1
Question
What is the electrophile in nitration of benzene reaction?
What is the electrophile in nitration of benzene reaction?
Open in App
Solution
Electrophiles:
- A reagent that takes away an electron pair is called electrophiles and it is represented as .
- Electrophiles are electron-deficient molecules that attack at nucleophilic centre of the substrate which is an electron-rich molecule.
Nitration of benzene:
- It is an electrophilic substitution reaction in which a nitro group is introduced into benzene ring when it is heated with a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid.
- In this reaction, when benzene is treated with concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid, it results in the formation of nitrobenzene.
- The nitration of benzene reaction is shown below in the image.

Mechanism for nitration of benzene:
- Sulfuric acid donates a proton to nitric acid, which subsequently dissociates to produce the nitronium ion .
- The process involves the nitronium ion acting as an electrophile, which then interacts with benzene to produce an arenium ion.
- The Lewis base then absorbs the arenium ion's proton, forming nitrobenzene.

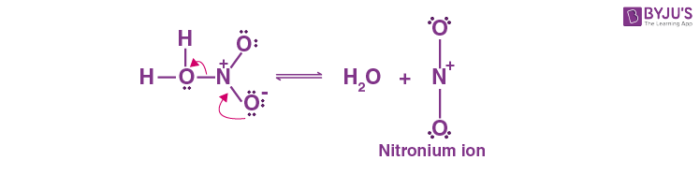
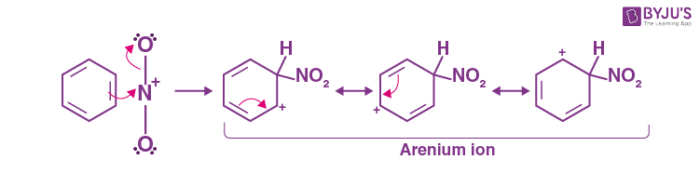
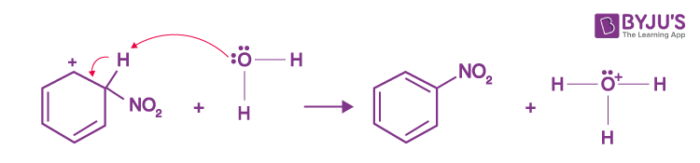
Thus, the electrophile in nitration of benzene reaction is nitronium ion .
Electrophiles:
- A reagent that takes away an electron pair is called electrophiles and it is represented as .
- Electrophiles are electron-deficient molecules that attack at nucleophilic centre of the substrate which is an electron-rich molecule.
Nitration of benzene:
- It is an electrophilic substitution reaction in which a nitro group is introduced into benzene ring when it is heated with a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid.
- In this reaction, when benzene is treated with concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid, it results in the formation of nitrobenzene.
- The nitration of benzene reaction is shown below in the image.

Mechanism for nitration of benzene:
- Sulfuric acid donates a proton to nitric acid, which subsequently dissociates to produce the nitronium ion .
- The process involves the nitronium ion acting as an electrophile, which then interacts with benzene to produce an arenium ion.
- The Lewis base then absorbs the arenium ion's proton, forming nitrobenzene.




Thus, the electrophile in nitration of benzene reaction is nitronium ion .
Suggest Corrections
9
View More
Join BYJU'S Learning Program
Join BYJU'S Learning Program
