All living organisms respond to stimuli. The ability to react to a particular stimulus in a particular situation is of great importance, in ensuring the survival of the organism. In AP Class 10 Biology chapter 5 Coordination, we learn about the coordination system of a human body. Nervous system and endocrine system are the two systems that control and coordinate various functions in the body.
Nervous System
The nervous system is a complex network of nerves and cells that carry messages to and from the brain and spinal cord to various parts of the body. Neurons are the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. The human nervous system is categorised into two divisions as:
- Central Nervous System
- Peripheral Nervous System
Classification of the Nervous System
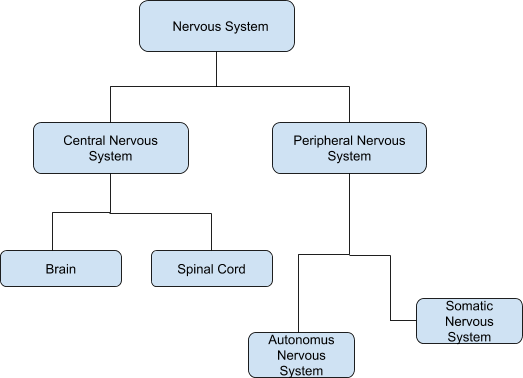
The responses of the nervous system are classified as:
- Reflex
- Voluntary
- Involuntary
Endocrine System
The endocrine system comprises glands that produce and secrete, chemical substances and hormones that regulate the activity of cells or organs. They are responsible for regulating the body’s growth, metabolism, and sexual development and function. The amount and timing of hormones released by endocrine glands are controlled by the feedback mechanism, which is inbuilt in our body. In the table below, various hormones secreted by different organs in the body and their function are listed.
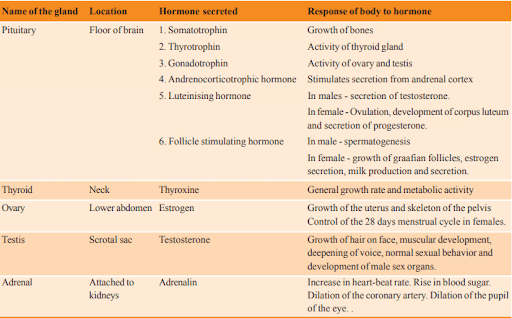
In the next section, let us look at a few chapter questions to better understand the concepts discussed here.
Class 10 Biology Chapter 5 Coordination Questions
- A point of contact between two neurons is _____.
Answer: Synapse
The point of contact between two neurons is synapse.
- A person has loss of control over emotions, which part of the brain stops its function?
- Diencephalon
- Mid Brain
- Cerebellum
- Cerebrum
Answer: Cerebrum
- Thyroxin is responsible for _____.
Answer: general growth rate and metabolic activity
Thyroxin is responsible for the general growth rate and metabolic activity.
2. What are afferent neurons?
Answer: Afferent (or ferrying towards) which carry messages towards the central nervous system (spinal cord or brain) from nerve endings on the muscles of different sense organs that sense the change in surroundings are called stimulus detectors. These are also called ‘sensory’ nerves.
3. What are functions of the cerebrum?
Answer: Functions of cerebrum are given below:
i) Seat of mental abilities, controls thinking, memory, reasoning, perception, emotions and speech.
ii) Interprets sensations and responds to cold, heat, pain and pressure.
Stay tuned to BYJU’S to get the latest notification on SSC exams, along with AP SSC model papers, exam pattern, marking scheme and more.
Comments