NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants presented here provide answers to the questions given in the NCERT Exemplar book. The NCERT Exemplar for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 helps you in grasping the topics better and assists you in preparation for CBSE Class 11 Biology examinations and entrance examinations, like NEET.
The NCERT Exemplar for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 comprises respiration questions and answers from the NCERT exemplar book and previous year question papers. Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Exemplar also provides NEET questions on Respiration in Plants, MCQs, important diagrams, cycles, numericals, worksheets and exercises.
Download the PDF of the NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants
Access Answers to the NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Biology Chapter 14
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. The ultimate electron acceptor of respiration in anaerobic organisms is:
a Cytochrome
b Oxygen
c Hydrogen
d Glucose
Solution:
Option (b) is the answer.
2. Phosphorylation of glucose during glycolysis is catalysed by
a. Phosphoglucomutase
b. Phosphoglucoisomerase
c. Hexokinase
d. Phosphorylase
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer.
3. Pyruvic acid, the key product of glycolysis can have many metabolic
fates. Under the aerobic condition, it forms
a. Lactic acid
b. CO2 + H2O
c. Acetyl CoA + CO2
d. Ethanol + CO2
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer.
4. Electron Transport System (ETS) is located in mitochondrial
a. Outer membrane
b. Inter membrane space
c. Inner membrane
d. Matrix
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer.
5. Which of the following exhibits the highest rate of respiration?
a. Growing shoot apex
b. Germinating seed
c. Root tip
d. Leaf bud
Solution:
Option (b) is the answer.
6. Mitochondria are called powerhouses of the cell. Which of the following
Do observations support this statement?
a. Mitochondria synthesise ATP
b. Mitochondria have a double membrane
c. The enzymes of the Krebs cycle are found in mitochondria.
d. Mitochondria are found in almost all plants and animal cells.
Solution:
Option (a) is the answer.
7. The end product of oxidative phosphorylation is
a. NADH
b. Oxygen
c. ADP
d. ATP + H2OSolution:
Option (d) is the answer.
8. Match the following and choose the correct option from those given
below.
| Column I
A. Molecular oxygen B. Electron acceptor C. Pyruvate dehydrogenase D. Decarboxylation |
Column II
i. α – Ketoglutaric acid ii. hydrogen acceptor iii. cytochrome C iv. acetyl Co A |
Options
a. A-ii, B-iii, C-iv, D-i
b. A-iii, B-iv, C-ii, D-i
c. A-ii, B-i, C-iii, D-iv
d. A-iv, B-iii, C-i, D-ii
Solution:
Option (a) is the answer.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Energy is released during the oxidation of compounds in respiration. How is this energy stored and released as and when it is needed?
Solution:
The energy which gets released during the oxidation of compounds in respiration is stored as Adenosine Triphosphate i.e., ATP. The ATP is stored in the form of chemical bonds.
ADP + IP + energy → ATP (ADP = Adenosine Diphosphate and IP = Inorganic phosphorous)
When energy is required then, this bond energy is broken and utilised
ATP → ADP + IP + energy.
2. Explain the term “Energy Currency”. Which substance acts as energy currency in plants and animals?
Solution:
The energy currency is the energy which is stored and released in living organisms. Adenosine Triphosphate ATP acts as energy currency in plants and animals.
3. Different substrates get oxidized during respiration. How does Respiratory Quotient (RQ) indicate which type of substrate, i.e., carbohydrate, fat or protein is getting oxidized?
R. Q. = A/B
What do A and B stand for?
What type of substrates have R.Q. of 1, < 1 or > 1?
Solution:
Respiratory Quotient (RQ) indicate which type of substrate, i.e., carbohydrate, fat or protein is getting oxidized by measuring the volume of carbon dioxide, i.e., CO2 released or evolved by the volume of oxygen O2 consumed.
A= Volume of CO2 released
B =Volume of Oxygen consumed
RQ equal to 1 = carbohydrate like glucose.
RQ higher than 1 = substrate can be organic acid like malic acid.
