Comparative anatomy refers to the study of the similarities and differences in the anatomy of two species. Generally, it involves comparing the body structures of two species as seen in evolutionary biology and phylogeny.
Evolution, in a population, refers to a genetic modification occurring over a period of time. Consequently, the progeny appear different compared to their parents. It is as a result of the shuffling of genes leading to new characteristics hence aiding the entity in survival.
The stream chiefly involves the study of vertebrate animals. However, how do we observe the evolution which took place several million years ago? Through a vast amount of evidence that observes the evolution taking place. One of the type of evidence is Comparative anatomy.
Analogous Structures and Homologous Structures are two main concepts of the comparative anatomy.
Analogous Structures
Analogous structures are the similar structures seen in different organisms; they are just contrary to that of the homologous structures. They appear the same, performing the same functions. For example, the wings of insects and birds – both perform the same function, taking a flight, however, structurally they are not similar. The wings of the birds are structurally similar to human hands compared to the wings of insects. The emergence of convergent evolution is from Analogous structure.
Homologous Structures
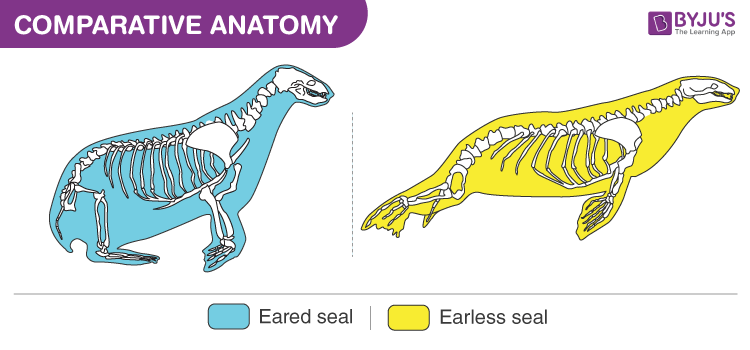
Homologous structures are similar in two entities having similar ancestors, however, functionality may or may not be the same. For example, birds, whales and humans have the same structure of the arm bone.
One more example of homologous structure is the forelimb structure which is same as that of cats and whales. It is believed that several million years ago, there thrived ancestors which were similar to whales and humans both. The evolved progeny was a new species. Further, even newer species evolved from such species.

To learn more about comparative anatomy, visit BYJU’S.

Comments