NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 12 – Free PDF Download
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 12 Introduction to Graphs are provided here in PDF so that students can practise them for exams. These exemplars are designed by the subject experts at BYJU’S with respect to the latest CBSE syllabus (2023-2024) for Class 8. In this chapter, students will be introduced to graphs and how to represent data on a graph. Along with this, they will also learn about the x-axis and y-axis of a graph. To learn how to draw graphs, students are advised to solve problems related to the graph from NCERT Exemplar for Class 8 Maths Chapter 12 Introduction to Graphs. BYJU’S provides exemplar solutions for all types of problems based on graphs.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 12 Introduction to Graphs:-Download PDF
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 12 Introduction to Graphs
In questions 1 to 10, there are four options, out of which one is correct.
Write the correct answer.
1. Comparison of parts of a whole may be done by a
(a) Bar graph (b) pie chart (c) linear graph (d) line graph
Solution: The correct answer is option (b) Pie chart
Explanation:
A pie chart is used to compare the parts of a whole because the circle represents the whole.
2. A graph that displays data that changes continuously over periods of time is
(a) Bar graph (b) pie chart (c) histogram (d) line graph
Solution: The correct answer is option (d) Line graph
Explanation:
A line graph displays the continuous change of data over a period of time, like speed or distance covered.
3. In the given graph, the coordinates of point x are
(a) (0, 2) (b) (2, 3) (c) (3, 2) (d) (3, 0)

Solution: The correct answer is option (c) (3, 2)
Explanation:
To find the coordinate, draw the perpendicular line from point x to the x-axis and y from the y-axis. From the given figure, the coordinate of the x-axis is 3, and the coordinate of the y-axis is 2.
Hence, the coordinate of x is (3, 2)
4. In the given graph, the letter that indicates the point (0, 3) is
(a) P (b) Q (c) R (d) S

Solution: The correct answer is option (c) R
Explanation:
From the given figure, the coordinates of S is (3, 3), the coordinates of P is (3, 0), and the Coordinates of R is (0, 3)
Hence, option c is correct.
5. Point (3, 4) is at a distance of
(a) 3 from both the axis (b) 4 from both the axis
(c) 4 from the x axis and 3 from y axis (d) 3 from x axis and from y axis
Solution: The correct answer is option (c) 4 from the x-axis and 3 from y-axis
Explanation:
In the coordinate (3, 4), the first number represents the distance on the x-axis or y-coordinate, whereas the second number, 4, represents the distance on the y-axis or the x-coordinate.
6. A point which lies on both the axis is __________
(a) (0, 0) (b) (0, 1) (c) (1, 0) (d) (1, 1)
Solution: The correct answer is option (a)
Explanation:
Both the x-axis and y-axis are perpendicular to each other, and they meet at a single point called the origin (0, 0)
7. The coordinates of a point at a distance of 3 units from the x-axis and 6 units from the y-axis is
(a) (0, 3) (b) (6, 0) (c) (3, 6) (d) (6, 3)
Solution: The correct answer is option (d) (6, 3)
Explanation:
It is known that the distance from the x-axis gives the y-coordinate, and the distance from the y-axis gives the x-coordinate. Hence, the coordinate point is (6, 3).
8. In the given figure, the position of the book on the table may be given by
(a) (7, 3) (b) (3, 7)
(c) (3, 3) (d) (7, 7)

Solution: The correct answer is option (b) (3, 7)
Explanation:
The book is positioned at a distance of 3 units from the y-axis and 7 units from the x-axis. Hence, the required coordinate point is (3, 7).
9. Data was collected on a student’s typing rate, and the graph was drawn as shown below. Approximately how many words had this student typed in 30 seconds?
(a) 20 (b) 24 (c) 28 (d) 34

Solution: The correct answer is option (c) 28
Explanation:
From the given graph, the time (in sec) is taken in the x-axis and the number of words in the y-axis. When the look for the line graph to find the number of words corresponding to 30 seconds in the x-axis, the words typed in 30 seconds come out is approximately 28 words.
10. Which graphs of the following represent the table below?
| Length of Side of a Square | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Perimeter | 4 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 20 |