4. F1 particles participate in the synthesis of ________________.
Solution:
It has the site for the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
5. When does anaerobic respiration occur in man and yeast?
Solution:
Anaerobic respiration occurs in man when there is intensive exercise or stress on a muscle which leads to inadequate oxygen in the cells. In yeast, it occurs when there is incomplete oxidation of glucose.
6. Which of the following will release more energy on oxidation? Arrange them in ascending order.
a. 1 gm of fat
b. 1 gm of protein
c. 1 gm of glucose
d. 0.5 g of protein + 0.5g glucose
Solution:
1 gm of glucose < 0.5 g of protein + 0.5g glucose < 1 gm of protein < 1 gm of fat.
This will be the ascending order based on their oxidation energy.
7. The product of glycolysis (under hypoxia) in skeletal muscle and anaerobic fermentation in yeast are respectively _____________ and ________________.
Solution:
The product of glycolysis (under hypoxia) in skeletal muscle Is lactic acid while anaerobic fermentation in yeast is ethanol and carbon dioxide i.e., C2H5OH and CO2.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. If a person is feeling dizzy, glucose or fruit juice is given immediately, but not a cheese sandwich Explain.
Solution:
Glucose or fruit juice is a simpler food product which is easily absorbed and assimilated by the body and it is easily oxidized to form energy
2. What is meant by the statement “aerobic respiration is more efficient.”?
Solution:
Aerobic respiration produces more energy as compared to anaerobic respiration. It is a high energy-yielding process. Also, it produces less energy when compared to anaerobic respiration.
3. Pyruvic acid is the end product of glycolysis. What are the three metabolic products of pyruvic acid produced under aerobic and anaerobic conditions? Write their name in the space provided in the diagram.

Solution:
i) CO2 + H2O
ii) Lactic acid
iii) C2H5OH + CO2
4. The energy yield in terms of ATP is higher in aerobic respiration than anaerobic respiration. Why anaerobic respiration occurs even in organisms that live in aerobic condition like human beings and angiosperms?
Solution:
Anaerobic respiration occurs in organisms that live in aerobic condition like human beings when there is intensive exercise or stress on a muscle. In angiosperms, the germination of seeds leads to anaerobic respiration for releasing the energy for the seedling to emerge from the soil.
5. Oxygen is an essential requirement for aerobic respiration but it enters the respiratory process at the end? Discuss.
Solution:
Oxygen is an essential factor for aerobic respiration because it removes hydrogen from the electron transport system. It also acts as a hydrogen acceptor. The absence of oxygen will inhibit the passage of electrons through the co-enzymes and also there won’t be a formation of proton pump and ATP will not be produced by oxidative phosphorylation.
6. Respiration is an energy-releasing and enzymatically controlled catabolic process which involves a step-wise oxidative breakdown of organic substances inside living cells.
In this statement about respiration explain the meaning of
1) Step-wise oxidative breakdown, and
2) Organic substances (used as substrates).
Solution:
1) Step-wise oxidative breakdown:
The energy will be released in a stepwise manner during cellular respiration which is moderated enzymatically.
2) Organic substances (used as substrates):
Organic substances like carbohydrates used as substrates and oxidized during the respiratory process for releasing energy.
7. Comment on the statement – Respiration is an energy-producing process but ATP is being used in some steps of the process.
Solution:
The phosphorylation reaction is the glycolysis process in which glucose is converted to glucose – 6 – phosphate which consumes one ATP.
Although the overall ATP produced by the complete oxidation of the substrate is more than the amount of energy spent on some metabolic processes.
8. The figure given below shows the steps in glycolysis. Fill in the missing steps A, B, C, D and also indicate whether ATP is being used up or released at step E?

Solution:

9. Why is respiratory pathway referred to as an amphibolic pathway? Explain.
Solution:
Respiratory pathway referred to as an amphibolic pathway because it comprises of the breakdown of substrates. The fatty acids are broken down into Acetyl CoA. Similarly, glycerol also enters a biochemical pathway and gets broken down into PGAL (3-phosphoglyceraldehyde). The amphibolic pathway involves both anabolic and catabolic pathway. Respiration can cause both the breakdown and synthesis of fatty acids. Thus it can be said to be an amphibolic pathway.
10. We commonly call ATP as the energy currency of the cell. Can you think of some other energy carriers present in a cell? Name any two.
