Table of Contents
Introduction
With the ever-increasing population, the requirement for nutritious food has risen steeply across the world. Since time immemorial, animals have been an integral part of agriculture. They have been used to derive milk, meat, eggs, wool, silk, for labour, etc. As animals are so crucial part of agriculture, they require proper care and management. According to some estimates, more than 70% of the world’s total livestock population is in India and China. However, their contribution to the world farm produce is only 25%. This means that productivity per unit is very low. This led to the concept of animal husbandry where a more scientific approach to caring for and breeding farm animals is provided.
Animal Husbandry
Animal husbandry is the science of caring for and breeding domestic animals and the development of genetic traits such as high yielding, disease resistance, etc. that are valuable to humanity. Animal husbandry involves breeding and raising livestock like buffaloes, cows, goats, camels, horses, sheep etc. and is even extended to poultry farming and fisheries. Some of the salient practices of animal husbandry are as follows:-
Management of Farms and Farm Animals
This is a professional approach to conventional farm management practices which gives a boost to food production.
- Dairy Farm Management – This is the management of the animals that provide milk (milch animals). The goal is to enhance the quantity and quality of the milk produced. For this purpose, high-yielding and disease-resistant breeds are maintained in a strictly hygienic manner with proper housing, adequate water supply, and nutrient-rich fodder. Regular inspection and record-keeping ensure that a good high-quality yield is generated.
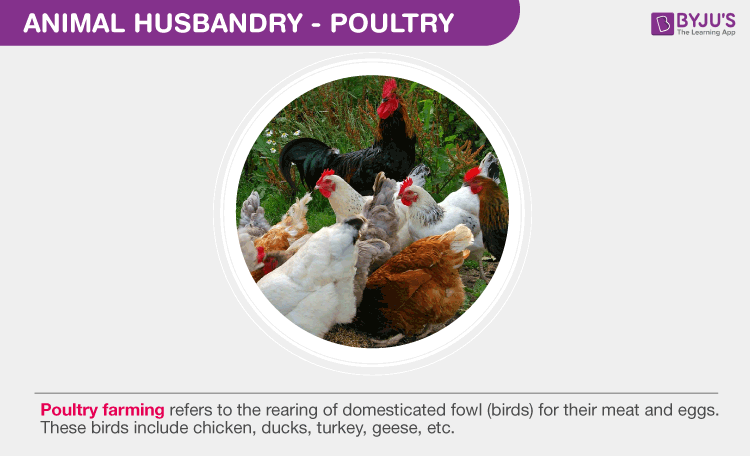
- Poultry Farm Management – Poultry farming refers to the rearing of domesticated fowl (birds) for their meat and eggs. These birds include chicken, ducks, turkey, geese, etc. Just like dairy farming, selection of disease-free and suitable breeds, maintenance of hygienic farm conditions, providing proper food and water, and health care, are the main goals of poultry farm management.
Animal Breeding
Another part of animal husbandry is animal breeding. Breeding of animals aims to develop high-yielding animals and improve the desirable qualities of the produce.
- Inbreeding – It refers to the practice of mating closely related superior males to superior females within the same breed for 4-6 generations. The superior males and females among the progenies are further mated for developing Mendelian pure lines which are homozygous in nature. However, continued close inbreeding eventually decreases fertility and productivity; a phenomenon known as inbreeding depression.
- Out-breeding – It is the breeding of unrelated animals that can be carried out in three different fashions. When two unrelated individuals of the same breed who do not have a common ancestor for the past 4-6 generations are mated, it is called out-crossing. Mating between a superior male of one breed and a superior female of another breed to give a progeny with the combined qualities of both breeds is known as crossbreeding. When males and females across different related species are mated, it is known as interspecific hybridization.
Apart from conventional breeding techniques, controlled breeding experiments are conducted utilizing artificial insemination to yield the desired mating. To improve the chances of obtaining successful hybrids, programs like Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Technology (MOET) are used.
To learn more about animal husbandry and cattle farming, visit BYJU’S.

Comments