Solution: The correct answer is option (d)
Explanation:
It is given that the x-axis represents the length of the square side, and the y-axis represents the perimeter. When you plot the given points in the graph, the answer should be option (d).
In questions 11 to 25, fill in the blanks to make the statements true.
11. __________ displays data that changes continuously over periods of time.
Solution: Line Graph
Explanation:
Line graph displays the relationship between the constantly varying quantities
12. The relation between dependent and independent variables is shown through a __________.
Solution: Graph
Explanation:
The graph defines the relationship between the two variables, where one is the dependent variable and the other one is the independent variable.
13. We need __________ coordinates to represent a point on the graph sheet.
Solution: two (a pair)
Explanation:
To represent the point on the graph, we need a pair of coordinates, where one represents the x coordinate and the other represents the y coordinate.
14. A point in which the x-coordinate is zero and the y-coordinate is nonzero will lie on the _________
Solution: y-axis
Explanation:
The point lies on the y-axis when the x-coordinate is zero.
15. The horizontal and vertical lines in a line graph are usually called
__________ and __________.
Solution: x-axis and y-axis
16. The process of fixing a point with the help of the coordinates is known as __________ of the point.
Solution: Plotting
Explanation:
The process of fixing the point using the coordinates is known as the plotting of points on a graph.
17. The distance of any point from the y-axis is the __________ coordinate.
Solution: x coordinate
Explanation:
The distance of any point from the x-axis is called the y-coordinate, and the distance of any point from the y-axis is called the x-coordinate.
18. All points with y-coordinate as zero lies on the __________.
Solution: x-axis
Explanation:
When all the points on the y coordinate are zero, then absolutely all the points lie on the x-axis.
19. For point (5, 2), the distance from the x-axis is __________ units.
Solution: 2 units.
Explanation:
We know that the y-coordinate represents the distance from the x-axis. So the answer is 2 units.
20. The x-coordinate of any point lying on the y-axis will be __________.
Solution: zero (0)
Explanation:
When the x-coordinate lies on the y-axis, then the x-coordinate of any point on the y-axis should be zero.
21. The y-coordinate of the point (2, 4) is __________.
Solution: 4 units.
Explanation:
In the ordered pair, the first number always represents the x coordinate, and the second number represents the y coordinate. Hence, the y coordinate is 4 units.
22. In the point (4, 7), 4 denotes the __________.
Solution: x- coordinate.
Explanation:
The first number in the ordered pair represents the x-coordinate, and the second number represents the y- coordinate.
23. A point has 5 as its x – coordinate and 4 as its y–coordinate. Then the coordinates of the point are given by __________.
Solution: (5, 4)
Explanation:
The point is represented using the ordered pair = (x coordinate, y coordinate)
24. In the coordinates of a point, the second number denotes the
__________.
Solution: y coordinate
Explanation:
The second number in the coordinate point represents the y coordinate.
25. The point where the two axes intersect is called the __________.
Solution: Origin (0, 0)
Explanation:
The two axis intersects at a common point in the graph is called the origin.
In questions 26 to 34, state whether the statements are true (T) or false (F).
26. For fixing a point on the graph sheet, we need two coordinates.
Solution: True
Explanation:
For plotting a point, we need two coordinates, the x coordinate and the y coordinate.
27. A line graph can also be a whole unbroken line.
Solution: False
Explanation:
A graph which has whole unbroken lines is called a linear graph.
28. The distance of any point from the x-axis is called the x-coordinate.
Solution: False
Explanation:
The distance of any point from the x-axis is called the y-coordinate
29. The distance of the point (3, 5) from the y-axis is 5.
Solution: False
Explanation:
The distance of the point (3, 5) from the y-axis is 3 and from x-axis is 5
30. The ordinate of a point is its distance from the y-axis.
Solution: False
Explanation:
The ordinate is also known as the y-coordinate, where it is defined as a distance from the x-axis
31. In the point (2, 3), 3 denotes the y-coordinate.
Solution: True
Explanation:
From the given point,
(2, 3) = (x coordinate, y coordinate)
32. The coordinates of the origin are (0, 0).
Solution: True
Explanation:
Both the axis, such as x-axis and y-axis intersects with each other when the coordinates of x and y are 0 and 0, respectively.
33. Points (3, 5) and (5, 3) represent the same point.
Solution: False
Explanation:
Points (3, 5) and (5, 3) do not represent the same point.
From point (3, 5), the x coordinate is 3, and the y coordinate is 5
From point (5, 3), the x coordinate is 5, and the y coordinate is 3
When these points are plotted in a graph, you will get a different graph.
34. The y-coordinate of any point lying on the x-axis will be zero.
Solution: True
Explanation:
For any y coordinate point, when it lies on the x-axis, then the y coordinate should be zero. For example, (5, 0) and (7, 0), when these points are plotted in the graph, both points will lie on the x-axis.
35. Match the coordinates given in Column A with the items mentioned
in Column B.
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) (0, 5) | (a) y coordinate is 2 × x – coordinate + 1. |
| (2) (2, 3) | (b) Coordinates of origin. |
| (3) (4, 8) | (c) Only y–coordinate is zero. |
| (4) (3, 7) | (d) The distance from x –axis is 5. |
| (5) (0, 0) | (e) y coordinate is double of the x-coordinate. |
| (6) (5, 0) | (f) The distance from y–the axis is 2. |
Solution:
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) (0, 5) | (d) the distance from the x-axis is 5. |
| (2) (2, 3) | (f) the distance from the y-axis is 2. |
| (3) (4, 8) | (e) y coordinate is double of x–the coordinate. |
| (4) (3, 7) | (a) y coordinate is 2 × x – coordinate + 1. |
| (5) (0, 0) | (b) Coordinates of origin. |
| (6) (5, 0) | (c) Only the y-coordinate is zero |
36. Match the ordinates of the points given in Column A with the items mentioned in Column B.
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) (7, 0) | (i) the ordinate is double the abscissa. |
| (b) (11, 11) | (ii) the ordinate is zero. |
| (c) (4, 8) | (iii) the ordinate is equal to the abscissa. |
| (d) (6, 2) | (iv) The abscissa is double the ordinate. |
| (e) (0, 9) | (v) the abscissa is triple the ordinate. |
| (f) (6, 3) | (vi) The abscissa is zero |
Solution:
Here, x coordinate represents the abscissa and y coordinate represents the ordinate.
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) (7, 0) | (ii) The ordinate is zero |
| (b) (11, 11) | (iii) the ordinate is equal to the abscissa |
| (c) (4, 8) | (i) the ordinate is double the abscissa. |
| (d) (6, 2) | (v) the abscissa is triple the ordinate. |
| (e) (0, 9) | (vi) The abscissa is zero. |
| (f) (6, 3) | (iv) The abscissa is double the ordinate |
37. From the given graph, choose the letters that indicate the location of the points given below.
(a) (2, 0) (b) (0, 4) (c) (5, 1) (d) (2, 6) (e) (3,3)

