Building the circuit requires the knowledge of various components like resistors, inductors, capacitors, battery sources, connecting wires and more. The resistor is one of the main components of the circuit. In this session, let us know in detail about the resistor.
What is Resistor?
Resistor is defined as
A passive electrical component with two terminals that are used for either limiting or regulating the flow of electric current in electrical circuits.
The main purpose of resistor is to reduce the current flow and to lower the voltage in any particular portion of the circuit. It is made of copper wires which are coiled around a ceramic rod and the outer part of the resistor is coated with an insulating paint.
What is the SI Unit of Resistor?
The SI unit of resistor is Ohm.
Symbol of Resistor
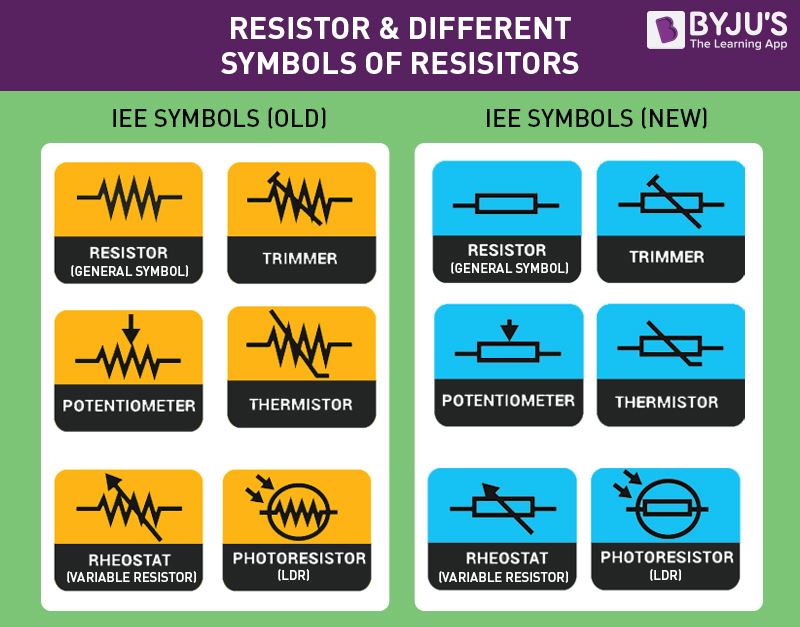
Each resistor has one connection and two terminals. We will look at the three types of symbols that are used to represent the resistor.


The terminals of the resistor are each of the lines extending from the squiggle (or rectangle). Those are what connect to the rest of the circuit. The resistor circuit symbols are usually enhanced with both a resistance value and a name. The value, displayed in ohms, is obviously critical for both evaluating and actually constructing the circuit.
Related articles:
Types of Resistors
Resistors are available in different shapes and sizes. Common types that are available are through-hole and surface mount. A resistor might be static, standard resistor, special, or a pack of variable resistors.
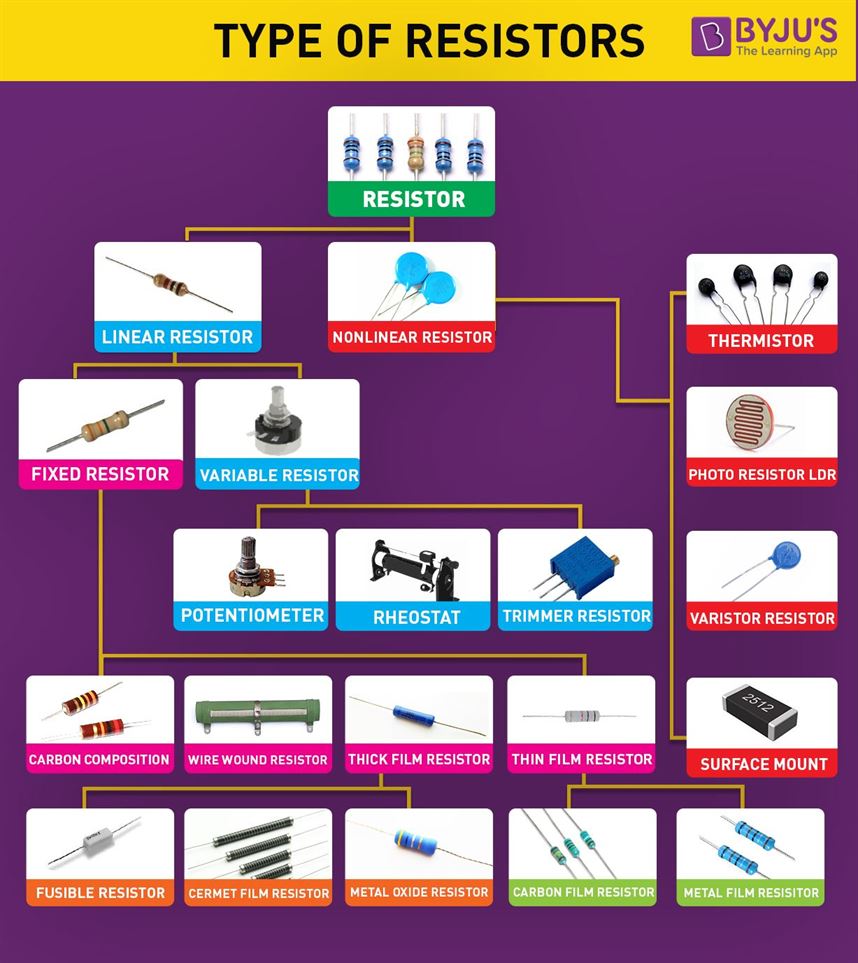
There are two basic types of resistors as follows:
- Linear resistor
- Non-linear resistor
Linear resistors
The resistors whose values change with change in applied temperature and voltage are known as linear resistors. There are two types of linear resistors:
Fixed resistors: These resistors have a specific value and these values cannot be changed. Following are the different types of fixed resistors:
- Carbon composition resistors
- Wire wound resistors
- Thin film resistors
- Thick film resistors
Variable resistors: These resistors do not have a specific value and the values can be changed with the help of dial, knob, and screw. These resistors find applications in radio receivers for controlling volume and tone. Following are the different types of variable resistors:
- Potentiometers
- Rheostats
- Trimmers
Non-linear resistors
The resistor values change according to the temperature and voltage applied and is not dependent on Ohm’s law. Following are the different types of non-linear resistors:
- Thermisters
- Varisters
- Photo resistors