Solution:
Some other energy carriers present in a cell are:
GTP (Guanine Triphosphate)
ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate)
11. ATP produced during glycolysis is a result of substrate-level phosphorylation. Explain.
Solution:
These are formed without the electron transport system and chemiosmosis during the glycolysis. The ATP is directly formed from ADP and Inorganic phosphatase.
12. Do you know any step in the TCA cycle where there is substrate-level phosphorylation? Which one?
Solution:
In the TCA cycle where there is substrate-level phosphorylation the step in which succinyl Co-A is converted to the succinic acid and there is one GTP molecule synthesized through the substrate-level phosphorylation.
13. A process is occurring throughout the day, in ‘X’ organism. Cells are participating in this process. During this process ATP, CO2 and water are evolved. It is not a light-dependent process.
a. Name the process.
b. Is it a catabolic or an anabolic process?
c. What could be the raw material of this process?
Solution:
a. The name of the process is cellular respiration.
b. It is a catabolic process because it involves the breakdown of the glucose molecule.
c. Raw materials involved in the cellular respiration process are Glucose molecule and oxygen.
14. When a substrate is being metabolized, why does not all the energy that released in one step? It is released in multiple steps. What is the advantage of step-wise release?
Solution:
The advantage of the stepwise release of energy is that each step helps in regulation of the energy. And energy is only released when formed or when required. Energy wastage as heat is avoided and energy is stored
15. Respiration requires O2. How did the first cells on the earth manage to survive in an atmosphere that lacked O2?
Solution:
The first cells on the earth managed to survive in an atmosphere that lacked O2 because they were anaerobes. They survived by breaking down the organic compounds like H2S. they don’t need oxygen for respiration
16. It is known that red muscle fibres in animals can work for longer periods continuously. How is this possible?
Solution:
Red muscle fibres in animals can work for more extended periods continuously as it contains an oxygen-transporting pigment called myoglobin. It is stored as oxymyoglobin as it is bounded to the molecule of oxygen.
17. The energy yield in terms of ATP is higher in aerobic respiration than during anaerobic respiration. Explain.
Solution:
Aerobic respiration produces 38 ATP molecules from a single glucose molecule while Anaerobic respiration produces only 2 ATP molecules from a single glucose molecule. That is why ATP is higher in aerobic respiration than during anaerobic respiration.
18. RuBP carboxylase, PEP carboxylase, Pyruvate dehydrogenase, ATPase, cytochrome oxidase, Hexokinase, Lactate dehydrogenase. Select/choose enzymes from the list above which are involved in
a. Photosynthesis
b. Respiration
c. Both in photosynthesis and respiration
Solution:
a. Enzymes used in photosynthesis are:
– RuBP
– PEP carboxylase
– ATPase
b. Enzymes used in respiration are:
– Hexokinase
– ATPase
– Pyruvate dehydrogenase
Cytochrome oxidase
c. The enzyme used in both photosynthesis and respiration are:
– ATPase
19. How does a tree trunk exchange gas with the environment although it lacks stomata?
Solution:
A tree trunk exchanges gas with the environment although it lacks the stomata because it has lenticels through which oxygen and other gas exchange occurs.
20. Write any two energy-yielding reactions of glycolysis
Solution:
Two energy-yielding reactions of glycolysis:
Conversion of 1,3 – bisphosphoglyceric acid (1,3 – BPGA) to 3 – phosphoglyceric acid (3 – PGA).
Conversion of 3- phosphoenolpyruvate (3 – PEP) to pyruvic acid.
21. Name the site (s) of pyruvate synthesis. Also, write the chemical reaction wherein pyruvic acid dehydrogenase acts as a catalyst.
Solution:
The site of pyruvate synthesis is Cytoplasm in the cell.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase → Pyruvic acid + CoA + NAD+ Acetyl CoA + CO2 + NADH + H+
22. Mention the important series of events of aerobic respiration that occur in the matrix of the mitochondrion and the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
Solution:
i) Citric Acid Cycle/ Tricarboxylic acid cycle: It occurs in the mitochondrial matrix of the cell.
ii) Electron transport system/ Oxidative phosphorylation: It occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane of the cell.