Solution:
From the given graph, the letters that indicate the location of the point is given below:
A indicates the points: (0, 4)
B indicates the points: (1, 5)
C indicates the points: (2, 6)
D indicates the points: (0, 2)
E indicates the points: (3, 3)
F indicates the points: (2, 0)
38. Find the coordinates of all letters in the graph given below.

Solution:
From the given graph, the coordinates of the given letters are:
A Coordinates = (0, 7.5)
B Coordinates = (4, 5)
C Coordinates = (7.5, 2.5)
D Coordinates = (11, 0)
E Coordinates = (14.5, 6.5)
F Coordinates = (18, 9.5)
39. Plot the given points on a graph sheet.
(a) (5, 4) (b) (2, 0) (c) (3, 1) (d) (0, 4) (e) (4,5)
Solution:
First, draw the x and y axis, and plot the given points.
The given points are A = (5, 4), B = (2, 0), C = (3, 1), D = (0, 4) and E = (4, 5)

40. Study the given map of a zoo and answer the following questions.

(a) Give the location of the lions in the zoo.
(b) (D, f) and (C, d) represent the locations of which animals in the zoo.
(c) Where are the toilets located?
(d) Give the location of the canteen.
Solution:
(a) The location of lions in the zoo is (A, f)
(b) (D, f) and (C, d) represent the locations of the Monkey and elephant, respectively
(c) The toilets are located in (0, e)
(d) The location of the canteen is (C, c)
41. Write the x -coordinate (abscissa) of each of the given points.
(a) (7, 3) (b) (5, 7) (c) (0, 5)
Solution:
We know that the abscissa represents the x coordinate in the ordered pair.
For the given points, the abscissa is as follows:
(a) (7, 3) – 7 is the abscissa
(b) (5, 7) – 5 is the abscissa
(c) (0, 5) – 0 is the abscissa
42. Write the y-coordinate (ordinate) of each of the given points.
(a) (3, 5) (b) (4, 0) (c) (2, 7)
Solution:
We know that the ordinate represents the y coordinate in the ordered pair.
For the given points, the ordinate is as follows:
(a) (3, 5) – 5 is the ordinate
(b) (4, 0) – 0 is the ordinate
(c) (2, 7) – 7 is the ordinate
43. Plot the given points on a graph sheet and check if the points lie on a straight line. If not, name the shape they form when joined in the given order.
(a) (1, 2), (2, 4), (3, 6), (4, 8).
(b) (1, 1), (1, 2), (2, 1), (2, 2).
(c) (4, 2), (2, 4), (3, 3), (5, 4).
Solution:
(a) For the given points, (1, 2), (2, 4), (3, 6), (4, 8), the obtained graph is given below:

All the points lie on the straight line.
(b) For the given points, (1, 1), (1, 2), (2, 1), (2, 2), the obtained graph is given below:

No, the points do not form a straight line. They form a square.
(c) For the given points, (4, 2), (2, 4), (3, 3), (5, 4), the obtained graph is given below:

The given points do not lie in a straight line. When the points are joined in the given order (also AD), a triangle is formed.
44. If y–coordinate is 3 times x -coordinate, form a table for it and draw a graph.
Solution:
Given that y = 3x
Let x = 1, 2, 3, 4
The corresponding y-coordinate values are given as follows:
When x = 1, y= 3(1) = 3 ⇒ (1, 3)
When x = 2, y= 3(2) = 6 ⇒ (2, 6)
When x = 3, y= 3(3) = 9 ⇒ (3, 9)
When x = 4, y= 3(4) = 12 ⇒ (4, 12)
Hence, the obtained points are:
(1, 3), (2, 6), (3, 9) and (4, 12)
The graph for the above-given points is:

45. Make a line graph for the area of a square as per the given table
| Side (in cm) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Area (in cm2) | 1 | 4 | 9 | 16 |
Is it a linear graph?
Solution:
From the given table, the coordinates are taken as:
(1, 1), (2, 4), (3, 9), (4, 16)
The graph for the given points are:

Here, the x-axis represents the square side, and the y-axis represents the area of a square.
From the given graph, it is shown that it is not a linear graph because the points are not in the same line (not collinear).
Hence, it is not a linear graph.
46. The cost of a notebook is Rs. 10. Draw a graph after making a table showing the cost of 2, 3, 4 … Notebooks. Use it to find
(a) The cost of 7 notebooks.
(b) The number of notebooks that can be purchased with Rs 50.
Solution:
It is given that the cost of one notebook is Rs.10
(a) Hence, the cost of 7 notebooks is 7×10 = 70 rs
(b) To find the number of notebooks that can be purchased for Rs. 50 is
= 50/10
= 5
Hence, the number of notebooks for Rs. 50 is 5.
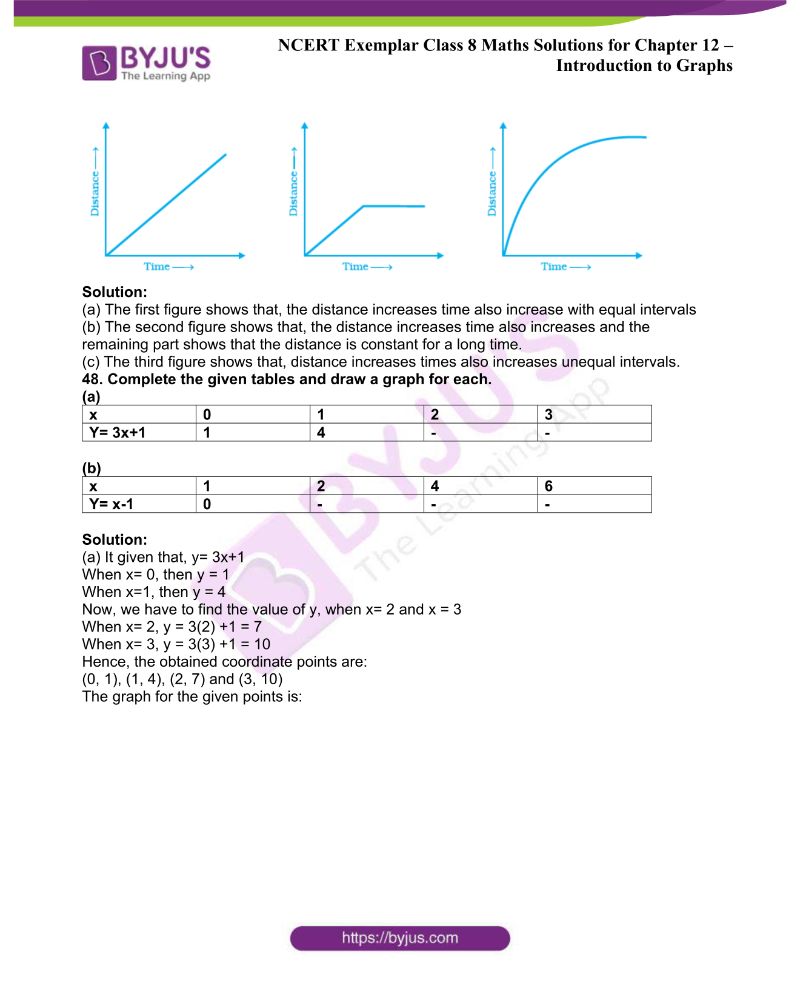
47. Explain the situations represented by the following distance-time graphs.

