Fossil Fuels
A majority of the world’s energy is provided by a few members of the conventional sources of energy: Fossil Fuels. Fossil fuels are natural energy sources formed by processes such as the decomposition of buried organic matter. The decomposing matter is buried deep underneath the surface over time and is exposed to heat and pressure in the earth’s crust for millions of years. Fossil fuels consist mainly of carbon-rich fuels such as coal, petroleum and natural gas. In the pie chart below, you will see that fossil fuels amount to almost 80% of the energy produced on Earth. Fossil fuels are used for heating stoves in villages to huge power plants that generate enough electricity for millions of people. So how is energy extracted from fossil fuels? Sometimes it can be used directly in the case of gas stoves and automobiles, but most of the time, fossil fuels are used to generate electricity. Let’s see how.

Thermal Power Plant
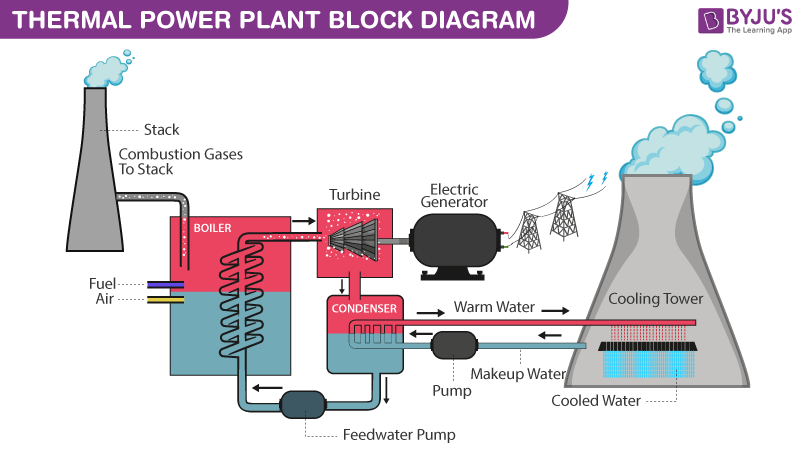
The thermal Power plant is a power generation station which burns fossil fuels like coal, petroleum etc., to produce electricity. It does so by utilizing the chemical energy stored in the fuel, burning it and then converting it into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is utilized to operate an electrical generator to generate electricity. Such thermal power plants are designed on a large scale for continuous operation for years. The device used here to convert the thermal energy released by the fuel to mechanical energy is called a Turbine. In most thermal power plants, the fuel is used to heat water. This water on heating turns to steam which is then pressurized and used to run the turbines. Depending on the medium used to obtain mechanical energy, the turbine can be classified into Steam turbines and gas turbines.
A turbine is a long column consisting of many rows of small blades; one row of which is fixed called ‘stators’ and one row is movably called ‘rotors’, alternatively. This arrangement of blades is mounted on a rotating horizontal axis, one end of which is connected to the electrical generator. The movement of the turbine results in the generation of electricity. Now pressurized steam is let out into the row of blades. The impulse of the hot pressurized gas on the rotating blades makes the blades go round. This movement is transferred via a shaft to the generator, which converts the mechanical energy to electrical. The typical efficiency for large-scale thermal power plants is around 20-25% for the plant using coal and oil and 40% for gas-powered turbines.
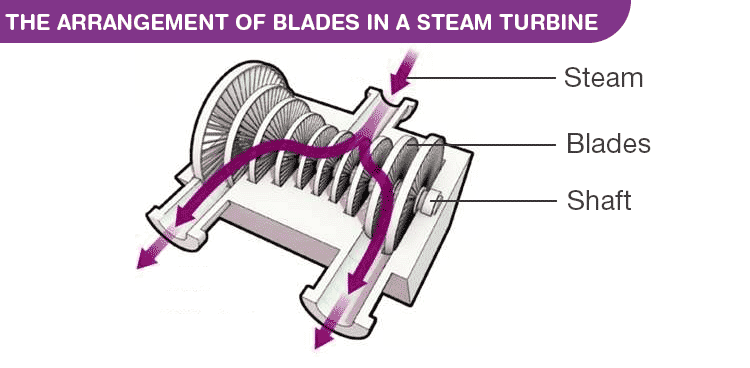
The arrangement of blades in a Steam Turbine
Read More: Natural Sources of Energy
Effect of Fossil Fuels
The world’s power demands are constantly on the rise and are expected to increase by 60% by 2030. There are 50,000 active coal plants worldwide and growing. Fossil fuel share in energy production is also expected to rise with 85% of the energy generated by fossil fuel by 2030. The combined carbon emission of thermal power plants in the world is enormous, almost twice the amount that can be removed from the atmosphere through natural processes. Out of the three conventional sources of energy, coal is the most inefficient and polluting. Our energy needs are increasing at an alarming rate, and the solution in sight is using coal unreservedly. This will only lead to more problems and hence it is imperative that we switch to less-polluting sources of energy.

Thank you, sir. Really Good Information