What is Colour Coding of Resistors?
Resistors may not display the value outside but their resistance can be calculated through their colour pattern PTH (plated-through-hole) resistors use a colour-coding system (which really adds some flair to circuits), and SMD (surface-mount-device)resistors have their own value-marking system.
Following is a table with colour code of resistors:
| Colour | Colour code |
| Black | 0 |
| Brown | 1 |
| Red | 2 |
| Orange | 3 |
| Yellow | 4 |
| Green | 5 |
| Blue | 6 |
| Violet | 7 |
| Grey | 8 |
| White | 9 |
What is Tolerance in Resistors?
Following is a table with tolerance of resistor:
| Colour | Tolerance |
| Brown | ±1% |
| Red | ±2% |
| Gold | ±5% |
| Silver | ±10% |
Resistors in Series
Resistors are said to be in series when the current flowing through all the resistors is the same. These resistors are connected from head to tail in series. The overall resistance of the circuit is equal to the sum of individual resistance values.
Resistors in Series Formula
| Rtotal = R1 + R2 + R3 +……+Rn |
Where,
- Rtotal is the sum of reciprocal of all the individual resistances
Resistors in Parallel
Resistors are said to be in parallel when the terminals of resistors are connected to the same two nodes. Resistors in parallel share the same voltage at their terminals.
Resistors in Parallel Formula
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{1}{R_{total}}=\frac{1}{R_{1}}+\frac{1}{R_{2}}+…..+\frac{1}{R_{n}}\end{array} \) |
Where,
- \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{1}{R_{total}}\,\,is\,\, the \,\,sum\,\, of\,\, all \,\,the\,\, individual\,\, resistances.\end{array} \)
Applications of Resistor
Following are the applications of resistors:
- Wire wound resistors find applications where balanced current control, high sensitivity, and accurate measurement are required like in shunt with ampere meter.
- Photoresistors find application in flame detectors, burglar alarms, in photographic devices, etc.
- Resistors are used for controlling temperature and voltmeter.
- Resistors are used in digital multi-meter, amplifiers, telecommunication, and oscillators.
- They are also used in modulators, demodulators, and transmitters.
Watch the video and solve important questions in the chapter Electricity Class 10

Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is a resistor?
Resistor is a passive two terminals electrical component used for limiting or regulating the flow of electricity in a circuit.
What is the SI unit of resistor?
The SI unit of resistor is Ohm.
What are the two types of resistors?
What are various types of non-linear resistors?
Which type of resistor is used in photographic devices?
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more interesting science topics with engaging videos!


Comments