Table of Contents
What is Central Nervous System?
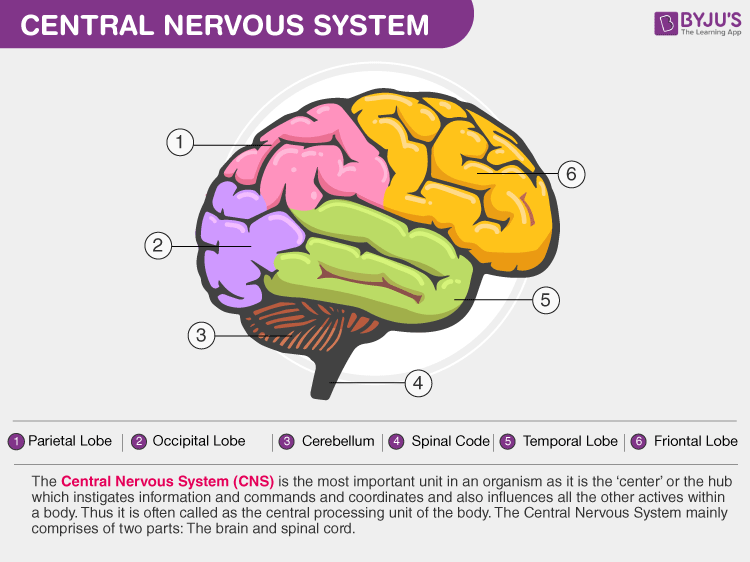
The Central Nervous System (CNS) is the most important unit in an organism as it is the ‘centre’ or the hub which instigates information, commands and coordinates and also influences all the other activities within a body. Thus it is often called the central processing unit of the body. The Central Nervous System comprises two parts: The brain and spinal cord.
Brain
The brain is the most important organ which is divided into three parts:
- The Forebrain
- The Midbrain
- The Hindbrain
The brain has approximately 30 per cent of oxygen. It interprets information from the five senses in a body along with the internal organ stomach. The Central Nervous System sometimes also includes the retina, optic nerves, olfactory epithelium and olfactory nerves as they connect directly with the tissues of the brain without any connecting nerve fibres. On the other hand, the spinal cord acts as a bridge between the brain and the body. Thus, if the spinal cord is injured or affected, the flow of information will be interrupted.
Cells of the Central Nervous System
There are various cells that act as the major unit to help in the function of the Central nervous system properly. Of which neurons, dendrites and glial cells are the major ones. These cells are connected to the brain where all the information is stored and enacted.
Neurons
Neurons are the fundamental unit of the brain which is responsible for processing and transmitting information to other nerve cells, glands, and muscles. There are about 100 billion neurons where each neuron consists of a cell body and an axon and dendrites create the extensions.
Dendrites
They are the specialized form extensions from the cell body which function to receive information from various cells and carry that information back to the cell body. Thus dendrites are often known as processes.
Glial cells
There are basically three different types of glial cells that function to provide the neutrons with metabolism and mechanical supports. These cells are:
- Astrocytes: They are star-shaped glial cells of the nervous system which perform various functions from biochemical supporting of the endothelial cells to repair and scan the process of the brain and the spinal cord during injuries.
- Microglia: They comprises about 10 to 15 percent of all the cells in the brain which acts as resistance cell. Their foremost role is to act as immune defence and helps in clearing out the dead and dying cells. In the process, they also produce small molecules called cytokines that act as a catalyst in helping the immune system.
- Oligodendrocytes: The primary function of Oligodendrocytes in glial cells is to provide support and wrap around the axons. To do this, they produce a fatty substance called myelin sheath which allows the nerve cells to send and receive signals quickly.
For more detailed information about Central Nervous System, visit BYJU’S.

I love this APP from the deepness of my heart