Solution:
(a) The first figure shows that the distance increases time also increases with equal intervals
(b) The second figure shows that the distance increases as time also increases, and the remaining part shows that the distance is constant for a long time.
(c) The third figure shows that the distance increases times also increases unequal intervals.
48. Complete the given tables and draw a graph for each.
(a)
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Y= 3x+1 | 1 | 4 | – | – |
(b)
| x | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| Y= x-1 | 0 | – | – | – |
Solution:
(a) It is given that y = 3x+1
When x= 0, then y = 1
When x=1, then y = 4
Now, we have to find the value of y, when x= 2 and x = 3
When x= 2, y = 3(2) +1 = 7
When x= 3, y = 3(3) +1 = 10
Hence, the obtained coordinate points are:
(0, 1), (1, 4), (2, 7) and (3, 10)
The graph for the given points is:

(b) It is given that y= x-1
When x= 1, then y = 0
Now, we have to find the value of y when x= 2, 4, 6,
When x= 2, y = 2 -1 = 1
When x= 4, y = 4- 1 = 3
When x= 6, y = 6- 1 = 5
Hence, the obtained coordinate points are:
(1, 0), (2, 1), (4, 3) and (6, 5)
The graph for the given points is:

49. Study the given graphs (a) and (b) and complete the corresponding tables below

(a)
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| y |
(b)
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Y |
Solution:
(a) From the given graph, the y coordinates of the first table are given as:
Let’s take x = 1, now draw a line parallel to the y-axis at 1, and check whether where it cuts the graph. So we get y=4
Similarly, for other x values, repeat the procedure.
Then, the coordinates are given in the table as follows:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| y | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
(b) From the given graph, the y-coordinates of the first table are given as:
Let’s take x = 1, now draw a line parallel to the y-axis at 1, and check whether where it cuts the graph. So we get y=1
Similarly, for other x values, repeat the procedure.
Then the coordinates are given in the table as follows:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Y | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
50. Draw a graph for the radius and circumference of a circle using a suitable scale.
(Hint: Take radius = 7, 14, 21 units and so on)
From the graph,
(a) Find the circumference of the circle when the radius is 42 units.
(b) At what radius will the circumference of the circle be 220 units?
Solution:
We know that the circumference of a circle is 2πr. The radius depends on the circumference of a circle.
So, now we have to plot the radius on the x-axis and the circumference on the y-axis. Because the radius is an independent variable and the circumference is a dependent variable.
Now, the equations in terms of x and y are given as:
y = 2πx
When x= 0, then y = 2π (0) = 0
When x= 7, then y = 2π (7) = 44
When x= 14, then y = 2π (14) = 88
When x= 21, then y = 2π (21) = 132
Hence, the coordinates are (0, 0), (7, 44, (14, 88) and (21, 132)
The graph of the points are:

(a) When the radius is 42 units, from the graph, the value of y (circumference) is 264
(b) From the graph, it is obtained that when the circumference is 220, the value of the radius is 35 units.
| Also Access |
| NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 12 |
| CBSE Notes for Class 8 Maths Chapter 12 |
Solve NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths, along with exemplars, to get better practice for the annual exam. Also, get notes, exemplar books, and question papers to prepare well for the final examination. Students are suggested to solve sample papers and previous years’ question papers to get an idea of the types of questions asked in the exam from the chapter, Introduction to Graphs.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 12
What is the main aim of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 12?
What are the key benefits of learning NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 12?
1. Students can easily access the solutions for exercise questions in each chapter.
2. The solutions also provide graphs and illustrations that will help them understand the concepts clearly.
3. These solutions are prepared by BYJU’S expert team focussing on accuracy.
Is NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 12 enough to prepare for the annual exams?
Also Check




















Comments