Magnetic Effect of Electric Current – A magnetic field is a force field that is created by magnetic dipoles and moving electric charges, and it exerts a force on other nearby moving charges and magnetic dipoles. Magnetic Field is a vector quantity because it has both magnitude and direction.
| Table of Contents: |
Magnetic Field Lines
A magnetic field line or lines of forces shows the strength of a magnet and the direction of a magnet’s force. It was discovered by Michael Faraday to visualise the magnetic field.
Direction of Field Lines
Magnetic field lines are directed from the south pole to the north pole inside the magnet and from the north pole to the south outside the magnet.
Strength of Magnetic Field Lines
A straight current-carrying conductor has a magnetic field in the shape of concentric circles around it. Magnetic field lines can visualise the magnetic field of a straight current-carrying conductor.
The direction of a magnetic field produced due to a current-carrying conductor relies upon the same direction in which the current is flowing.
The direction of the magnetic field gets reversed if the direction of the electric current changes.
Let Us Understand Magnetic Effect of Electric Current Using a Simple Experiment:

Suppose a straight current-carrying conductor is hung vertically, and an electric current is flowing from north to south, i.e. from up to down. In this situation, the direction of the magnetic field will be clockwise. And if the same current is flowing from south to north through the same conductor, the direction of the magnetic field will be anti-clockwise.
The direction of the magnetic field in electric current through a straight conductor can be represented by using the Right-Hand Thumb Rule.

Watch the video and solve the NCERT exercise in the chapter Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class 10

Right-Hand Thumb rule
Assume that you are holding a straight current-carrying conductor in your right hand such that the thumb points towards the direction of the current. Then your fingers will wrap around the conductor in the direction of the magnetic field lines.
The Right-Hand Thumb rule is also known as Maxwell’s corkscrew rule. If we consider ourselves driving a corkscrew in the current direction, then the corkscrew’s direction is in the direction of the magnetic field.

Magnetic Field Due to Flow of Current through a Circular Loop
The magnetic field produced in a circular current carrying conductor is the same as that of the magnetic field due to a straight current-carrying conductor and the current-carrying circular loop will behave like a magnet.
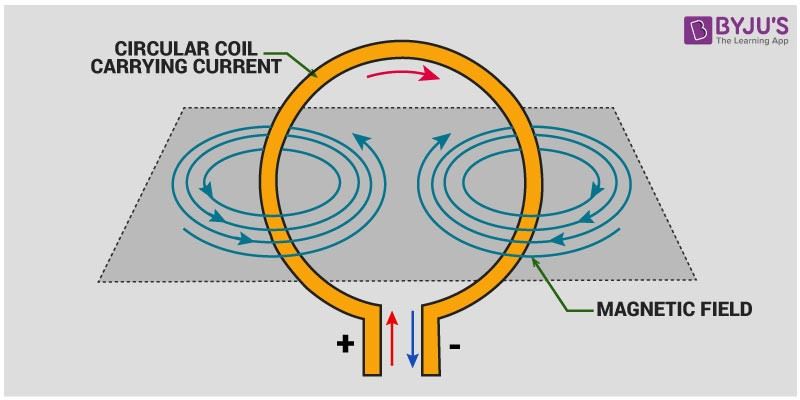
The magnetic field lines in a current-carrying circular loop would be in the shape of concentric circles, and at the centre of the circular wire, field lines will become straight and perpendicular to the plane of the coil.
The direction of the magnetic field in a circular loop can be recognised using the Right-Hand Thumb Rule.
Magnetic Field Due to Flow of Current in a Solenoid
A solenoid is a tightly wound helical coil of wire whose diameter is smaller than its length.

The magnetic field produced by the current-carrying solenoid is similar to a bar magnet. The magnetic field produced inside a solenoid is parallel which is similar to a bar magnet. One solenoid end behaves as a south pole, and the other end behaves as a north pole.
The strong magnetic force produced by a solenoid can be used to magnetize a piece of magnetic material. The magnet so formed is known as an electromagnet.
Direct Current
- Direct Current is the unidirectional flow of electric current. The flow of current does not change periodically. In the case of direct current, the current flows in a single direction at a steady voltage.
- Direct current power is widely used in low voltage applications such as charging batteries and light aircraft electrical systems.
- A direct current can be obtained from an alternating current using a rectifier. A rectifier contains electronic elements or electromechanical elements that allow current to flow only in one direction.
- Direct current can also be converted into alternating current using a motor-generator set or an inverter.
- The direction of the magnetic field in electric current through a straight conductor can be represented by using Right-Hand Thumb Rule.
The below videos help to revise the chapter Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class 10
 |
 |
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
State Fleming’s left-hand rule.
What would be the shape of the magnetic field lines in a circular current carrying loop?
State Right Hand Thumb Rule.
The Right-Hand Thumb rule is also known as Maxwell’s corkscrew rule. If we consider ourselves driving a corkscrew in the current direction, then the corkscrew’s direction is in the direction of the magnetic field.
What is the direction of Magnetic field lines?
Watch the video and solve the previous year questions in the chapter Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class 10

Study more about Magnetic Effect of Current, Fleming’s left-hand rule and right-hand rule at BYJU’S.

Byjus is very useful to me
I love learning from byjus app as I came and learn from this app I clear all my doubts . it is a great opportunity for me from learning from this app