Like any Science subject, practical plays an important role in Botany as well. It helps the students to be more acquainted with the terms, facts, concepts and principles related to the subject. TN Board Class 11 Practicals, especially help them to understand the concepts more clearly by making them perform exercises related to the concept. Here in this article below, we have tried to compile for the students of Class 11, the experiments and activities from the Tamil Nadu Board Class 11 Botany Practicals.
TN Board Class 11 Botany Practicals
These experiments and practical activities are designed to help make difficult and abstract concepts more real, remove misconceptions and even increase as well as sustain the interest of students in the subject. For this reason, the Tamil Nadu Board students should be taught via practical activities to acquire useful practical skills in concepts.
Download Tamil Nadu Board Class 11 Botany Practical PDF
Meanwhile, you can also have a look at the list of experiments and the index from here:
|
INDEX |
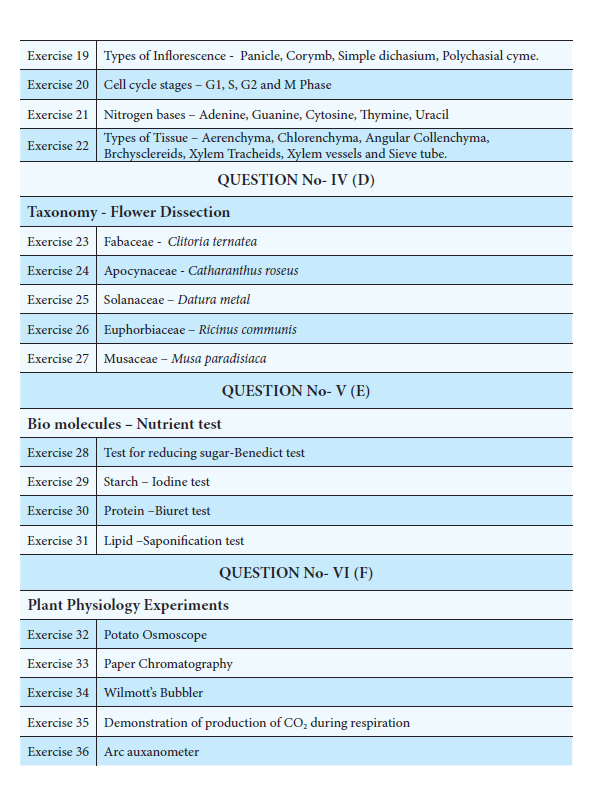
|
| Description | Pg.No |
| Introduction | 1 |
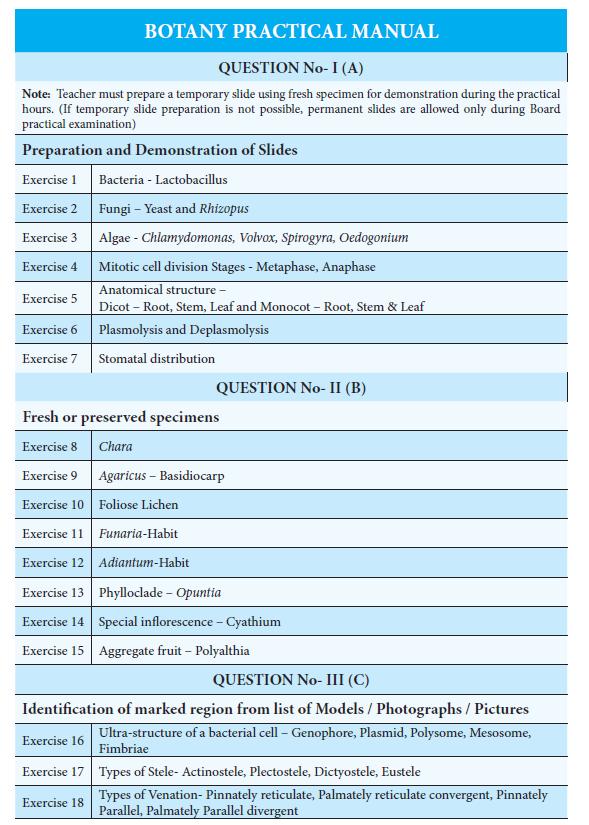
| I. Preparation and Demonstration of Slides | 10 |
| II. Fresh or Preserved Specimens | 19 |
| III. Identification of marked region from list of Models/ Photographs/Pictures | 23 |
| IV. Plant taxonomy- Flower Dissection | 31 |
| V. Bio molecules-Nutrient Test | 34 |
| VI. Plant Physiology Experiments | 36 |
Contents of Tamil Nadu Board Class 11 Biology Practical Manual
- Objectives of Biology Practicals– to train students in the scientific method of learning
- Instructions to Students
- Safety and Precautionary methods to adopt while doing the experiments
- Steps involved in performing a practical
Steps For Students To Follow While Doing Practicals
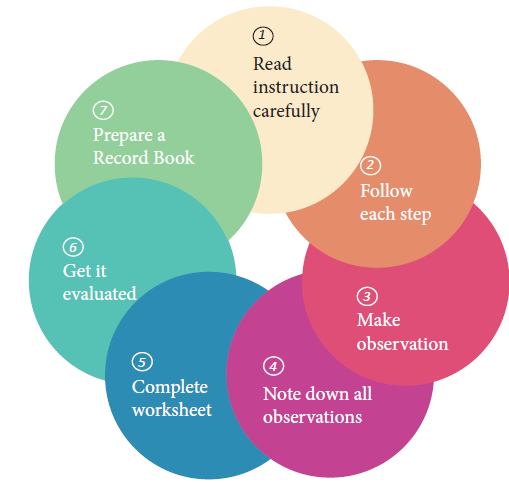
BASIC EQUIPMENTS USED IN BIOLOGY PRACTICALS
Microscope:
a. Dissection Microscope: Used to observe ground plan of T.S / L.S root, stem, leaf ovule and
small organisms.
b. Compound Microscope: It consists of objective lens and ocular lens, which is used to
magnify the object. The light entering into the microscope is adjusted by diaphragm.