23. The respiratory pathway is believed to be a catabolic pathway. However, the nature of the TCA cycle is amphibolic. Explain.
Solution:
The respiratory pathway is believed to be a catabolic pathway because it breakdown the substrate. In the TCA cycle, the pyruvate is further broken down to Acetyl CoA, and this Acetyl CoA can also be synthesized to fatty acid whenever it is required for fatty acid metabolism or synthesis. In this cycle both breakdown and synthesis take place.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
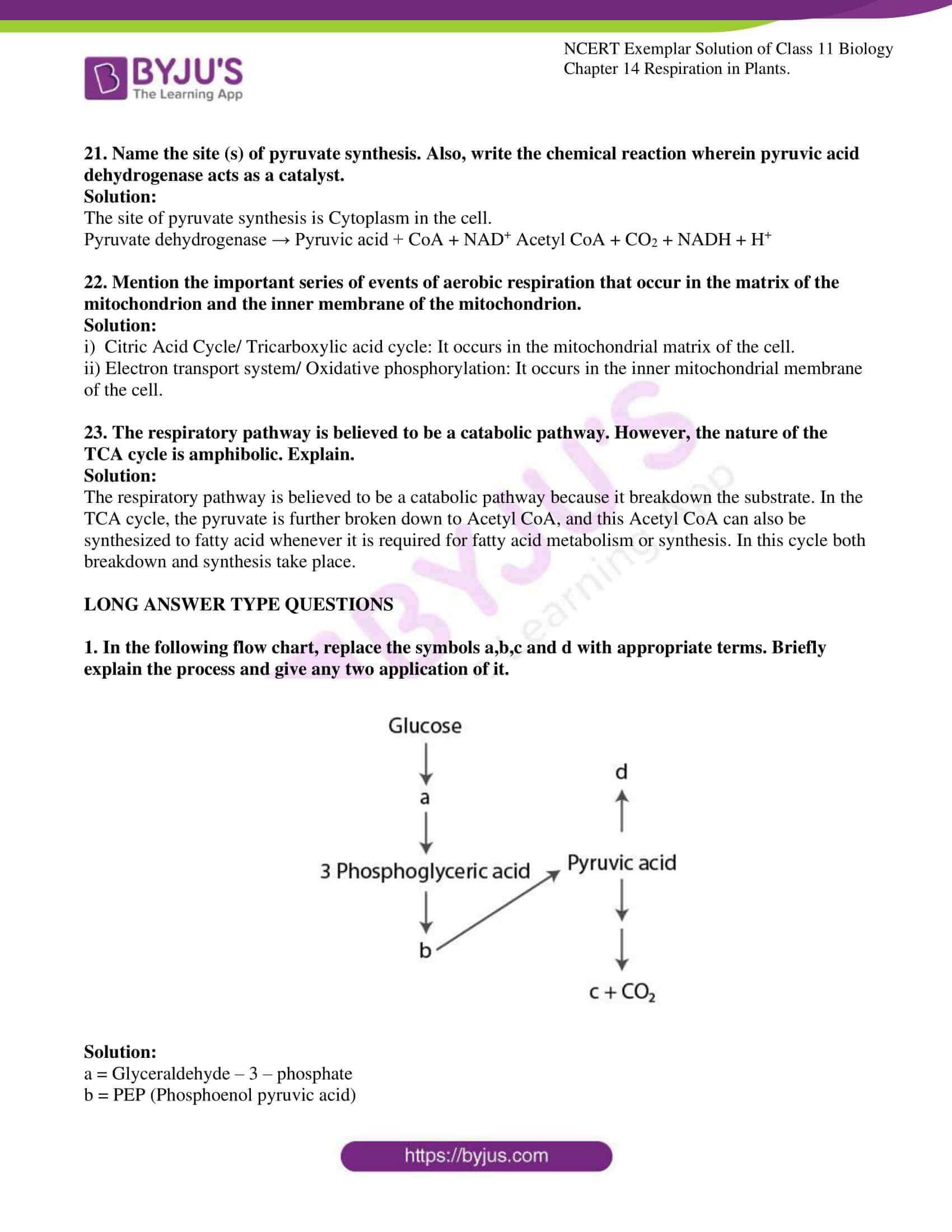
1. In the following flow chart, replace the symbols a,b,c and d with appropriate terms. Briefly explain the process and give any two application of it.

