Lead (IV) Acetate, also known as lead tetraacetate, is a colourless solid that has a chemical formula of Pb(C2H3O2)4. It is easily degraded by moisture and is typically stored with extra acetic acid. In this short piece article, learn more about the lead (IV) acetate formula, along with the properties and structure of Lead tetraacetate and few of its uses.
Lead (IV) Acetate Properties
| Properties of Lead (IV) Acetate | |
| Name | Lead (IV) Acetate |
| Other Names | Lead tetraacetate, Plumbic acetate |
| Appearance and odour | Pink or colourless crystals
Odour – Vinegar |
| Chemical Formula | Pb(C2H3O2)4 |
| Melting Point | 175 °C |
| Boiling Point | Decomposes |
| Density | 2.228 g/cm3 |
| Molar Mass | 443.376 g/mol |
| Solubility in Water | Soluble |
Lead IV Acetate Structure
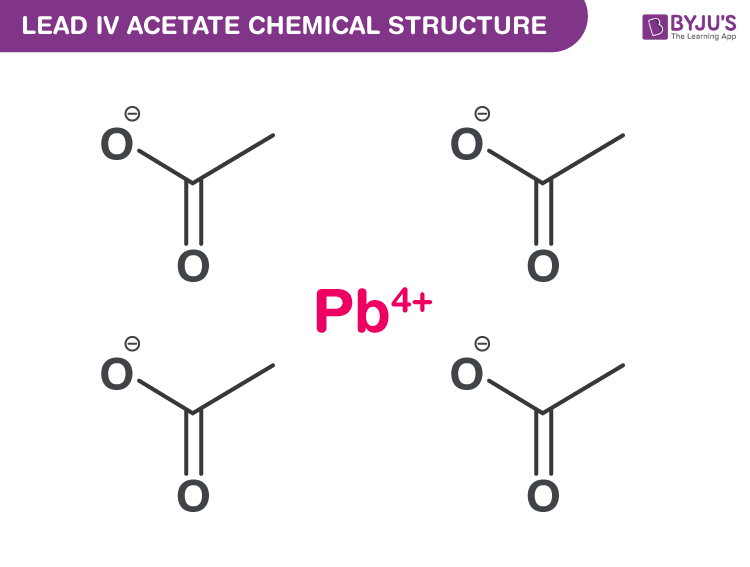
Lead (IV) Acetate Uses
- Used as an oxidizing agent in organic synthesis
Safety Measurements
- Lead (IV) acetate causes irritation in the skin, eye and respiratory tract.
- Lead (IV) acetate is a neurotoxin.
- Lead (IV) acetate affects the reproductive system, blood, kidney, gum tissues and central nervous system.
To learn more about such chemistry topics register to BYJU’S now!
Comments