Specimen slide placed on the stage is illuminated by light. It is observed through low power or
high power by changing objective lens. Using coarse and fine adjustment fine details of slide
can be studied.
Glassware:
Test tubes, Beakers, Flasks, Watch glass, Petri dishes, Slides, Cover slips, Reagent bottles,
Pipette, Funnel and Graduated cylinder.
Tools for dissection:
Scalpel, Forceps, Needle, Brushes, Blade
Fixatives:
Formalin, F.A.A (Formalin-aceto-alcohol).), Ethanol and Acetone
Stains:
Safranin (used to stain lignified and cutinised cells)
Haematoxylin (used to stain nucleus)
Iodine (used to find starch)
Eosin (used to stain cytoplasm)
Acetocarmine (used to stain chromosomes)
Crystal Violet (used to stain bacteria)
Mounting agents:
Glycerine and Canada balsam
Reagents and Solutions:
Benedict’s reagent, Biuret reagent, Fehling’s solution, Starch solution, Iodine solution, and
NaOH.
Indicators:
pH paper
Temperature measurement:
Thermometer
METHODS USED IN PREPARATION OF SLIDES
Basic techniques used in Biology laboratory during the preparation of micro slide and
demonstration of experiments.
How to take peel?
step: 1. Remove an intact leaf epidermal layer
step: 2. Use needle and forceps to separate out peel from leaf
step: 3. Keep peeling on the slide, add a drop of water or stain
step: 4. Observe through the microscope.
What is Smear?
A technique used to spread the cells uniformly on the slide from the sample or section.
step: 1. Section placed in stain
step: 2. Crushed with the help of scalpel or another slide
step: 3. Slide gently heated over the flame, mounted with mounting medium
step: 4. Cover the slide with coverslip and seal with melting wax.
How to take Sections?
A thin and transparent section is cut with the help of sharp razor or blade. Sections are basically
two types: Transverse Sections (T.S) and Longitudinal sections (L.S)
step: 1. Keep the material between thumb and first finger using pith
step: 2. Cut several thin sections using razor or blade
step: 3. Take out the section with the help of brush and place it in a watch glass containing water.
step: 4. select a thin floating section, avoid oblique/incomplete section.
Fixation:
Fixation is the technique adopted to kill the cells and stop the cellular activities. It also protects
the cells from drying and decaying.
Some common fixatives: Formalin, Ethanol and FAA (Formalin-aceto-alcohol).
Procedures followed in Staining:
Staining is the technique used to view and differentiate the cells using specific dyes or Stains.
Some common Stains: Safranin, Haematoxylin, Iodine, Eosin, Acetocarmine and Crystal Violet.
Mounting:
Technique adopted to preserve the sections for a longer period of time and also protect the
section from drying.
Some common mounting media: Glycerine, DPX and Canada balsam.
Step: 1. Pore a drop of mounting medium on the section over the slide
Step: 2. Place the cover slip very gently over the slide
Step: 3. Avoid air bubbles while mounting
Step: 4. Wipe out excess mounting medium with blotting paper.
Tamil Nadu Board Class 11 Botany Practical Manual
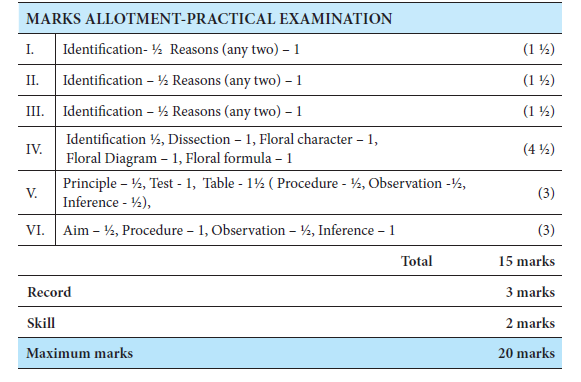
Marks – Allotment Practical Examination
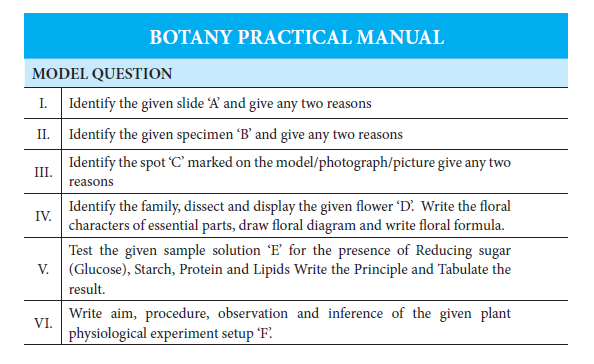
Format of the Experiment Recorded In the Manual
The details and steps mentioned in the manual for the experiments will be in the below format as required:
- Aim
- Principle
- Requirements
- Procedure
- Observation
- Inference
For a more detailed explanation and experiments of the TN Board Class 11 Botany Practical with procedure, observations and results, students can access the downloadable pdf from the link given in the article above.
Students can also refer to other resources of TN Board to prepare for the exams.
Comments