Table of Contents
- Dengue Fever
- Dengue Life Cycle
- Sign and Symptoms of Dengue Fever
- Diagnosis of Dengue Fever
- Treatment of Dengue Fever
- Prevention of Dengue Fever
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs

Dengue Fever
About Dengue
Dengue is a mosquito-borne viral disease caused by the Dengue virus. In this case, the dengue virus is transmitted by female mosquitoes – Aedes aegypti. These dengue mosquitos generally bite during the daytime and are found everywhere (Both inside and outside the house). These mosquitos are found to be at the peak of their activeness at dawn and dusk. The symptoms can develop only after 6 to 10 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is transmitted by mosquitos which carry the dengue virus, which has four varied serotypes to infect human beings. The serotypes mentioned above denote a set of microorganisms that are exceptionally closely associated. These microorganisms can only be distinguished due to them having somewhat dissimilar antigens (the alien unit that affects the body and makes us produce antibodies) which prompt the body to create some dissimilar antibodies. Dengue cases are more common in subtropical and tropical regions of our planet, including our country.
Dengue Life Cycle
Following its departure from sylvatic cycles, the dengue virus has spread worldwide, and its primary lifecycle now only involves transmission between people and Aedes mosquitoes. The four life stages of the Aedes aegypti mosquito are egg, larva, pupa, and adult. About 8 to 10 days are needed to complete the life cycle from egg to adult. Mosquitoes can survive and breed both inside and outside the house.
Eggs
- Above the waterline, adult female mosquitoes lay their eggs on the interior, wet walls of water-filled containers.
- Usually, mosquitoes lay a hundred eggs at a time.
- Eggs are highly resilient; they can withstand drying up to eight months and adhere to container walls like glue.
- A female mosquito can be attracted to very little water. Any object storing water, including cups, bowls, fountains, barrels, tires, vases, and other containers, makes an excellent “nursery.”
Larva
- Mosquito eggs hatch into larvae only once the water level rises enough to cover the eggs. Humans or rains will cause the larvae to emerge from containers containing eggs.
- Larvae consume aquatic bacteria as food. The larva develops into a pupa after going through three moults.
Pupa
Pupae continue to grow until the newly formed adult flying mosquito’s body breaks through the pupal skin and exits the water.
Adult
- The adult female mosquito feeds on human and animal blood to generate eggs, while the male mosquito feeds on nectar from flowers.
- Female mosquitoes search for water sources to lay additional eggs after feeding.
- Throughout its lifespan, Aedes aegypti flies only a few blocks.
- Aedes aegypti mosquitoes prefer to attack humans above other mosquito species.
- Mosquitoes of the Aedes aegypti species favour areas with humans. They can be found inside residences, buildings, and workplaces when windows and doors lack screens or are left open.
Sign and Symptoms of Dengue Fever
Dengue has an unexpected attack, viz. a sudden start and these symptoms could be an indicator of its onset.
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhoea and vomiting
- Gum and nose bleedings
- Severe joint and muscle pain
- Fatigue, nausea, and vomiting
- A sudden drop in blood pressure
- Multiple rashes and wounds on the skin
- Pain behind the eyes coupled with extreme headaches
- The patient might feel weak with a high fever for 3-7 days
Diagnosis of Dengue Fever
The presence of the Dengue virus in the blood cells can be diagnosed by isolation of the virus, testing serum samples, and other molecular methods. A patient with this syndrome is allowed to have a few blood tests to check the total count of red blood cells, and blood platelets, and other physical examinations conducted by the physician to evaluate whether the symptoms are caused by a dengue infection.
Treatment of Dengue Fever
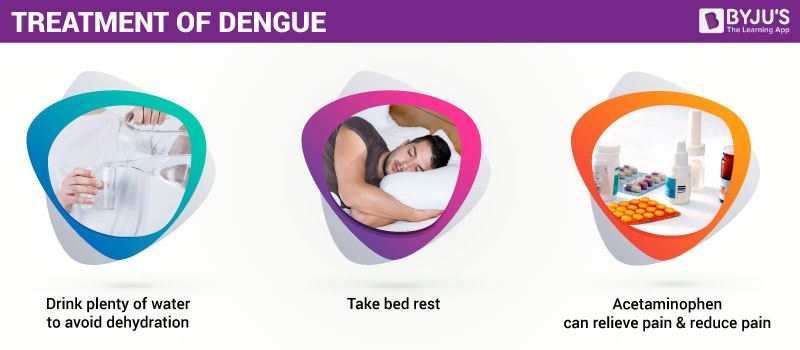
Till today, there is no definite treatments or specific medicine to treat dengue infection. In general, the doctor may generally recommend regulating the pain and fever by using paracetamol instead of aspirin (as it might stimulate bleeding) and increasing fluid ingestion. Children below the age of 12 should not be given aspirin until and unless specially prescribed by the doctor.
In severe cases, blood transfusions, intravenous (IV) fluid supplementation and 24 hours hospitalization are required.
Prevention of Dengue Fever

The patient should take proper bed rest, especially during the days when the fever is at its peak and take leave from work, school preschool or childcare.
People suffering from dengue must stay away from places where they could get bitten by mosquitoes and should stay at home until they are no longer infectious (around 3-5 days).
For avoiding this illness, make sure your surroundings are free of any water logging issues, as the Aedes mosquito prefers to breed in stagnant clean water that could be found easily nearby our habitats.
Until now, no vaccine has been developed to prevent the Dengue virus. The only prevention is to avoid mosquito bites.
- Cover your skin by wearing long pants, and long-sleeved shirts.
- Use of mosquito repellents, traps, and nets.
- Keep all the doors and windows closed especially at dawn, dusk, and early evening to avoid the entry of Dengue mosquitoes.
- Keep your surroundings clean by removing all the waste and cleaning the standing water.
For more detailed information about Dengue fever, visit BYJU’S.


Comments