Solution:
a = Glyceraldehyde – 3 – phosphate
b = PEP (Phosphoenol pyruvic acid)
c = C2H5OH
d = Lactic acid
The process is fermentation. Aerobic conditions are present in the cell. When there are anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid gets converted to either lactic acid and it is known as homolactic fermentation. In some micro-organisms which are naturally anaerobic like yeast. They form C2H5OH and release CO2. This is known as alcoholic fermentation.
Application:
i) Fermentation is widely used for the production of alcoholic beverage products like Whisky, Beer, etc.
ii) Fermentation is widely used for the production of acids like citrus acid, lactic acid, alpha-amylase, etc.
2. Given below is a diagram showing ATP synthesis during aerobic respiration, replace the symbols A, B, C, D and E by appropriate terms given in the box.

F1, Particle, Pi, 2H+, Inner mitochondrial membrane, ATP, F0 particle, ADP
Solution:
A = ATP
B = F1 particle
C = Pi
D = 2H+
E = inner mitochondrial membrane
3. Oxygen is critical for aerobic respiration. Explain its role concerning ETS.
Solution:
Oxygen plays a crucial role at the end of ETC because it removes the hydrogen from the electron transport system. It acts as a hydrogen acceptor in the electron transport chain. If oxygen is absent then the transportation of electron will not happen through the coenzymes and there will be no formation of proton pump and ATP will not be produced by oxidative phosphorylation.
4. Enumerate the assumptions that we undertake in making the respiratory balance sheet. Are these assumptions valid for a living system? Compare fermentation and aerobic respiration in this context.
Solution:
The metabolic pathway for respiration is sequential as Glycolysis Kreb’s Cycle Electron transport system. Each of them occurs one after the other in sequential order.
i) The NADH which is synthesized during the glycolysis process is taken from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria of the cell, where oxidation occurs along with electron transport.
ii) The intermediate which is formed by the various biochemical respiration pathways is not used as raw material for any other respiration pathway.
iii) Glucose is the sole respiratory substrate, and no other substrate can enter the glycolytic pathway at any particular step of the process.
Fermentation is the partial breakdown of glucose molecule whereas aerobic respiration is the complete oxidation of the glucose molecule.
In fermentation, the end product will be organic compounds whereas in aerobic respiration the end product will be carbon dioxide and water
5. Give an account of Glycolysis. Where does it occur? What is the end product? Trace the fate of these products in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Solution:
Glycolysis is the process which involves the splitting of glucose (a 6C compound) into two molecules of pyruvic acid (a 3C compound). It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. The end products of glycolysis are two pyruvates (pyruvic acid) molecules, a total of four ATP molecules, and two molecules of NADH. Glycolysis occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic organisms. After glycolysis, if the cells have oxygen, then it goes on to a process known as a citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic cycle. And if there is no oxygen, then the fermentation process occurs.
Through respiration, plants obtain energy. Glucose is one of the major food compounds, which breaks down to form carbon dioxide and water, in the presence of oxygen. Respiration primarily occurs through the leaves and the roots of the plant; it is essential for the survival of plants. Stomata are the tiny pores present on the surface of leaves of plants, through which gas exchange occurs.
Important Topics of Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants
- Do Plants Breathe?
- Glycolysis
- Fermentation
- Aerobic Respiration
- Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
- Electron Transport System (ETS) and Oxidative Phosphorylation
- The Respiratory Balance Sheet
- Amphibolic Pathway
- Respiratory Quotient
| Also Access |
| NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 |
| CBSE Notes for Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 |
Why Opt for BYJU’S
BYJU’S provides quality educational materials for CBSE students of all subjects and classes. Our study materials help you in boosting your preparation and get well-versed in concepts to pass your exam with flying colours.
NCERT Exemplars provided by us will help you grasp topics thoroughly and make you well-equipped to write answers for all kinds of possible questions.












Comments