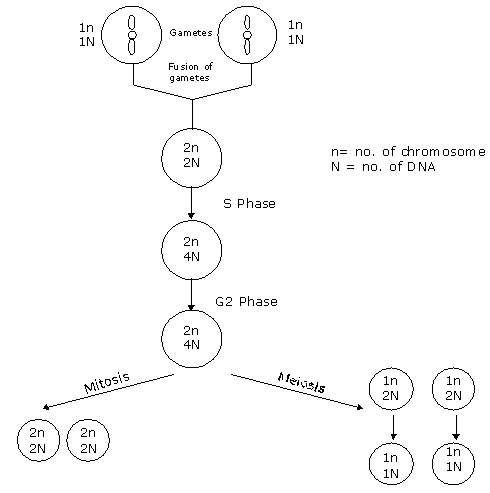
Question 27: Which one of the following is likely to occur upon heating a solution of eukaryotic protein from 200C to 950C?
a. Breakage of disulphide bonds
b. Change in primary structure
c. Hydrolysis of peptide bonds
d. Change in tertiary structure
Answer: (d)
Tertiary structure is stabilized by disulfide bonds, ionic interactions, hydrogen bonds, metallic bonds, and hydrophobic interactions. Disulfide bonds are the strongest forces holding the tertiary structure together, as they are covalent bonds. Protein-unfolding curves were recorded from 20o C to 94o C at a heating rate of 1o/min. During this temperature, disulphide bonds break and changes were seen in tertiary protein.
Question 28: Which one of the following statements is incorrect about the hexokinase catalysed reaction given below?
Glucose + ATP → Glucose -6-phosphate + ADP
a. This reaction takes place in the cytoplasm
b. This is an endergonic reaction
c. Folding of hexokinase to fit around the glucose molecule excludes water from the active site
d. This reaction involves an induced-fit mechanism in hexokinase
Answer: (b)
Glycolysis is the first step of respiration in which the glucose molecule is converted into two molecules of pyruvic acid. In glycolysis reaction, the first step is the conversion of glucose into glucose -6- phosphate. This reaction is catalysed by the enzyme hexokinase which is also known as a pacemaker. To complete this reaction one ATP donates its terminal phosphate to 6 carbon of glucose hence there is a loss of energy or we can say this is an energy-consuming process or an endergonic process.

Question 29: An ecologist samples trees in multiple forest plots to determine species richness. Which one of the following can help determine the adequacy of sampling effort?
a. Graph the number of new tree species in each successive sampling plot
b. Graph the total number of tree species per total area for all plots combined
c. Graph the number of individuals per tree species in each successive sampling plot
d. 30 sampling plots are sufficient, irrespective of the forest area
Answer: (a)
According to Alexander von Humboldt that within a region species richness increased with increasing explored area, but only up to a limit.
The graph between new tree species in each successive sampling plot shows the actual growth in a particular plot, not the population.
Question 30: In medical diagnostics for a disease, sensitivity (denoted a) of a test refers to the probability that a test result is positive for a person with the disease whereas specificity (denoted b) refers to the probability that a person without the disease tests negative. A diagnostic test for influenza has the values of a=0.9 and b=0.9. Assume that the prevalence of influenza in a population is 50%. If a randomly chosen person tests negative, what is the probability that the person actually has influenza?
a. 0.01
b. 0.02
c. 0.05
d. 0.10
Answer: (d)
(1) Sensitivity of a Test i.e. (a) = the probability that a test comes out to be positive for a person who is actually infected with that disease. In the given question it is a = 0.9 which means Test Results are 90% Reliable.
(2) Specificity of a test i.e. (b) = the probability that a person tests Negative who is actually not having the disease in the given question it is b = 0.9 again than means Test Results are 90% reliable. After analyzing this much data it is clear that this particular Influenza Diagnostic test is 90% (0.9) effective/Accurate with a 10% (0.1) chance of producing false results.
(3) Prevalence of Influenza in population = 50%
Let us calculate the total Probability of a randomly chosen person for this population to test either negative or positive.
Total probability of a randomly choosen person to test negative or positive = Probability × sensitivity/specificity + Probability × error – Rate of Test kit
= 50/100 x 0.9 + 50/100 x 0.1
= 0.5
Now if we randomly choose a person from this population and his test results comes out to be negative after using above given Diagnostic Test (90% effective) then what is the chance that this person actually has influenza; (it means what is the chance of the test to produce false results.) It can be calculated as below.
Probability of a person tested –ve of having influenza in actual. (it means the probability of that person’s test result to come false; he was actually positive instead of negative)
Probability of a person tested negative (–ve) of having influenza in actual = (Probability of person to positive actually)/(Total probability)
= 0.1
So, the probability of that chosen person, who tested negative to actually having influenza is option (d) = 0.10.
Comments